Can Policy Market Interventions Cause Consumer Or Producer Surplus
Can Policy Market Interventions Cause A Change In Consumer Or Producer While price controls, subsidies and other forms of market intervention might increase consumer or producer surplus, economic theory states that any gain would be outweighed by the losses sustained by the other side. this net harm is what causes deadweight loss. deadweight loss can be visually represented on supply and demand graphs. 2. government intervention: how can the government intervene and what is the effect 3. deadweight loss: what it is, why it is important and how it is calculated 4. numeric examples: two exercises to understand how all concepts work together 1. review of consumer and producer surplus 1.1 consumer surplus 1.2 producer surplus 1.1 consumer surplus.

Producer Surplus Tutor2u Economics Governments intervene in markets to try and overcome market failure. the government may also seek to improve the distribution of resources (greater equality). the aims of government intervention in markets include. stabilise prices. provide producers farmers with a minimum income. to avoid excessive prices for goods with important social welfare. 1. which government interventions cause a consumer or producer surplus? subsidies, price controls, and other interventions may increase producer or consumer surplus. that said, one must remember that according to economic theory, losses sustained by the other side may outweigh any gain. this net harm causes deadweight loss. From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve. With that much wheat on the market, there is market pressure on the price of wheat to fall. to prevent price from falling, the government buys the surplus of (w 2 – w 1) bushels of wheat, so that only w 1 bushels are actually available to private consumers for purchase on the market. the government can store the surpluses or find special uses.
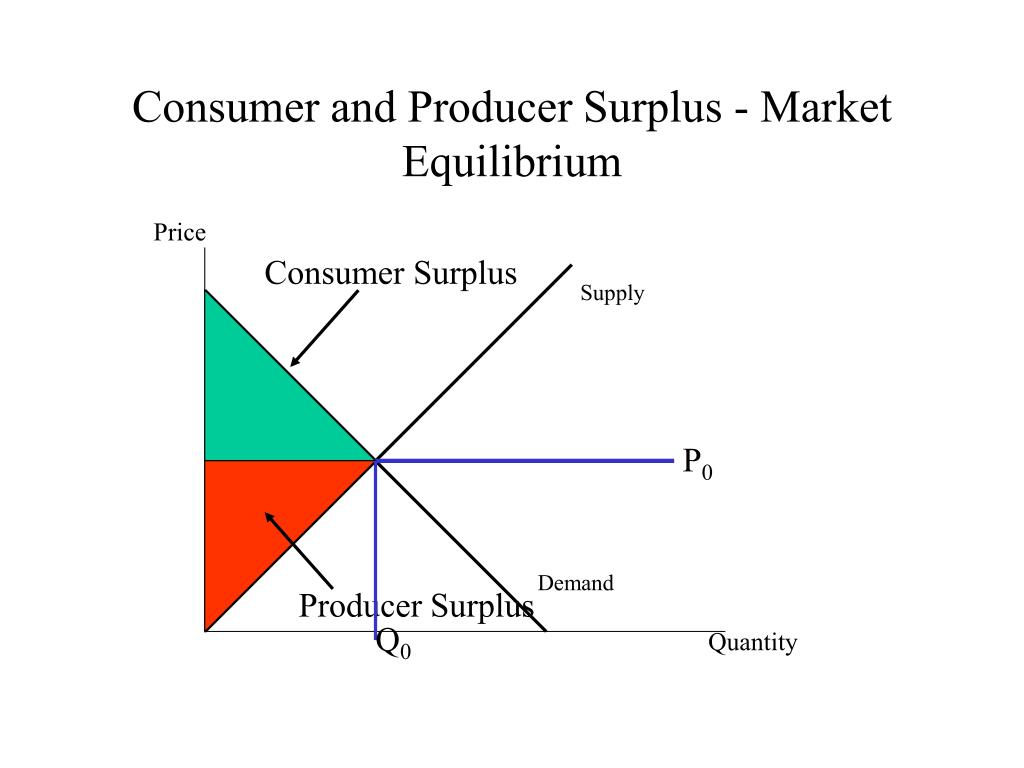
Ppt Policy Analysis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4857968 From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve. With that much wheat on the market, there is market pressure on the price of wheat to fall. to prevent price from falling, the government buys the surplus of (w 2 – w 1) bushels of wheat, so that only w 1 bushels are actually available to private consumers for purchase on the market. the government can store the surpluses or find special uses. Chapter 5. government interventions. we have so far focused on unimpeded markets, and we saw that markets may perform efficiently. the standard term for an unimpeded market is a free market, which is free in the sense of “free of external rules and constraints.”. in this terminology, ebay is a free market, even though it charges for the use. Summary. both consumer surplus and producer surplus are economic terms used to define market wellness by studying the relationship between the consumers and suppliers. the consumer surplus refers to the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay and what they paid for a product. the producer surplus is the difference between the.
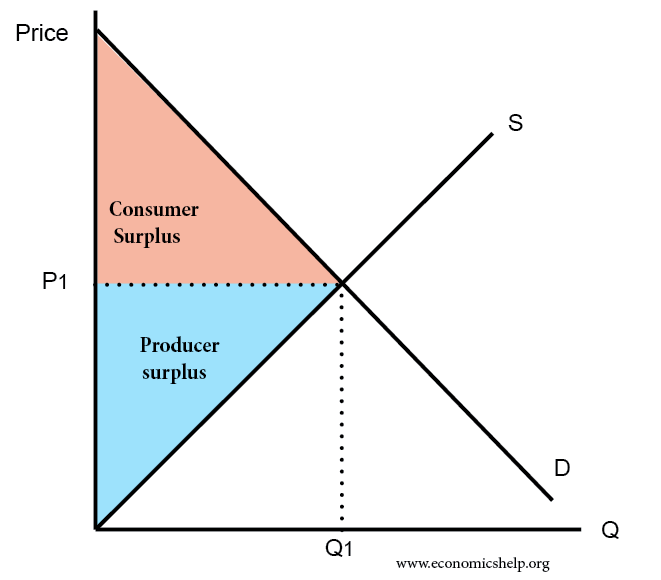
Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Economics Help Chapter 5. government interventions. we have so far focused on unimpeded markets, and we saw that markets may perform efficiently. the standard term for an unimpeded market is a free market, which is free in the sense of “free of external rules and constraints.”. in this terminology, ebay is a free market, even though it charges for the use. Summary. both consumer surplus and producer surplus are economic terms used to define market wellness by studying the relationship between the consumers and suppliers. the consumer surplus refers to the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay and what they paid for a product. the producer surplus is the difference between the.

