Carnot Cycle Diagram Eigenplus

Carnot Cycle Diagram Eigenplus Carnot cycle: the thermodynamic cycle with the maximum possible thermal efficiency working between two temperatures. carnot engine: carnot engine is a theoretical engine that works on the carnot cycle operating between two temperatures, th (source) and tl (sink). heat engines can’t be 100% efficient: heat is low grade energy, and complete. For the above carnot engine, the thermodynamic cycle, i.e., the carnot cycle, looks like this: carnot cycle p v diagram and t s diagram. it comprises four processes two isothermal processes and two isentropic processes: isothermal process: processes 1 2 and 3 4 are isothermal processes, i.e., the temperature remains constant.

Carnot Cycle Example Eigenplus A carnot cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle proposed by french physicist sadi carnot in 1824 and expanded upon by others in the 1830s and 1840s. by carnot's theorem, it provides an upper limit on the efficiency of any classical thermodynamic engine during the conversion of heat into work, or conversely, the efficiency of a refrigeration system in creating a temperature difference through. Say hello. join our mission to bridge the gap between industry and academia by following our linkedin page. we're building a community of like minded industry experts and students to connect, share insights and grow together. join us. The carnot cycle. the carnot cycle consists of the following four processes: a reversible isothermal gas expansion process. in this process, the ideal gas in the system absorbs qin q i n amount heat from a heat source at a high temperature thigh t h i g h, expands and does work on surroundings. a reversible adiabatic gas expansion process. 3. the work done on the gas in one cycle of the carnot refrigerator is shown and given by the area enclosed by the loop mponm. the work done on the ideal gas is equal to the area enclosed by the path of the pv diagram. from the first law, this work is given by. w = qh −qc. (4.6.13) (4.6.13) w = q h − q c.
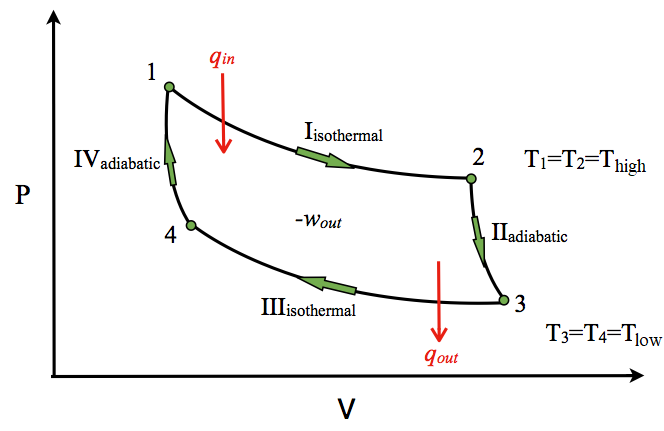
Carnot Cycle Chemistry Libretexts The carnot cycle. the carnot cycle consists of the following four processes: a reversible isothermal gas expansion process. in this process, the ideal gas in the system absorbs qin q i n amount heat from a heat source at a high temperature thigh t h i g h, expands and does work on surroundings. a reversible adiabatic gas expansion process. 3. the work done on the gas in one cycle of the carnot refrigerator is shown and given by the area enclosed by the loop mponm. the work done on the ideal gas is equal to the area enclosed by the path of the pv diagram. from the first law, this work is given by. w = qh −qc. (4.6.13) (4.6.13) w = q h − q c. The carnot cycle forms a closed loop on a pv diagram (a plot of pressure vs. volume) or indeed on a t s diagram of temperature vs. entropy. carnot efficiency in a full carnot cycle, the total change in internal energy is zero because the final state and the initial state are the same. Educ., 1944, 21, 600 601. salter, c. j. chem. educ., 2000, 77, 1027 1030. 13.1: carnot cycle is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the carnot cycle has the greatest efficiency possible of an engine (although other cycles have the same efficiency) based on the assumption of the absence of.

Carnot Efficiency Formula Derivation Explanation Eigenplus The carnot cycle forms a closed loop on a pv diagram (a plot of pressure vs. volume) or indeed on a t s diagram of temperature vs. entropy. carnot efficiency in a full carnot cycle, the total change in internal energy is zero because the final state and the initial state are the same. Educ., 1944, 21, 600 601. salter, c. j. chem. educ., 2000, 77, 1027 1030. 13.1: carnot cycle is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the carnot cycle has the greatest efficiency possible of an engine (although other cycles have the same efficiency) based on the assumption of the absence of.

Comments are closed.