Calculation Of Equivalent Dose And Effective Dose Moe
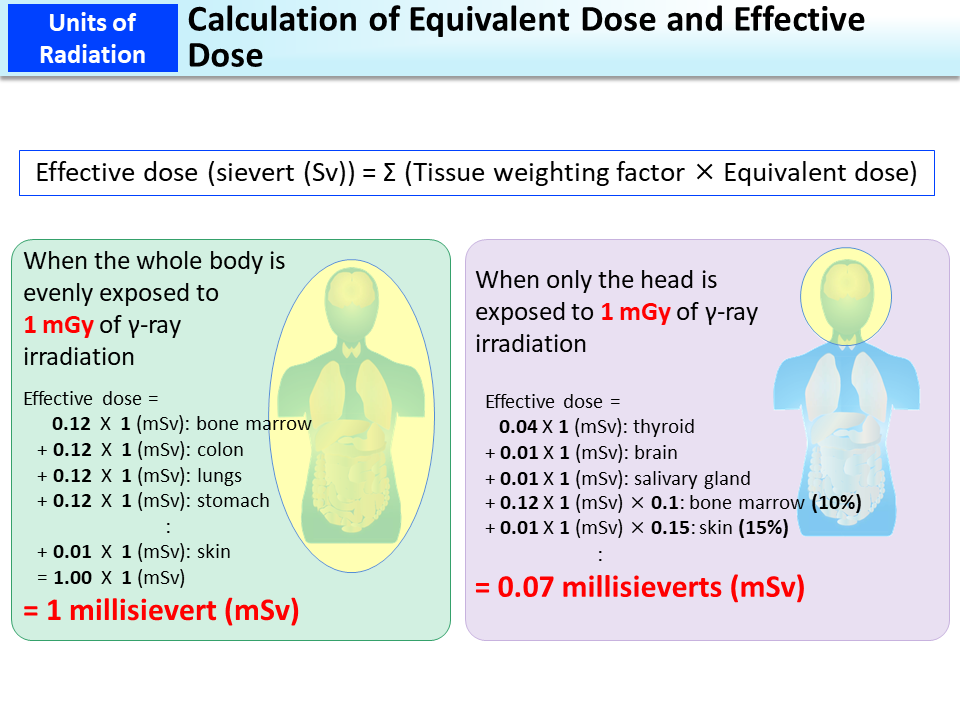
Calculation Of Equivalent Dose And Effective Dose Moe Icrp26: effective dose equivalent in 1977, icrp report 261 defined the effective dose equivalent as he5swtŁht, where wt is the weighting coefficient per tissue~t! or organ, ht is the dose equivalent to tissue t, and he is the summa tion over all tissues of the product wtŁht. it is important to recall the definition of dose equivalent ht5qŁdt,. Absorbed dose is the amount of energy deposited by radiation in a mass. the mass can be anything: water, rock, air, people, etc. absorbed dose is expressed in milligrays (mgy). equivalent dose. equivalent dose is calculated for individual organs. it is based on the absorbed dose to an organ, adjusted to account for the effectiveness of the type.
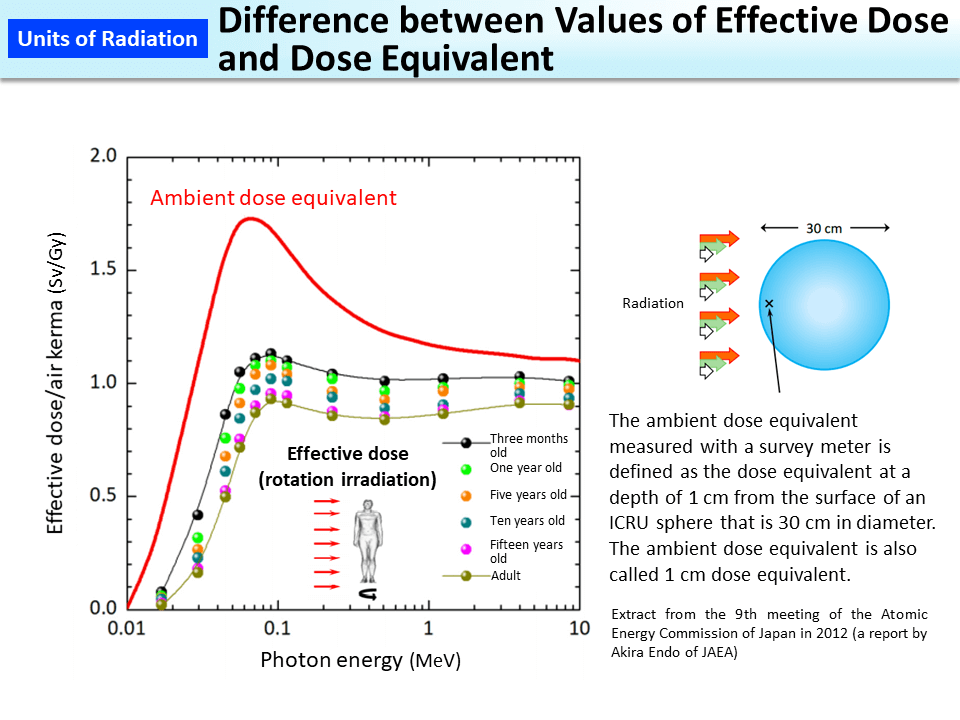
Difference Between Values Of Effective Dose And Dose Equivalent Moe That is, equivalent doses are 1 msv for all organs and tissues. to calculate effective doses, the equivalent doses for individual tissues are multiplied by their respective tissue weighting factors and the products are summed. bone marrow, colon, lungs, stomach and breasts are given a high factor of 0.12 because these are organs with high risks. The effective dose is calculated as the weighted average of the mean absorbed dose to the various body organs and tissues, where the weighting factor is the radiation detriment for a given organ (from a whole body irradiation) as a fraction of the total radiation detriment. in this review, effective dose equivalent and effective dose, as. Conversion from gray to sievert. to calculate the effective dose that expresses the effects of radiation exposure on the whole body, it is necessary to first determine the absorbed doses of individual tissues and organs exposed. the