Brain Anatomy Pituitary Gland
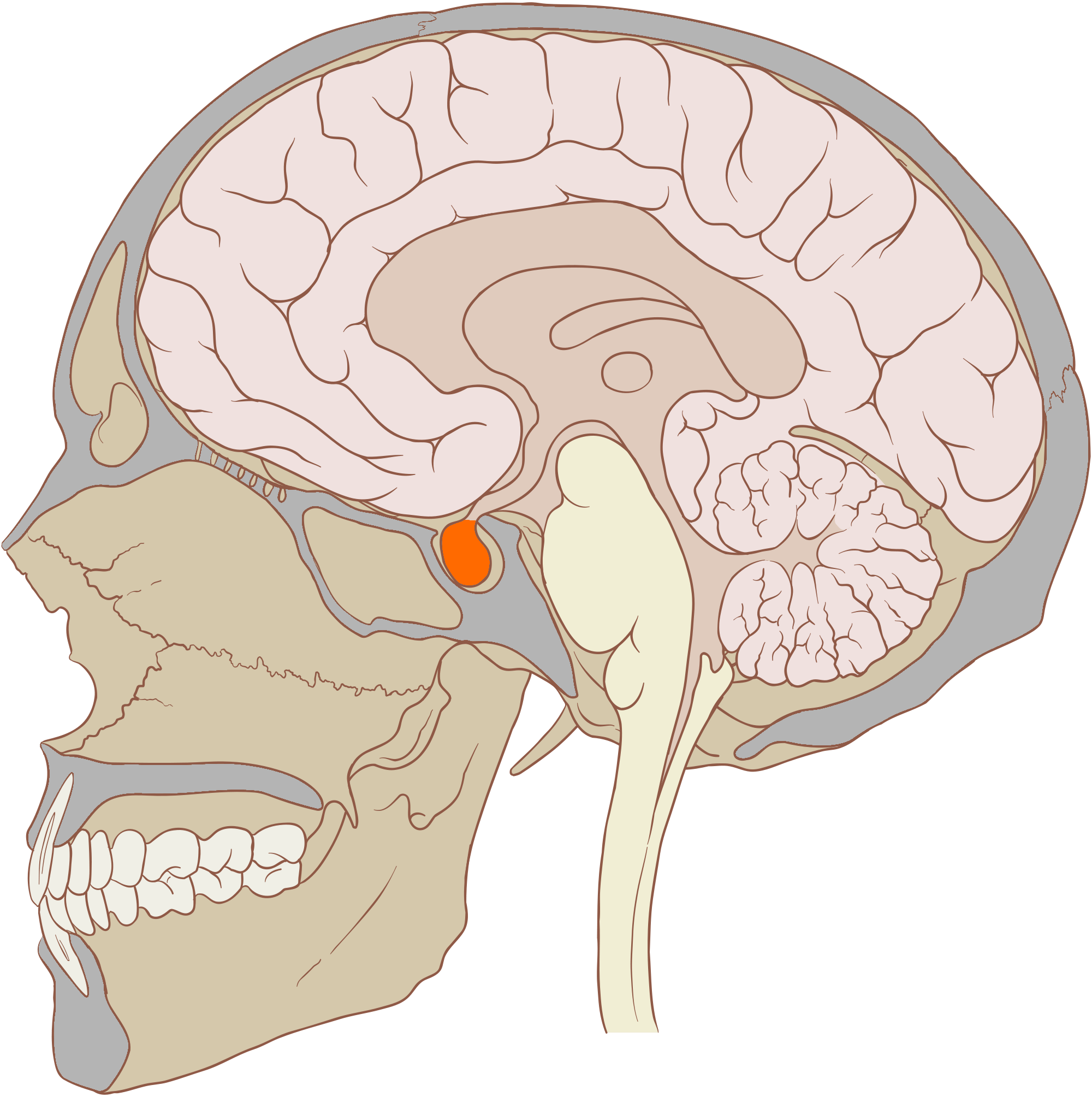
What Is The Function Of The Pituitary Gland Example Your pituitary gland (also known as hypophysis) is a small, pea sized gland located at the base of your brain below your hypothalamus. it sits in its own little chamber under your brain known as the sella turcica. it’s a part of your endocrine system and is in charge of making several essential hormones. your pituitary gland also tells other. The pituitary gland is a pea sized oval structure, suspended from the underside of the brain by the pituitary stalk (known as the infundibulum). it sits within a small depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the sella turcica (‘’turkish saddle’’). the superior surface of the gland is covered by a reflection of the dura mater – the.