Solved Can Policy Market Interventions Cause Consumer Or Producer
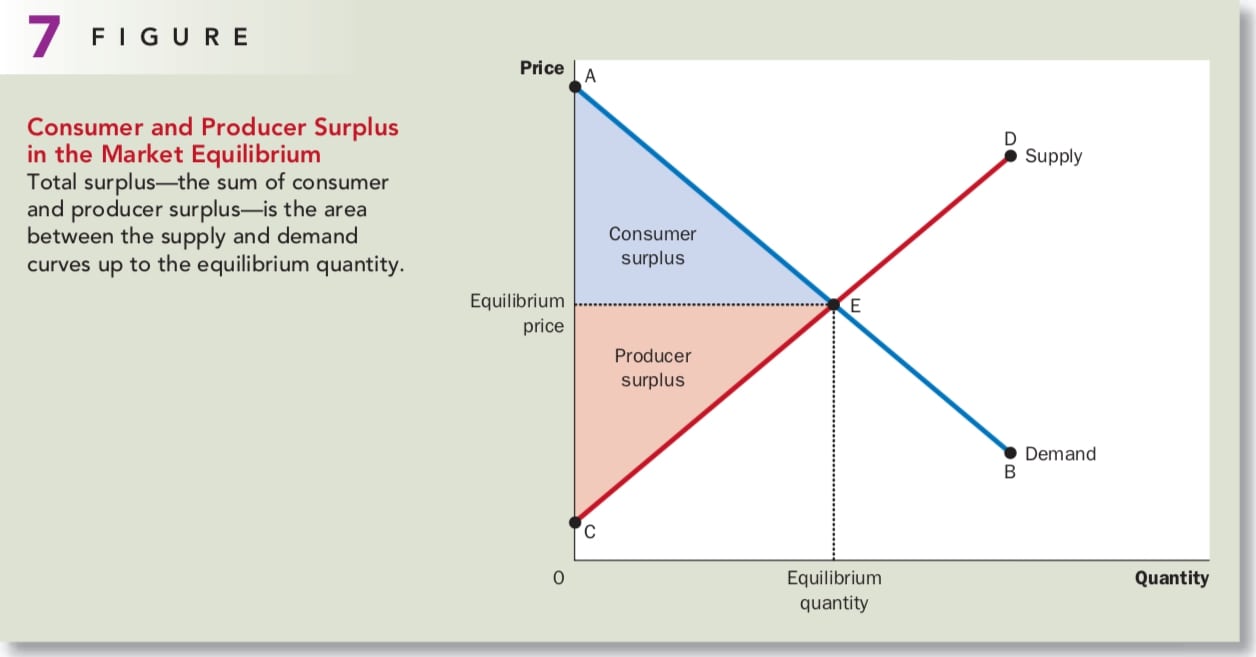
Microeconomics Consumers Producers And The Efficiency Of Markets

Comments are closed.