Carnivores And Herbivores Characteristics Types And Examples
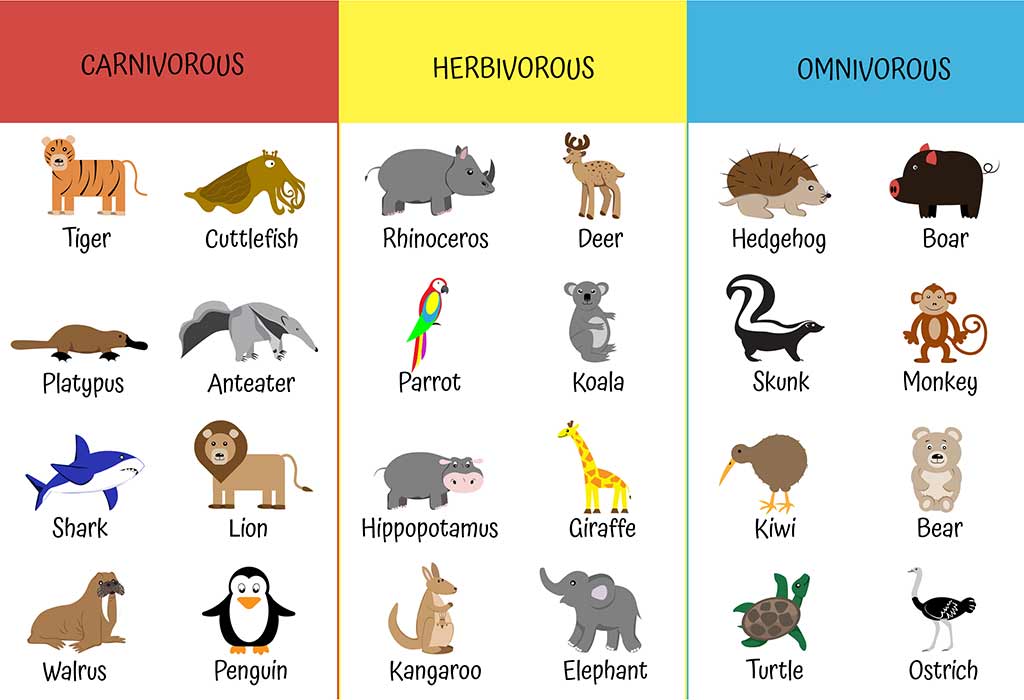
Herbivores Carnivores And Omnivores Types Of Animals For Kids The animal kingdom is diverse, with species adapted to a wide range of diets. these diets fall into three broad categories: herbivorous, carnivorous, and omnivorous. herbivores are animals that primarily consume plant material. carnivores are those that eat other animals. omnivores have a diet that includes both plant and animal matter. Herbivores or herbivorous animals are those animals that feed on plants, leaves, fruits and other plant based food for nutrition. they are known as primary consumers and occupy level 2 or higher in the food chain. cow, goat, giraffe, sheep, and zebra are common examples of herbivores. interestingly, there are herbivores that specialize in.

Carnivores And Herbivores Characteristics Types And Examples Omnivores are animals that eat both plant and animal derived food. in latin, omnivore means to eat everything. humans, bears (shown in figure 3a), and chickens are example of vertebrate omnivores; invertebrate omnivores include cockroaches and crayfish (shown in figure 3b). figure 3. omnivores like the (a) bear and (b) crayfish eat both plant. Herbivores can be classified further into fruit eaters (frugivores), seed eaters (granivores), nectar eaters (nectivores), and leaf eaters (folivores). examples of herbivores can include goat, deer, koalas, some birds, caterpillars, crickets and more. carnivores are animals that depend on other animals for their primary source of food and energy. Herbivores, or herbivorous animals, are those that primarily feed on plant matter, such as leaves, fruits, and other plant based foods for their nutrition. they are also known as primary consumers and are at level 2 or higher in the food chain. examples of herbivores include animals like elephants, rabbits, and deer. Carnivores are animals that eat other animals. the word carnivore is derived from latin and literally means “meat eater.”. wild cats such as lions, shown in figure 2a and tigers are examples of vertebrate carnivores, as are snakes and sharks, while invertebrate carnivores include sea stars, spiders, and ladybugs, shown in figure 2b.

Carnivores And Herbivores Differences And Its Characteristics Herbivores, or herbivorous animals, are those that primarily feed on plant matter, such as leaves, fruits, and other plant based foods for their nutrition. they are also known as primary consumers and are at level 2 or higher in the food chain. examples of herbivores include animals like elephants, rabbits, and deer. Carnivores are animals that eat other animals. the word carnivore is derived from latin and literally means “meat eater.”. wild cats such as lions, shown in figure 2a and tigers are examples of vertebrate carnivores, as are snakes and sharks, while invertebrate carnivores include sea stars, spiders, and ladybugs, shown in figure 2b. Carnivores and omnivores occupy the third trophic level. an omnivore, such as a human, is an organism that eats plants and animals. many carnivores get their energy and nutrients by eating herbivores, omnivores, and other carnivores. the animals that eat secondary consumers, like owls that eat rodents, are known as tertiary consumers. Humans, bears, and chickens are examples of vertebrate omnivores; invertebrate omnivores include cockroaches and crayfish. figure 34.2.1 34.2. 1: examples of omnivores: omnivores such as the (a) bear and (b) crayfish eat both plant and animal based food. while their food options are greater than those of herbivores or carnivores, they are.

Comments are closed.