Cells Free Full Text Structure And Function Of Human Matrix
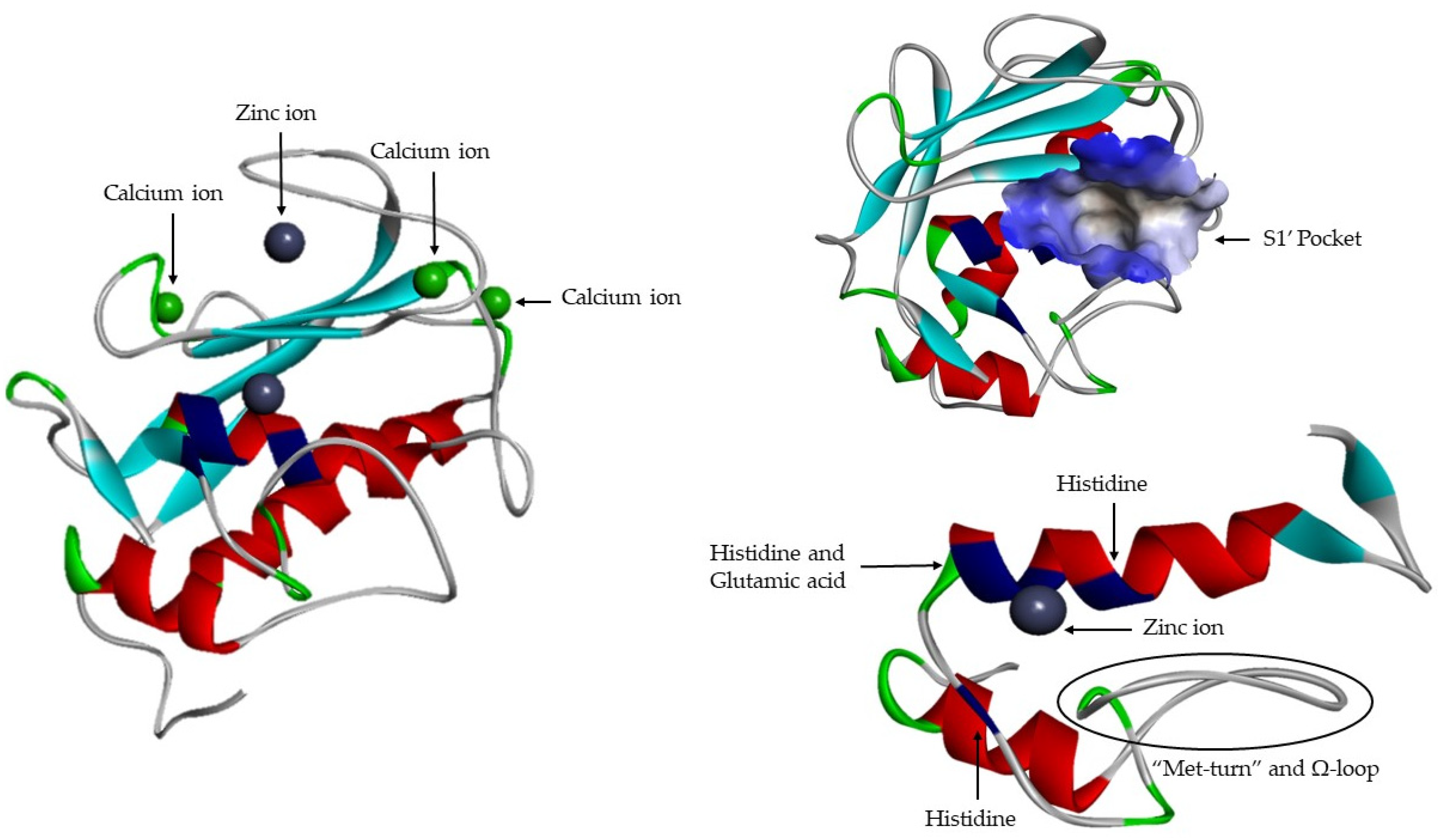
Cells Free Full Text Structure And Function Of Human Matrix The extracellular matrix (ecm) is a macromolecules network, in which the most abundant molecule is collagen. this protein in triple helical conformation is highly resistant to proteinases degradation, the only enzymes capable of degrading the collagen are matrix metalloproteinases (mmps). this resistance and maintenance of collagen, and. The extracellular matrix (ecm) is a macromolecules network, in which the most abundant molecule is collagen. this protein in triple helical conformation is highly resistant to proteinases degradation, the only enzymes capable of degrading the collagen are matrix metalloproteinases (mmps). this resistance and maintenance of collagen, and consequently of ecm, is involved in several biological.