equivalent dose (expressed in sieverts) is obtained by multiplying the absorbed doses of individual tissues and. Mbq. open in a new tab. the dosimetric quantity kerma (or dose) area product (p ka or dap) is used for radiography, fluoroscopy and interventional procedures and takes into account the radiation produced by the x ray system and the irradiated area during the radiological procedure. it is usually measured in gy.cm 2.
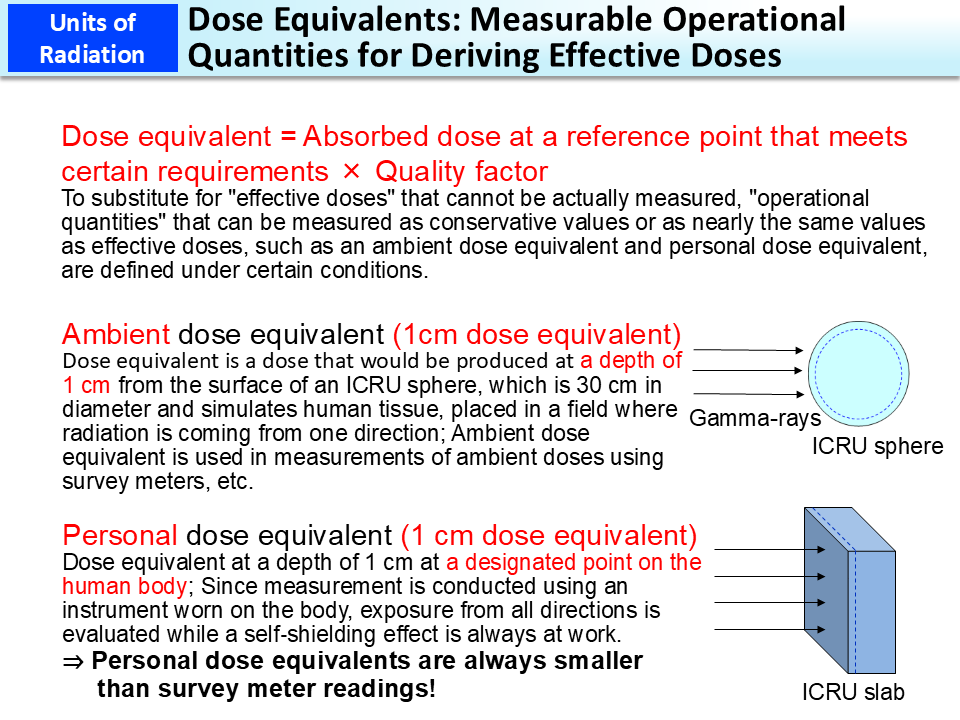
Dose Equivalents Measurable Operational Quantities For Deriving Conversion from gray to sievert. to calculate the effective dose that expresses the effects of radiation exposure on the whole body, it is necessary to first determine the absorbed doses of individual tissues and organs exposed. the equivalent dose (expressed in sieverts) is obtained by multiplying the absorbed doses of individual tissues and. Mbq. open in a new tab. the dosimetric quantity kerma (or dose) area product (p ka or dap) is used for radiography, fluoroscopy and interventional procedures and takes into account the radiation produced by the x ray system and the irradiated area during the radiological procedure. it is usually measured in gy.cm 2. Calculate the primary photon dose rate, in sieverts per hour (sv.h 1), at the outer surface of a 5 cm thick lead shield. then calculate the equivalent and effective dose rates for two cases. assume that this external radiation field penetrates uniformly through the whole body. that means: calculating the effective whole body dose rate. Abstract. equivalent and effective dose are protection quantities defined by the the international commission on radiological protection (icrp). they are frequently referred to simply as dose and may be misused. they provide a method for the summation of doses received from external sources and from intakes of radionuclides for comparison with.