Parts Of Pituitary Gland Pituitary gland (glandula pituitaria) endocrine system sella turcica of sphenoid bone hypothalamus. the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, also known as the adenohypophysis, produces and secretes the majority of pituitary hormones. its function is controlled by the releasing hormones of the hypothalamus. the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. in humans , the pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain , protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus . the human pituitary gland is oval shaped , about 1 cm in diameter, 0.5–1 gram (0.018–0.035 oz) in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean . Pituitary gland, ductless endocrine gland located on the underside of the brain that secretes hormones into the bloodstream. the pituitary gland is sometimes referred to as the ‘master gland’ because its hormones regulate other important endocrine glands, including the adrenal, thyroid, and reproductive glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. the gland is attached to the hypothalamus (a part of the brain that affects the pituitary gland) by nerve fibers and blood vessels. the pituitary gland itself consists of 2 major structures: anterior lobe. posterior lobe.
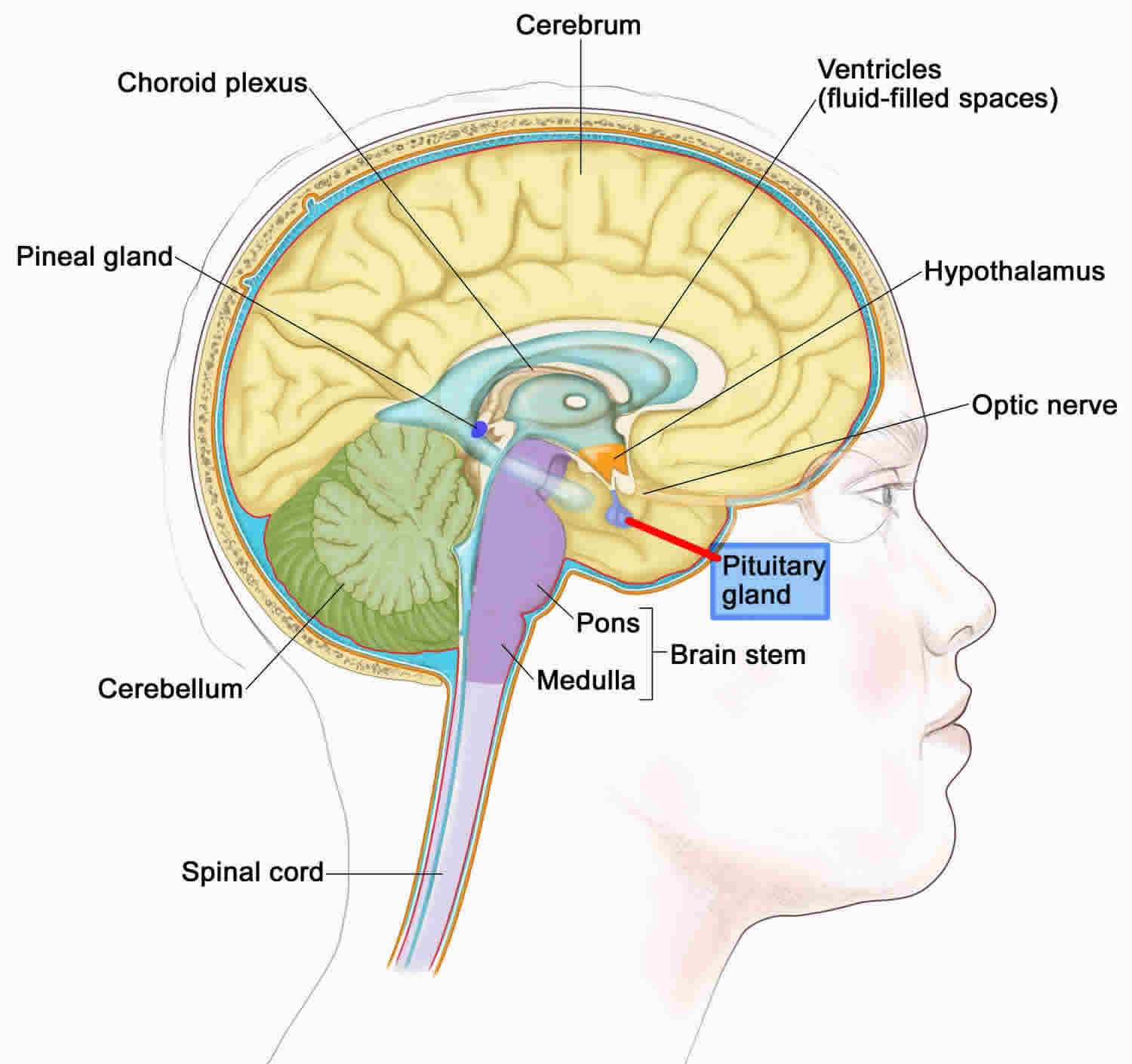
Pituitary Gland Anterior And Posterior Pituitary gland, ductless endocrine gland located on the underside of the brain that secretes hormones into the bloodstream. the pituitary gland is sometimes referred to as the ‘master gland’ because its hormones regulate other important endocrine glands, including the adrenal, thyroid, and reproductive glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. the gland is attached to the hypothalamus (a part of the brain that affects the pituitary gland) by