Cells Cell Biology Definition Types Of Cells Their Functions

Cells Cell Biology Definition Types Of Cells Their Functions Cell, in biology, the basic membrane bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. a single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. Cell definition. “a cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes.”. cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. a cell can replicate itself independently. hence, they are known as the building blocks of life.

Cell Definition Types Functions Diagram Division Theory Facts There are countless different functions that cells must perform to obtain energy and reproduce. depending on the cell, examples of these functions can include photosynthesis, breaking down sugar, locomotion, copying its own dna, allowing certain substances to pass through the cell membrane while keeping others out, etc. The cell diagram typically represents the structure and components of a biological cell. they can illustrate various organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and cell membrane. these diagrams help scientists and students understand the internal organization of cells, aiding in the study of cell. Types of cells in the human body. adult human beings are made up of around 37 trillion individual cells, and approximately 200 different types of cells. some key cell types of the human body include stem cells, muscle cells, blood cells, bone cells, nerve cells, fat cells, sperm cells, and egg cells. the human body contains about 200 different. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. together, trillions of cells make up the human body. cells have three parts: the membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm.
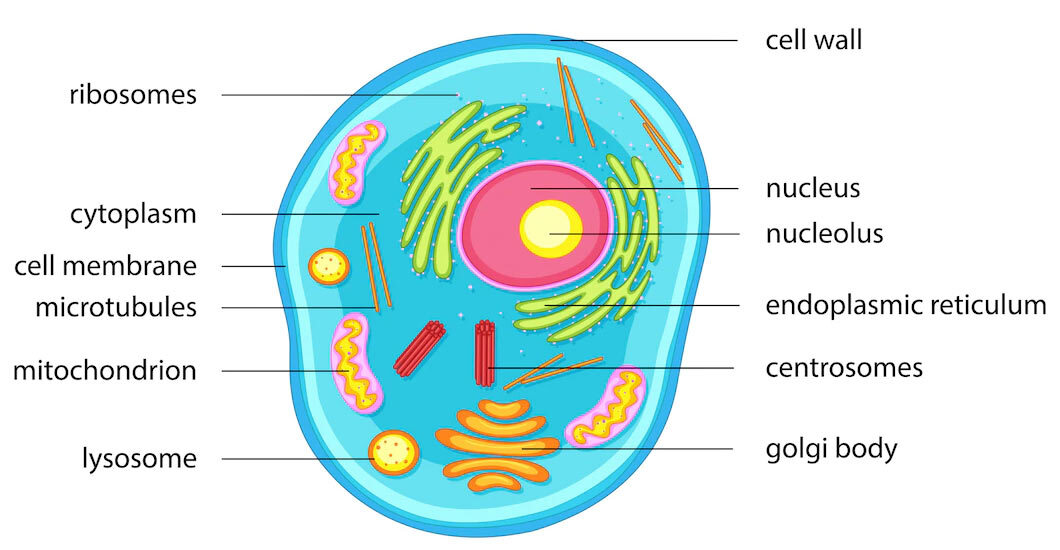
Cell Organelles Definition Structure Types Functions Geeksforgeeks Types of cells in the human body. adult human beings are made up of around 37 trillion individual cells, and approximately 200 different types of cells. some key cell types of the human body include stem cells, muscle cells, blood cells, bone cells, nerve cells, fat cells, sperm cells, and egg cells. the human body contains about 200 different. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. together, trillions of cells make up the human body. cells have three parts: the membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. Conclusion. cells are the smallest common denominator of life. some cells are organisms unto themselves; others are part of multicellular organisms. all cells are made from the same major classes. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all forms of life. every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. the term comes from the latin word cellula meaning 'small room'. most cells are only visible under a microscope.

Comments are closed.