Biology Definitions Actin Filament Biology Dictionary Defining

Diagram Of Actin And Myosin Microfilament definition. microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are polymers of the protein actin that are part of a cell’s cytoskeleton. the cytoskeleton is the network of protein filaments that extends throughout the cell, giving the cell structure and keeping organelles in place. microfilaments are the smallest filaments of the. Actin and myosin are both proteins that are found in all types of muscle tissue. myosin forms thick filaments (15 nm in diameter) and actin forms thinner filaments (7nm in diameter). actin and myosin filaments work together to generate force. this force produces the muscle cell contractions that facilitate the movement of the muscles and.

Biology Definitions Actin Filament Biology Dictionary Defining Cytoskeleton definition. the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. it is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms. the cytoskeleton supports the cell, gives it shape. Actin filaments, also known as microfilaments, are thin, thread like protein structures that are a key component of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells. they play a crucial role in maintaining cell shape, enabling cell movement, and facilitating intracellular transport. by forming networks and interacting with other proteins, actin filaments are essential for various cellular activities. Definition. actin filaments, also known as microfilaments, are thin protein fibers made of actin monomers that play a crucial role in various cellular processes, including motility, shape maintenance, and division. they are part of the cytoskeleton, providing structural support and enabling cellular movements by interacting with myosin and. Cell actin filaments, cytoskeleton, proteins: actin is a globular protein that polymerizes (joins together many small molecules) to form long filaments. because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin filament is polar, with different ends, termed “barbed” and “pointed.” an abundant protein in nearly all eukaryotic cells, actin has been extensively studied in muscle.

Actin Filament Structure Illustration Stock Image F038 0999 Definition. actin filaments, also known as microfilaments, are thin protein fibers made of actin monomers that play a crucial role in various cellular processes, including motility, shape maintenance, and division. they are part of the cytoskeleton, providing structural support and enabling cellular movements by interacting with myosin and. Cell actin filaments, cytoskeleton, proteins: actin is a globular protein that polymerizes (joins together many small molecules) to form long filaments. because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin filament is polar, with different ends, termed “barbed” and “pointed.” an abundant protein in nearly all eukaryotic cells, actin has been extensively studied in muscle. Definition. noun. plural: microfilaments. mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī’krō fil’ă mĕnts. a thin, helical, single stranded filament of the cytoskeleton found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell s, composed of actin subunits, and functions primarily in maintaining the structural integrity of a cell and cell movements. Actin, protein that is an important contributor to the contractile property of muscle and other cells. in muscle, two long strands of actin molecules are twisted together to form a thin filament, bundles of which alternate with bundles of myosin. the temporary fusion of actin and myosin results in muscle contraction.

The Cytoskeleton Biology For Majors I Definition. noun. plural: microfilaments. mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī’krō fil’ă mĕnts. a thin, helical, single stranded filament of the cytoskeleton found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell s, composed of actin subunits, and functions primarily in maintaining the structural integrity of a cell and cell movements. Actin, protein that is an important contributor to the contractile property of muscle and other cells. in muscle, two long strands of actin molecules are twisted together to form a thin filament, bundles of which alternate with bundles of myosin. the temporary fusion of actin and myosin results in muscle contraction.

Actin Filaments The Biology Blog
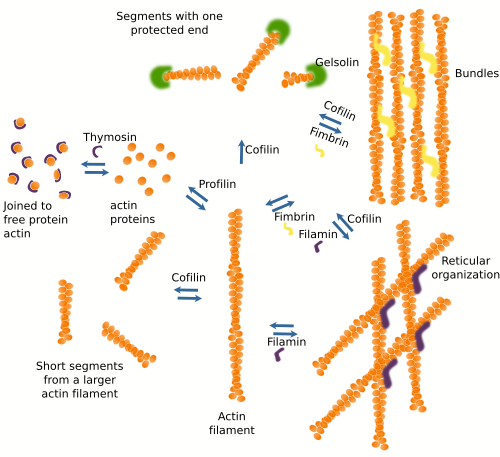
The Cell 7 Cytoskeleton Actin Filaments Atlas Of Plant And Animal

Comments are closed.