Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Organism

Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Organism The population of lions in kenya, plus the populations of gazelles, giraffes, elephants, dung beetles, and all other species in that area, add up to a community. ecosystem an ecosystem is made up of all the communities in a certain area, as well as all the non living, physical components of the environment. What are the 5 levels of ecology? organism. population. community. ecosystem. biosphere. ecology is the scientific study of the distribution and abundance of life along with the interactions between different organisms and their natural environment. it is the branch of biology, and the name ecology was derived from the greek word, which refers.
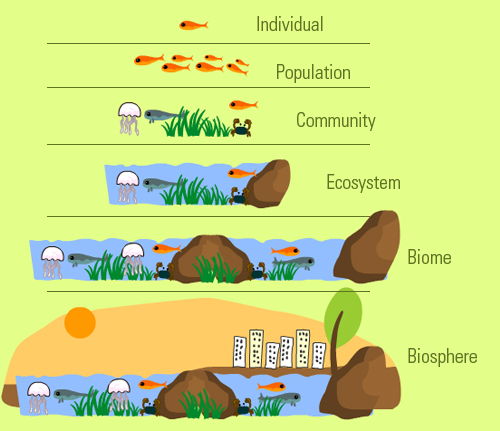
What Is The Difference Between Organism Population Community Community: it includes all the populations in a specific area at a given time. a community includes populations of organisms of different species. in the diagram above, note how populations of goldfish, salmons, crabs, and herrings coexist in a defined location. a great community usually includes biodiversity. ecosystem:. Populations of prokaryotes or eukaryotes interact within communities, contribute to ecosystem functions, and are part of the biosphere. 10. community level. examples: coral reef, rainforest; a community is the collection of all the different populations that live together in an area. 11. ecosystem level. examples: sahara desert, amazon. Ecosystems may be further subdivided into smaller biotic units called communities. examples of communities include the organisms in a stand of pine trees, on a coral reef, and in a cave, a valley, a lake, or a stream. the major consideration in the community is the living component, the organisms; the abiotic factors of the environment are. There are five levels of organization in the ecosystem. they are arranged from smallest to largest in the following order: levels of ecological organization. 1. organism. it is the lowest level of organization in an ecosystem. an organism or individual is a single organism, plant, animal, or microorganism, such as bacteria and fungi, capable of.

Biosphere Cycle Cycle Ecosystem Communities Population Vetor Stock Ecosystems may be further subdivided into smaller biotic units called communities. examples of communities include the organisms in a stand of pine trees, on a coral reef, and in a cave, a valley, a lake, or a stream. the major consideration in the community is the living component, the organisms; the abiotic factors of the environment are. There are five levels of organization in the ecosystem. they are arranged from smallest to largest in the following order: levels of ecological organization. 1. organism. it is the lowest level of organization in an ecosystem. an organism or individual is a single organism, plant, animal, or microorganism, such as bacteria and fungi, capable of. The ecology of the earth can be studied at various levels: an individual (organism), a population, a community, an ecosystem, a biome or the entire biosphere. the variety of living organisms that inhabit an environment is a measure of its biodiversity. Welcome to levels of ecology (organism, population, community, and ecosystem) with mr. j! need help with the difference between these ecological levels. you'.

Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biosphere Science Biology The ecology of the earth can be studied at various levels: an individual (organism), a population, a community, an ecosystem, a biome or the entire biosphere. the variety of living organisms that inhabit an environment is a measure of its biodiversity. Welcome to levels of ecology (organism, population, community, and ecosystem) with mr. j! need help with the difference between these ecological levels. you'.

Comments are closed.