Cavidad Abdominalperitoneo

Qué Es La Cavidad Peritoneal Curiosoando So let’s start with the basics; the peritoneum is a serous membrane which lines the walls of the abdominal cavity and lies on abdominal and pelvic organs. between its two layers – parietal and visceral – is the peritoneal cavity. the peritoneum functions to support and protect abdominopelvic organs. this article will discuss the anatomy. Entre sus dos capas, parietal y visceral, se encuentra la cavidad peritoneal. el peritoneo funciona para apoyar y proteger los órganos abdominopélvicos. este artículo explicará la anatomía y la función del peritoneo y la cavidad peritoneal. puntos clave sobre el peritoneo. cuestionario de la tabla.
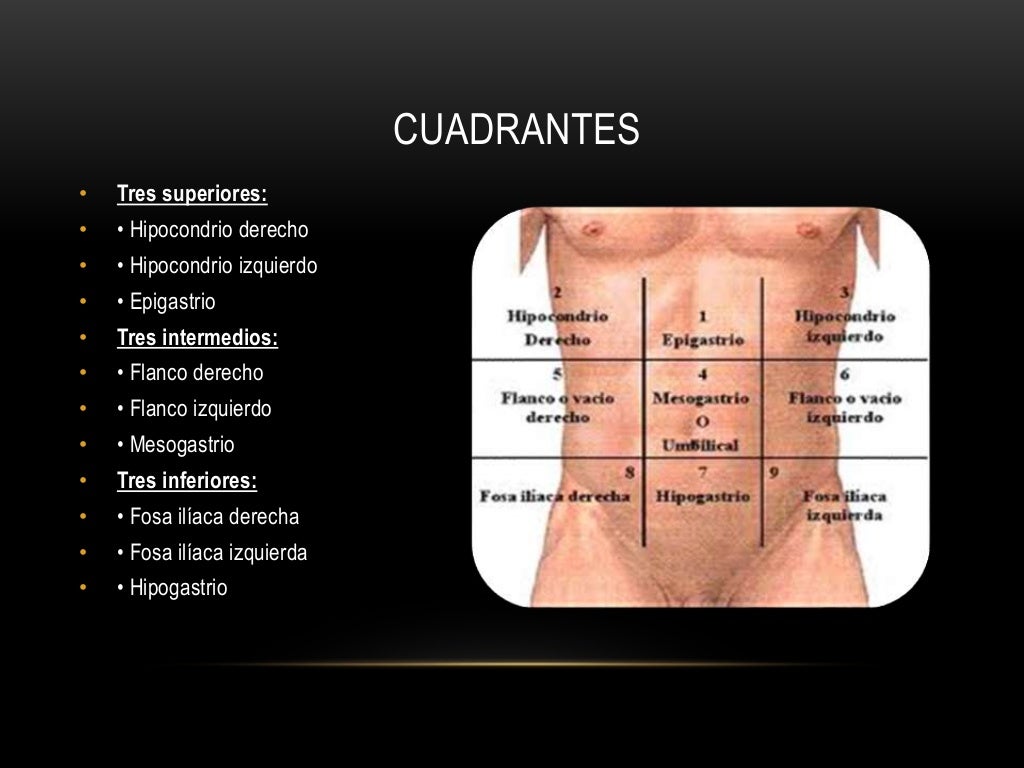
Peritoneo Y Cavidad Abdominal Y Sus Cuadrantes The abdominal cavity is divided into two major compartments, the peritoneum and retroperitoneum, early in fetal development. the parietal peritoneum is reflected over the peritoneal organs, forming supporting peritoneal ligaments, mesenteries, and omenta. the peritoneal reflections carry vessels, nerves, and lymphatics from the retroperitoneum. Justin from the institute of human anatomy discusses the anatomy of the abdominal cavity.get a 10% discount on kenhub premium today! khub.me institut. In males, the peritoneum forms a closed sac while in females, the peritoneum is open due to the communication of the fallopian tubes with the peritoneal spaces 3. the peritoneal cavity can be divided into the following spaces: supramesocolic space: right supramesocolic space. right subphrenic space. anterior right subhepatic space. Abdominal cavity, largest hollow space of the body. its upper boundary is the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle and connective tissue that separates it from the chest cavity; its lower boundary is the upper plane of the pelvic cavity. vertically it is enclosed by the vertebral column and the abdominal and other muscles.