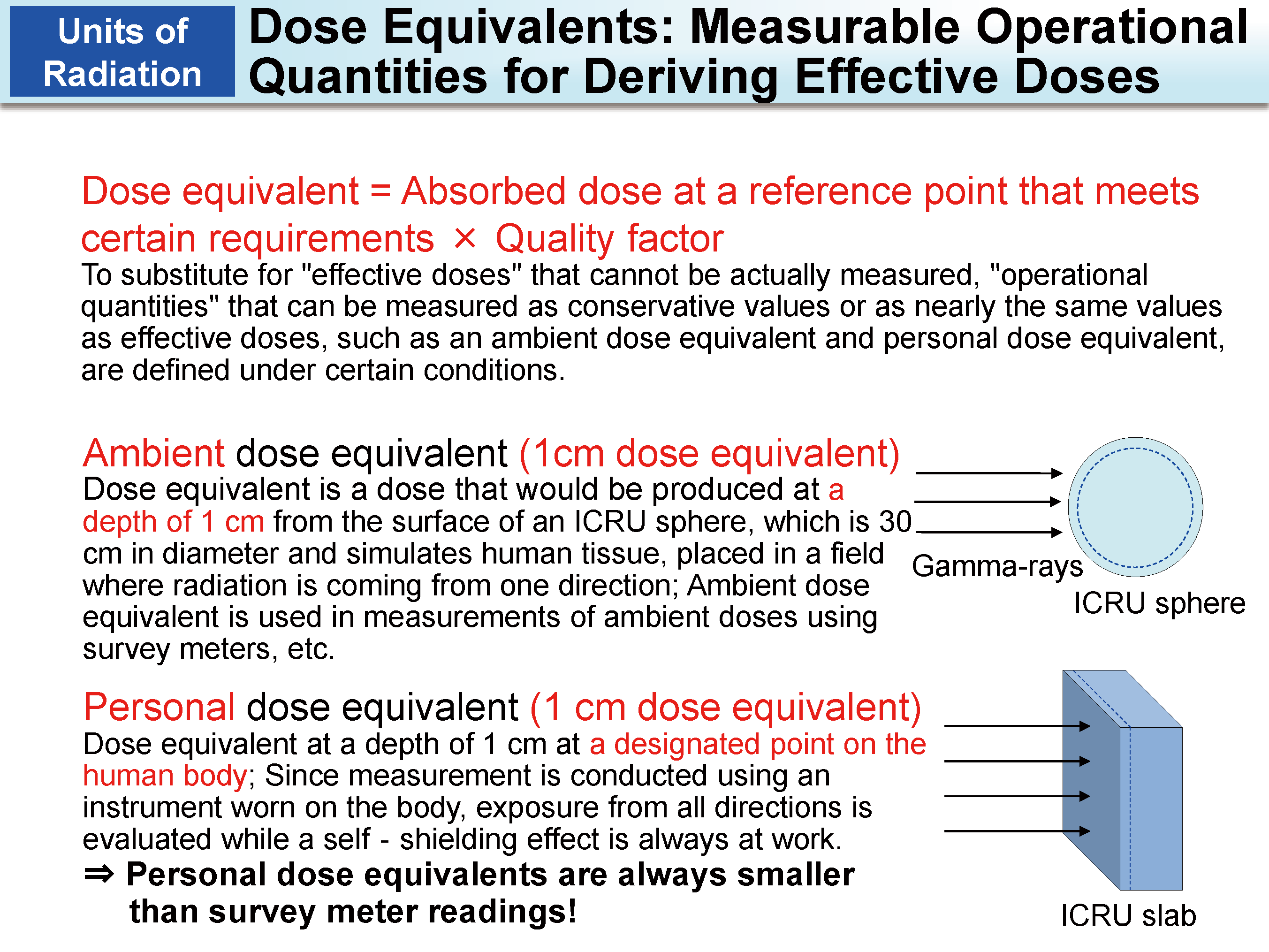
Dose Equivalents Measurable Operational Quantities For Deriving Calculate the primary photon dose rate, in sieverts per hour (sv.h 1), at the outer surface of a 5 cm thick lead shield. then calculate the equivalent and effective dose rates for two cases. assume that this external radiation field penetrates uniformly through the whole body. that means: calculating the effective whole body dose rate. Abstract. equivalent and effective dose are protection quantities defined by the the international commission on radiological protection (icrp). they are frequently referred to simply as dose and may be misused. they provide a method for the summation of doses received from external sources and from intakes of radionuclides for comparison with.

Comments are closed.