Cardiovascular Heart Intro To The Heart And Thoracic Cavity

Heart Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology Dr. glenn fox discusses the heart and thoracic cavity in relation to the lectures for the anat 403 course at the university of michigan. Location of the heart. the human heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the space known as the mediastinum. figure 19.2 shows the position of the heart within the thoracic cavity. within the mediastinum, the heart is separated from the other mediastinal structures by a tough membrane known as the pericardium.

Cardiovascular Heart Intro To The Heart And Thoracic Cavity Youtube The slight deviation of the apex to the left is reflected in a depression in the medial surface of the inferior lobe of the left lung, called the cardiac notch. figure 17.2.1 17.2. 1: location of heart in the thorax. the heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the mediastinum. The heart is subdivided by septa into right and left halves, and a constriction subdivides each half of the organ into two cavities, the upper cavity being called the atrium, the lower the ventricle. the heart, therefore, consists of four chambers: right atrium. left atrium. right ventricle. left ventricle [6]. The heart consists of several layers of a tough muscular wall, the myocardium. a thin layer of tissue, the pericardium, covers the outside, and another layer, the endocardium, lines the inside. the heart cavity is divided down the middle into a right and a left heart, which in turn are subdivided into two chambers. The shape of the heart is similar to a pinecone, broad at the superior surface (called the base) and tapering to the apex. a typical heart is approximately the size of your fist: 12 cm (5 in) in length, 8 cm (3.5 in) wide, and 6 cm (2.5 in) in thickness. given the size difference between most members of the sexes, the weight of a female heart.

Heart Located In The Mediastinum Of The Thoracic Cavity Specifically The heart consists of several layers of a tough muscular wall, the myocardium. a thin layer of tissue, the pericardium, covers the outside, and another layer, the endocardium, lines the inside. the heart cavity is divided down the middle into a right and a left heart, which in turn are subdivided into two chambers. The shape of the heart is similar to a pinecone, broad at the superior surface (called the base) and tapering to the apex. a typical heart is approximately the size of your fist: 12 cm (5 in) in length, 8 cm (3.5 in) wide, and 6 cm (2.5 in) in thickness. given the size difference between most members of the sexes, the weight of a female heart. The aortic semilunar valve is between the left ventricle and the opening of the aorta. it has three semilunar cusps leaflets: left left coronary, right right coronary, and posterior non coronary. in clinical practice, the heart valves can be auscultated, usually by using a stethoscope. 6.1 heart anatomy. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: describe the location and position of the heart within the body cavity. describe the internal and external anatomy of the heart. identify the tissue layers of the heart. relate the structure of the heart to its function as a pump.
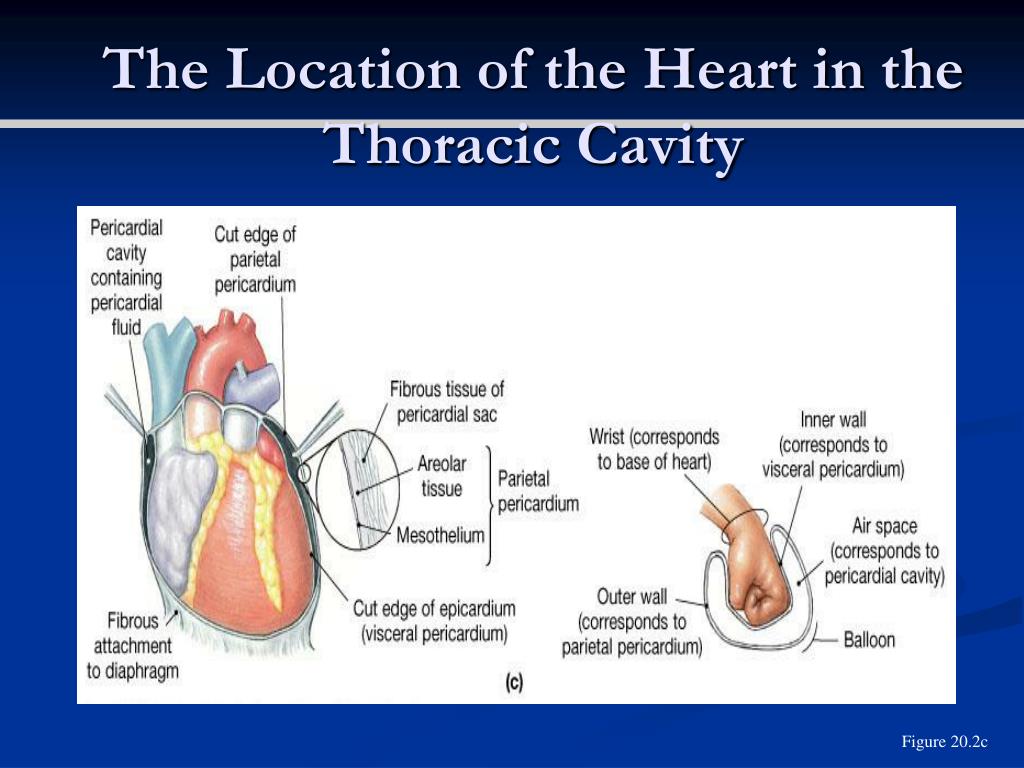
Ppt The Heart Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6926770 The aortic semilunar valve is between the left ventricle and the opening of the aorta. it has three semilunar cusps leaflets: left left coronary, right right coronary, and posterior non coronary. in clinical practice, the heart valves can be auscultated, usually by using a stethoscope. 6.1 heart anatomy. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: describe the location and position of the heart within the body cavity. describe the internal and external anatomy of the heart. identify the tissue layers of the heart. relate the structure of the heart to its function as a pump.

Anatomy Of The Thoracic Aorta And Of Its Branches Thoracic Surgery

What Is Thoracic Cavity Anatomy Info Hub Youtube

Comments are closed.