Peritoneo Anatomia In males, the peritoneum forms a closed sac while in females, the peritoneum is open due to the communication of the fallopian tubes with the peritoneal spaces 3. the peritoneal cavity can be divided into the following spaces: supramesocolic space: right supramesocolic space. right subphrenic space. anterior right subhepatic space. Abdominal cavity, largest hollow space of the body. its upper boundary is the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle and connective tissue that separates it from the chest cavity; its lower boundary is the upper plane of the pelvic cavity. vertically it is enclosed by the vertebral column and the abdominal and other muscles. The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans [1] and many other animals that contain organs. it is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. [2] it is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. its dome shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet. The space between the parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum is named the peritoneal cavity; but under normal conditions this cavity is merely a potential one, since the parietal and visceral layers are in contact. the peritoneal cavity gives off a large diverticulum, the omental bursa, which is situated behind the stomach and adjoining structures; the neck of communication between the.
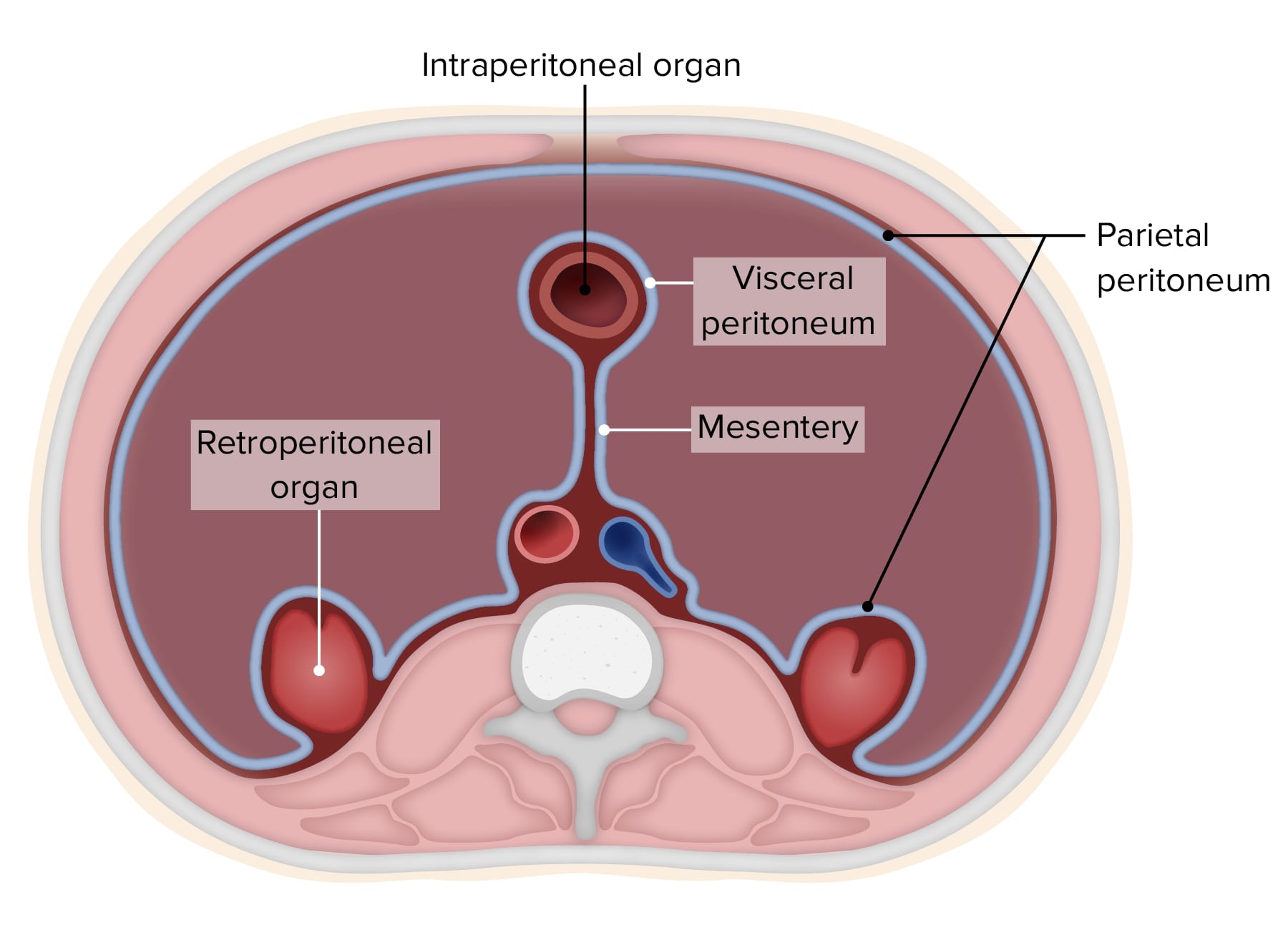
Peritoneum Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans [1] and many other animals that contain organs. it is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. [2] it is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. its dome shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet. The space between the parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum is named the peritoneal cavity; but under normal conditions this cavity is merely a potential one, since the parietal and visceral layers are in contact. the peritoneal cavity gives off a large diverticulum, the omental bursa, which is situated behind the stomach and adjoining structures; the neck of communication between the.
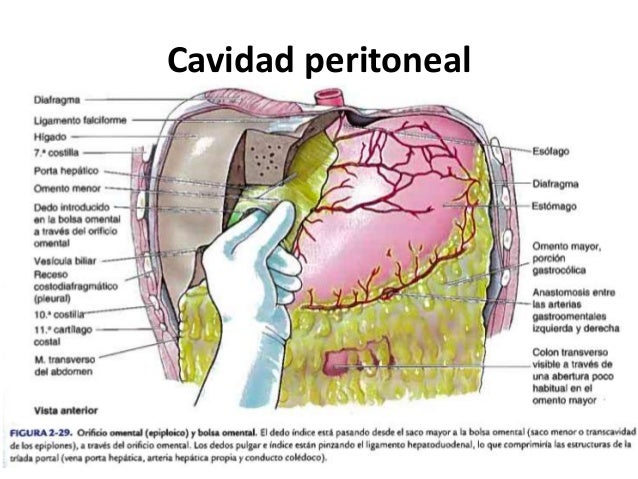
Peritoneo Y Cavidad Peritoneal

Comments are closed.