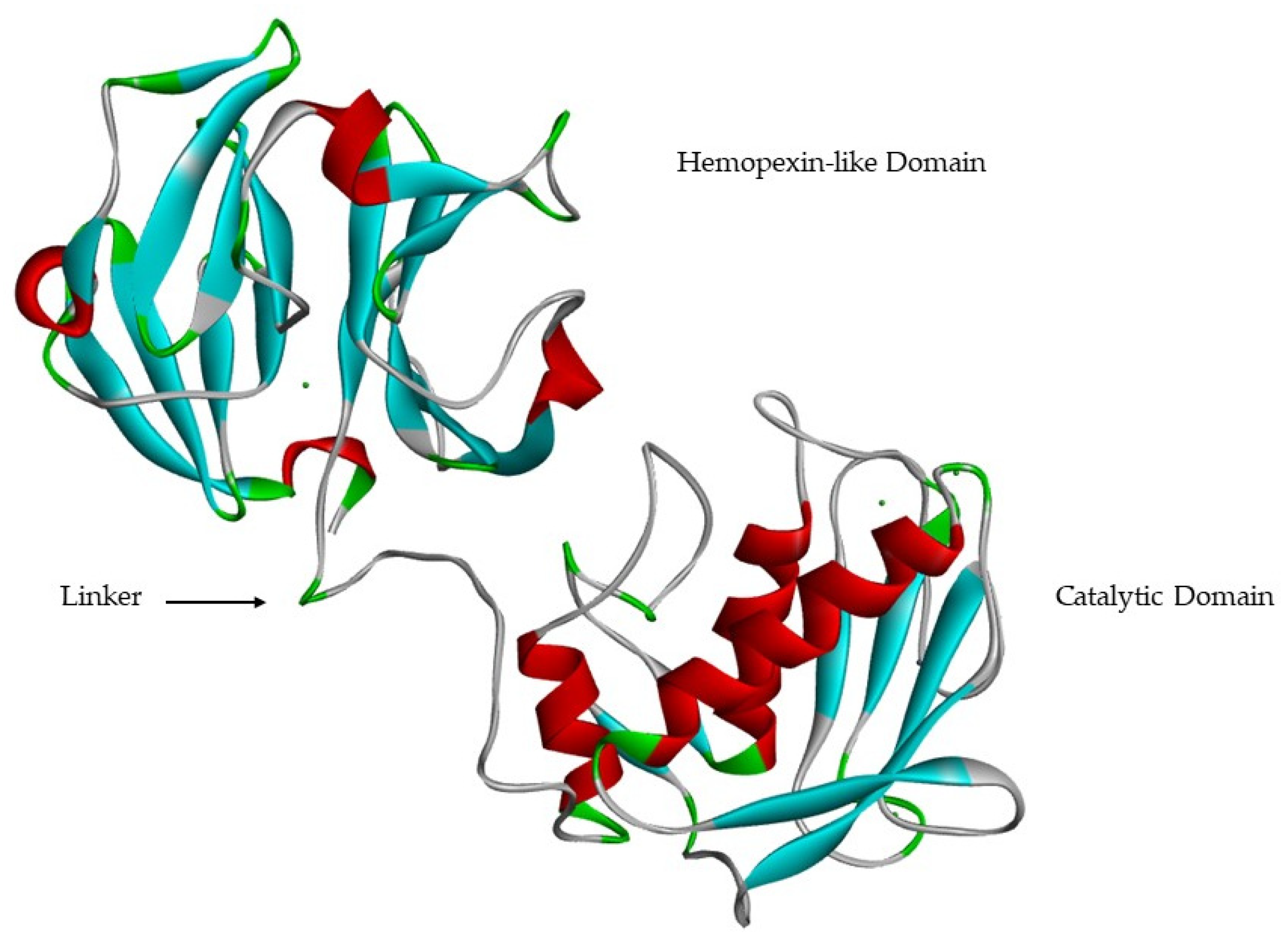
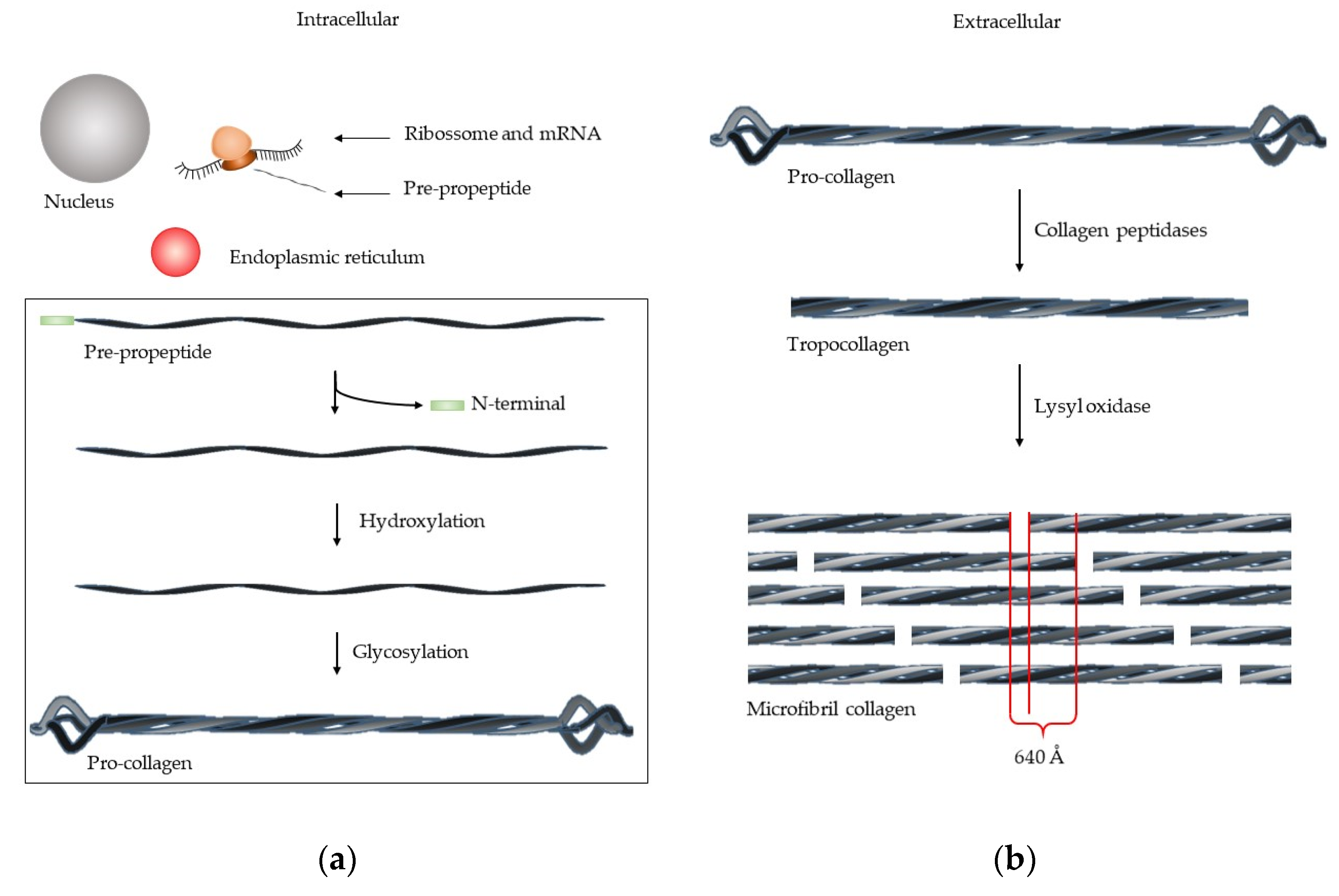
Cells Free Full Text Structure And Function Of Human Matrix Download full text pdf read full text. structure and function of human matrix . the collagen is the most abundant protein in ecm which gives structural support for cells [1, 3]. Matrix metalloproteinases (mmps), also called matrixins, function in the extracellular environment of cells and degrade both matrix and non matrix proteins. they play central roles in morphogenesis, wound healing, tissue repair and remodelling in response to injury, e.g. after myocardial infarction, and in progression of diseases such as. The timely breakdown of extracellular matrix (ecm)1 is essential for embryonic development, morphogenesis, reproduction, and tissue resorption and remodeling. the matrix metalloproteinases (mmps), also called matrixins, are thought to play a central role in these processes. the expression of most matrixins is transcriptionally regulated by growth factors, hormones, cytokines, and cellular. The ecm is a composite of cell secreted molecules that offers biochemical and structural support to cells, tissues, and organs 1.in humans, the composition of the ecm can be broadly summarized as.
