Caching Simply Explained

Caching Simply Explained Youtube Caches are used everywhere in our modern devices. it's found in many hardware components and throughout software. the goal of caching is to store data from slow memory into fast memory so it can be retrieved quicker. that's why browsers keep a cache: so they don't have to re download everything from the internet over and over again. sources. What is a cache? how does it work, and why is it important?caches are used everywhere in our modern devices. it's found in many hardware components and throu.
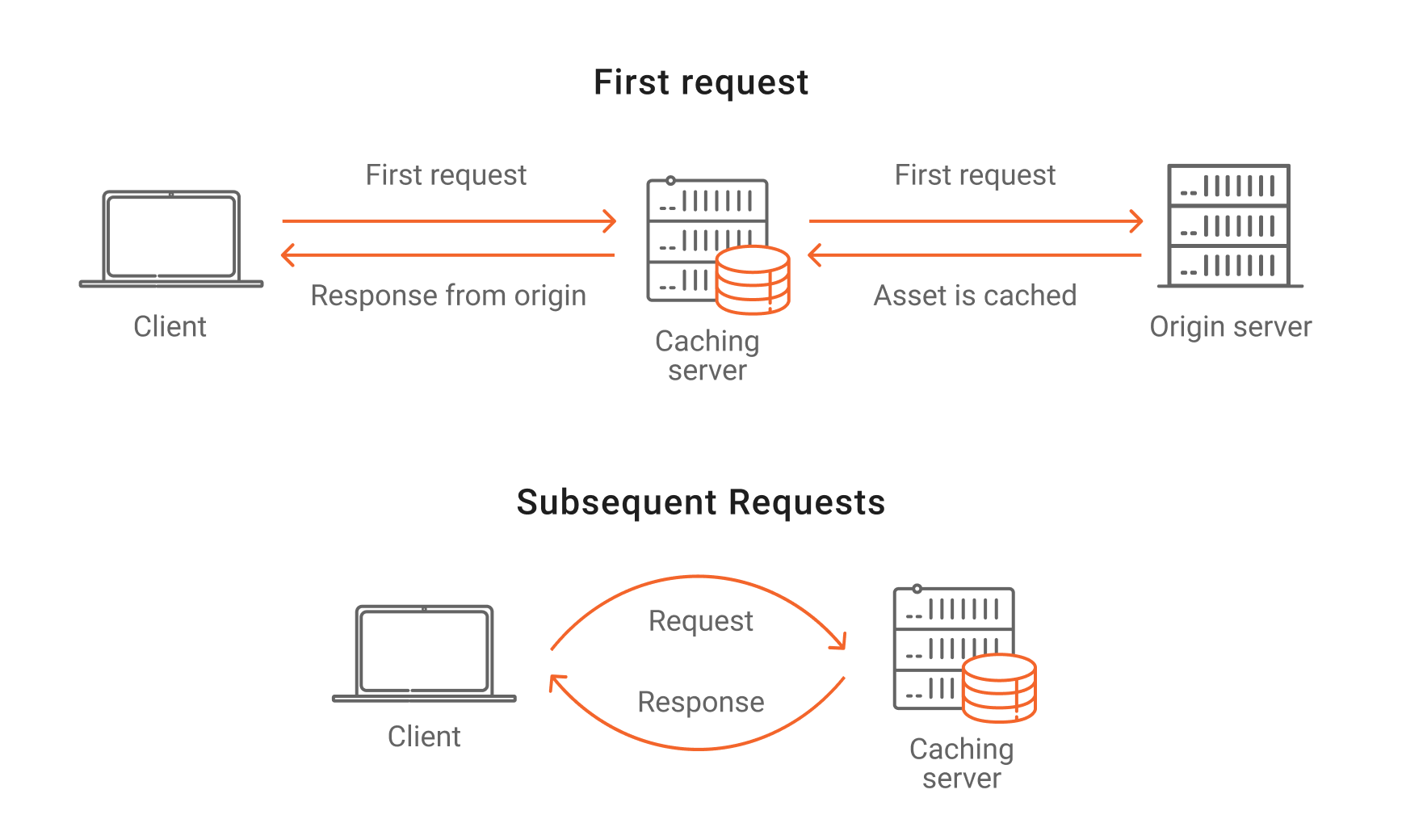
What Is Http Caching And How Does It Work Azion Caching is the process of storing copies of files in a cache, or temporary storage location, so that they can be accessed more quickly. technically, a cache is any temporary storage location for copies of files or data, but the term is often used in reference to internet technologies. web browsers cache html files, javascript, and images in. What is caching? in computing, a cache is a high speed data storage layer which stores a subset of data, typically transient in nature, so that future requests for that data are served up faster than is possible by accessing the data’s primary storage location. caching allows you to efficiently reuse previously retrieved or computed data. Cache (pronounced “cash”) is a type of computing memory used to improve the speed at which we access frequently requested data. caching improves performance, efficiency and the user experience. in computing, the term caching refers to storing frequently accessed data temporarily in a faster memory or storage. Caching is a system design concept that involves storing frequently accessed data in a location that is easily and quickly accessible. the purpose of caching is to improve the performance and efficiency of a system by reducing the amount of time it takes to access frequently accessed data.
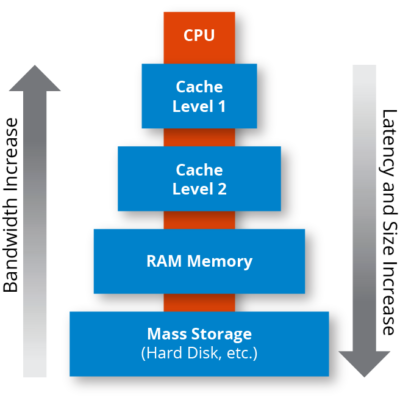
What Is Caching How Caching Works And Its Limitations Cache (pronounced “cash”) is a type of computing memory used to improve the speed at which we access frequently requested data. caching improves performance, efficiency and the user experience. in computing, the term caching refers to storing frequently accessed data temporarily in a faster memory or storage. Caching is a system design concept that involves storing frequently accessed data in a location that is easily and quickly accessible. the purpose of caching is to improve the performance and efficiency of a system by reducing the amount of time it takes to access frequently accessed data. Here are the five stages of the caching process and what they entail: request for data: the system, such as a computer, website, or application, requests data from a specific resource. checking the cache: the system then checks the cache to see if there’s a copy of this data from a previous request. Level 1: browser cache: browser cache or personal cache is available in all modern browsers (like firefox, chrome, ie). it works on the simple rules and stores a specific amount of web objects (html, css and js) on your hard disk. for example if you hit the back button, your browser will display the page from cache instead of sending a request.

Comments are closed.