nerve fibers and blood vessels. the pituitary gland itself consists of 2 major structures: anterior lobe. posterior lobe. Posterior pituitary lobe: the rear facing lobe of the gland is an extension of the hypothalamus brain region that is connected to the main body via the infundibular stalk, which is itself considered a part of the posterior pituitary lobe. this stalk runs from the tuber cinereum, a hollowed out eminence of the hypothalamus, to pierce the sellar. The pituitary endocrine gland, which is located in the bony sella turcica, is attached to the base of the brain and has a unique connection with the hypothalamus. the pituitary gland consists of two anatomically and functionally distinct regions, the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) and the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis). between these lobes lies a small region called the intermediate lobe.
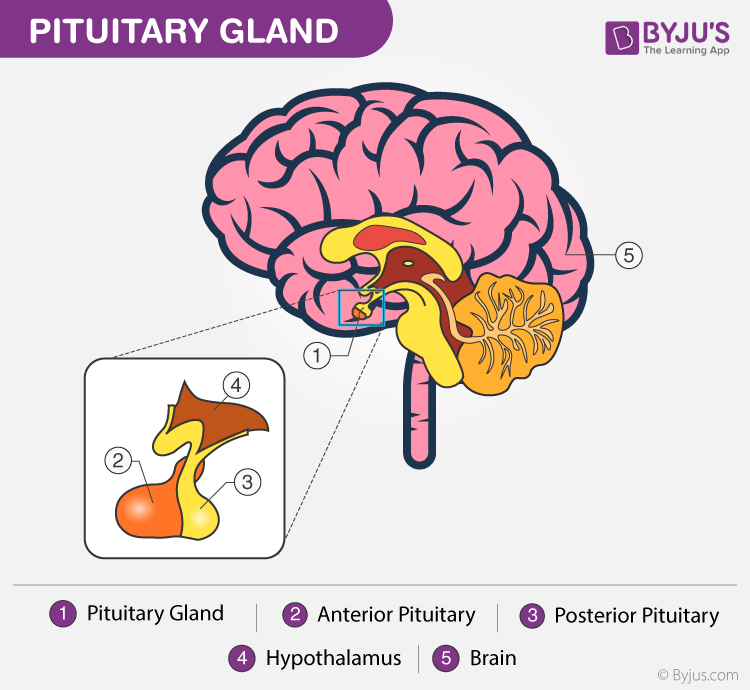
Pituitary Gland Discover Its Anatomy Functions And Its Disorders Posterior pituitary lobe: the rear facing lobe of the gland is an extension of the hypothalamus brain region that is connected to the main body via the infundibular stalk, which is itself considered a part of the posterior pituitary lobe. this stalk runs from the tuber cinereum, a hollowed out eminence of the hypothalamus, to pierce the sellar. The pituitary endocrine gland, which is located in the bony sella turcica, is attached to the base of the brain and has a unique connection with the hypothalamus. the pituitary gland consists of two anatomically and functionally distinct regions, the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) and the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis). between these lobes lies a small region called the intermediate lobe.

Comments are closed.