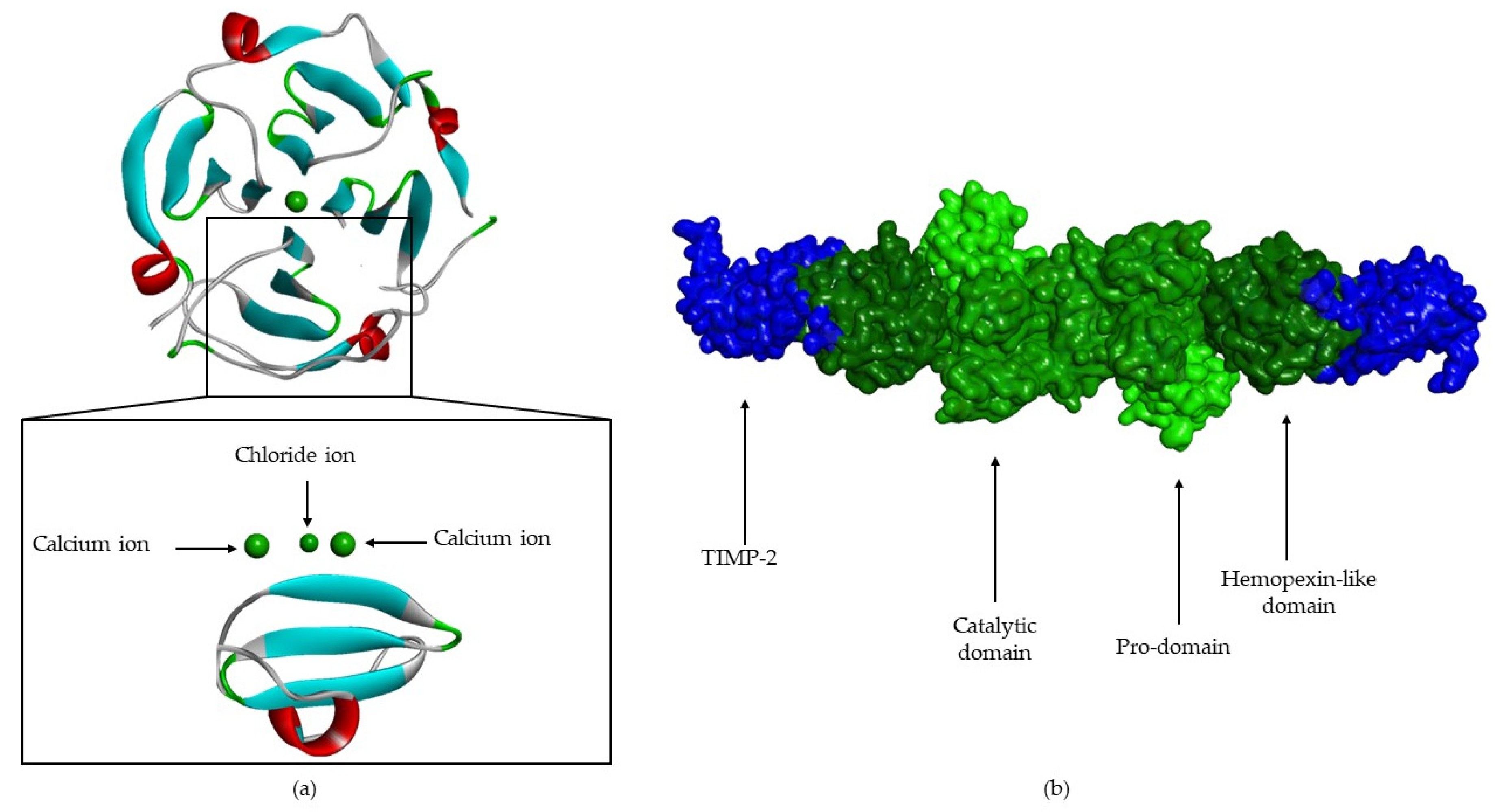
Cells Free Full Text Structure And Function Of Human Matrix The timely breakdown of extracellular matrix (ecm)1 is essential for embryonic development, morphogenesis, reproduction, and tissue resorption and remodeling. the matrix metalloproteinases (mmps), also called matrixins, are thought to play a central role in these processes. the expression of most matrixins is transcriptionally regulated by growth factors, hormones, cytokines, and cellular. The ecm is a composite of cell secreted molecules that offers biochemical and structural support to cells, tissues, and organs 1.in humans, the composition of the ecm can be broadly summarized as. The extracellular matrix (ecm) regulates many cellular functions, and its remodelling by enzymes such as metalloproteinases has a crucial role during development, as exemplified by intestinal. 13.1: introduction to extracellular matrix and cell adhesion. the extracellular matrix is a generic term encompassing mixtures of polysaccharides and proteins, including collagens, bronectins, laminins, and proteoglycans, all secreted by the cell. the proportions of these components can vary greatly depending on tissue type.
