Buec 311 Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony W17 Handout Pptx Market

Buec 311 Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony W17 Handout Pptx Market View buec 311 market power monopoly and monopsony w17 handout.pptx from busi 5703 at dalhousie university. market power: monopoly and monopsony definitions monopoly market with only one seller no. Chapter 10 monopoly and monopsony | ppt. ai enhanced description. yesica adicondro. follow. this document discusses monopoly and monopoly power. it begins by reviewing perfect competition and then defines monopoly as a market with one seller and many buyers of a unique product where there are barriers to entry.
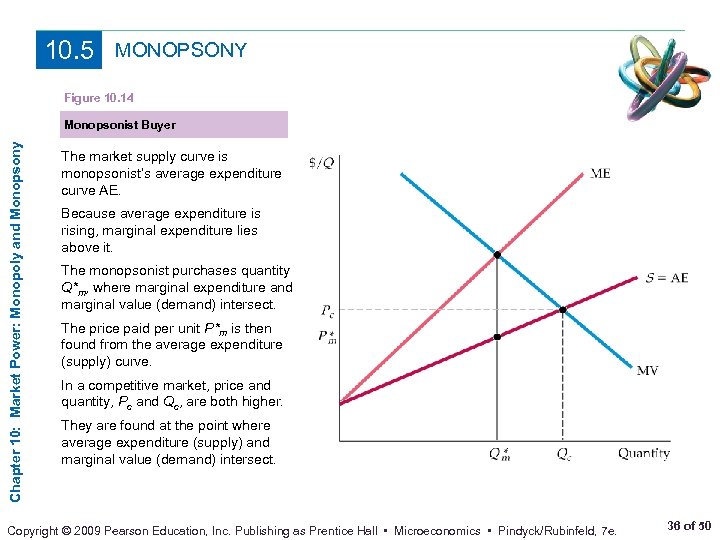
Chapter 10 Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony Prepared Microeconomics market power monopoly and monopsony.pptx. apr 18, 2024 • download as pptx, pdf •. 0 likes • 42 views. n. nazminawi1. follow. microeconomics market power monopoly and monopsony. read more. 1 of 41. Social costs of market power i in a competitive market, price is equal to marginal cost i for firms with monopoly power, firms charge a price that is a markup over marginal costs. i due to this, we see some deadweight loss ec 311 selby monopolies 24 50. 89 monopsony power bilateral monopoly market where there is only one buyer and one seller bilateral monopoly is rare, however, markets with a small number of sellers with monopoly power selling to a market with few buyers with monopsony power is more common even with bargaining, in general, monopsony and monopoly power will counteract each. Monopoly and monopsony power are two forms of. market power. true false. the monopolist is the market and completely controls the amount of output offered for sale. this means that the monopolist can charge any price it wants. false at least not if its objective is to maximize profit. to maximize profit, the monopolist must first determine.

Solution Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony Microeconomics Studypool 89 monopsony power bilateral monopoly market where there is only one buyer and one seller bilateral monopoly is rare, however, markets with a small number of sellers with monopoly power selling to a market with few buyers with monopsony power is more common even with bargaining, in general, monopsony and monopoly power will counteract each. Monopoly and monopsony power are two forms of. market power. true false. the monopolist is the market and completely controls the amount of output offered for sale. this means that the monopolist can charge any price it wants. false at least not if its objective is to maximize profit. to maximize profit, the monopolist must first determine. These buyers have monopsony power. monopoly and monopsony power. these are two forms of market power: the ability of either seller or buyer to affect the price of a good. monopolists. to maximize profit, the monopolists must first determine its costs and the characteristics of market demand. the monopolists must then determine how much to. Monopsony. a market that has many sellers and one buyer. monopolist demand curve. because the monopolist is the sole producer of a product the demand curve that it faces is the market demand curve. monopsonist. pays a price that depends on the quantity that it purchases. the monopsonist's problem is to choose the quantity that maximizes its net.

Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony Ppt Download These buyers have monopsony power. monopoly and monopsony power. these are two forms of market power: the ability of either seller or buyer to affect the price of a good. monopolists. to maximize profit, the monopolists must first determine its costs and the characteristics of market demand. the monopolists must then determine how much to. Monopsony. a market that has many sellers and one buyer. monopolist demand curve. because the monopolist is the sole producer of a product the demand curve that it faces is the market demand curve. monopsonist. pays a price that depends on the quantity that it purchases. the monopsonist's problem is to choose the quantity that maximizes its net.
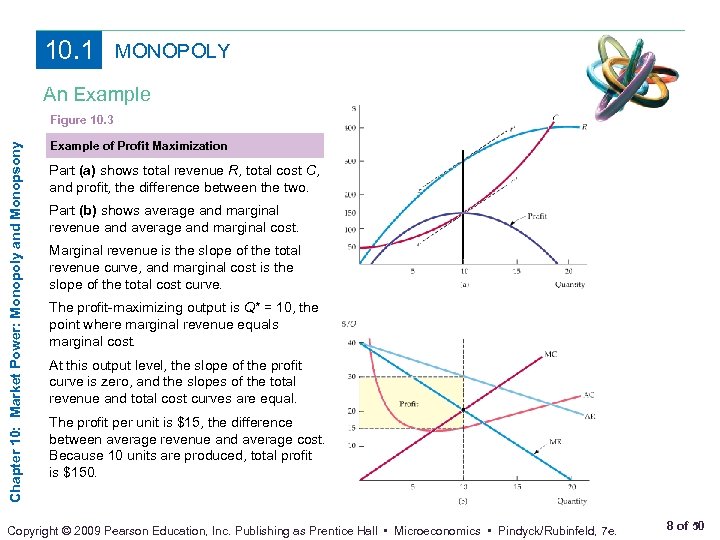
Chapter 10 Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony Prepared

Comments are closed.