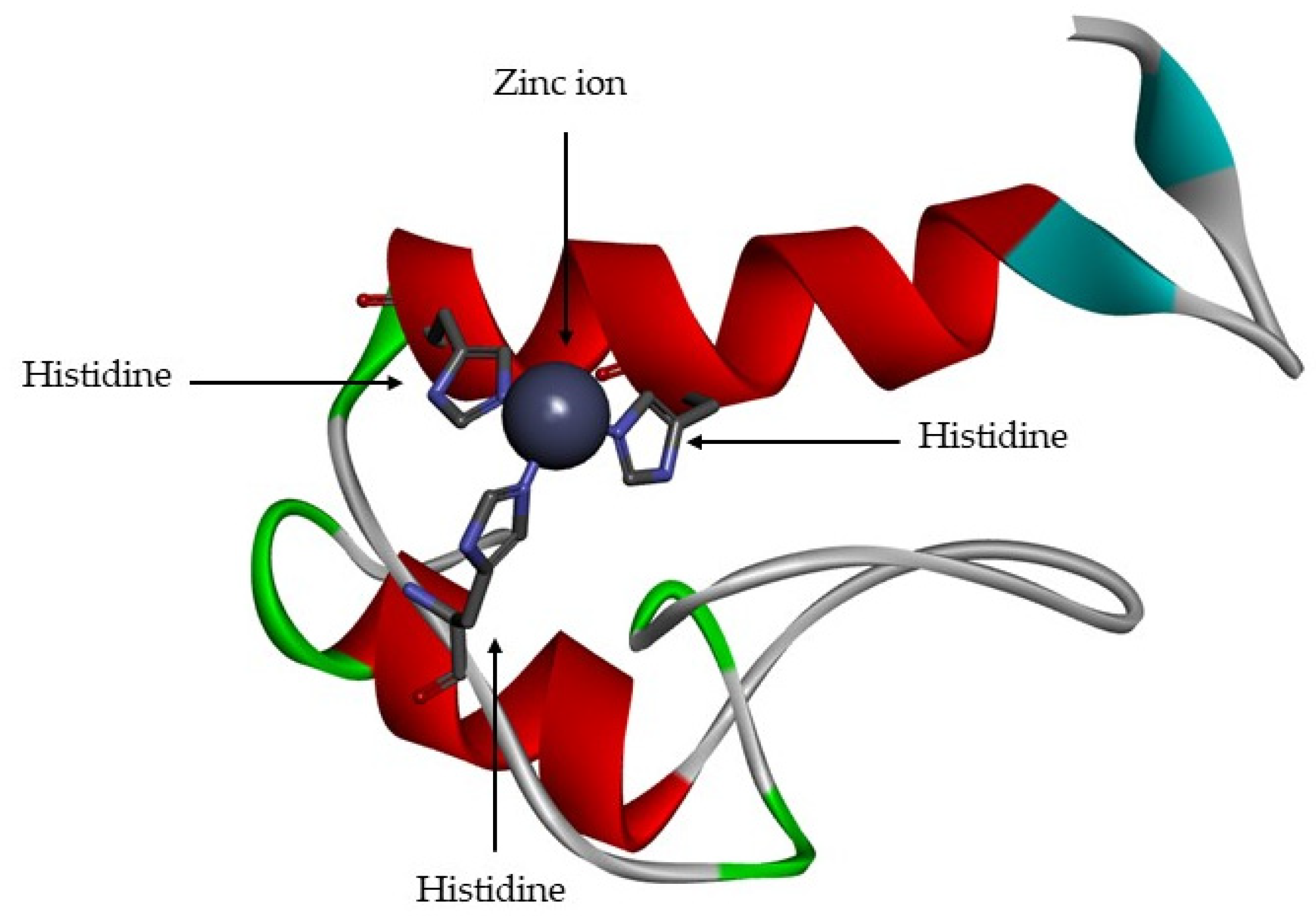
Cells Free Full Text Structure And Function Of Human Matrix The extracellular matrix (ecm) regulates many cellular functions, and its remodelling by enzymes such as metalloproteinases has a crucial role during development, as exemplified by intestinal. 13.1: introduction to extracellular matrix and cell adhesion. the extracellular matrix is a generic term encompassing mixtures of polysaccharides and proteins, including collagens, bronectins, laminins, and proteoglycans, all secreted by the cell. the proportions of these components can vary greatly depending on tissue type.
Cells Free Full Text Structure And Function Of Human Matrix

Comments are closed.