Benign Vs Malignant Tumors Technology Networks
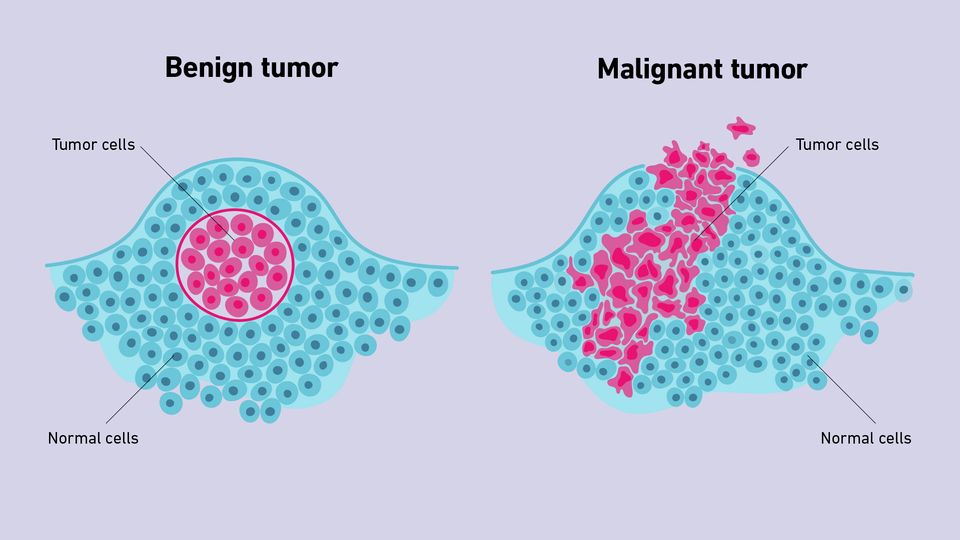
Benign Vs Malignant Tumors Technology Networks Benign tumors can grow to a large size, but do not expand into other tissues or other areas of the body. malignant tumors, on the other hand, are more aggressive. these can invade neighboring tissues or even spread through the blood and lymph systems to distant parts of the body. A tumor (also called neoplasm) is an abnormal mass of cells in the body. it is caused by cells dividing more than normal or not dying when they should. tumors can be classified as benign or malignant. benign tumors are those that stay in their primary location without invading other sites of the body.

Benign Tumor Vs Malignant A total of 3791 parotid gland region images were cropped from the mr images. a label (pleomorphic adenoma and warthin tumor, malignant tumor or free of tumor), which was based on histology results, was assigned to each image. to train the deep learning model, these data were randomly divided into a training dataset (90%, comprising 3035 mr. Smith says that in general, cancerous, or malignant, tumours would grow quicker than a benign tumour. “they’re more active. they tend to spread more through the tissue locally and, generally, they also have the ability to spread to other regions of the body, through the blood or lymph nodes.”. smith says he often gives his patients the. Ultrasound features also differed significantly between benign and malignant adnexal tumors. malignant tumors had larger diameters for both mass and solid components (74 vs. 55 mm, p < 0.001; 50 vs. 24 mm, p < 0.001) and more abundant blood flow (p < 0.001). there were also notable differences in tumor type between the two groups, with. While benign tumors generally don’t invade and spread, malignant cells are more likely to metastasize, or travel to other areas of the body. they also grow faster. while it may seem easy to categorize benign tumors as harm less and malignant tumors as harm ful, the distinctions are often more of a gray area.

Benign Vs Malignant Tumors Diagram Quizlet Ultrasound features also differed significantly between benign and malignant adnexal tumors. malignant tumors had larger diameters for both mass and solid components (74 vs. 55 mm, p < 0.001; 50 vs. 24 mm, p < 0.001) and more abundant blood flow (p < 0.001). there were also notable differences in tumor type between the two groups, with. While benign tumors generally don’t invade and spread, malignant cells are more likely to metastasize, or travel to other areas of the body. they also grow faster. while it may seem easy to categorize benign tumors as harm less and malignant tumors as harm ful, the distinctions are often more of a gray area. Benign vs malignant tumors. benign vs malignant tumors jama oncol. 2020 sep 1;6(9):1488. doi: 10.1001 jamaoncol.2020.2592. author aisha patel 1. Tumor forms when cells start to multiply and produce an abnormal growth. malignant cells can invade nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body and form cancers. when tumor cells do not have the ability to spread, they are called benign. in many cases, benign tumors can be managed by observation. but depending upon their location, they.
/514240-article-img-malignant-vs-benign-tumor2111891f-54cc-47aa-8967-4cd5411fdb2f-5a2848f122fa3a0037c544be.png)
Differences Between A Malignant And Benign Tumor Benign vs malignant tumors. benign vs malignant tumors jama oncol. 2020 sep 1;6(9):1488. doi: 10.1001 jamaoncol.2020.2592. author aisha patel 1. Tumor forms when cells start to multiply and produce an abnormal growth. malignant cells can invade nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body and form cancers. when tumor cells do not have the ability to spread, they are called benign. in many cases, benign tumors can be managed by observation. but depending upon their location, they.
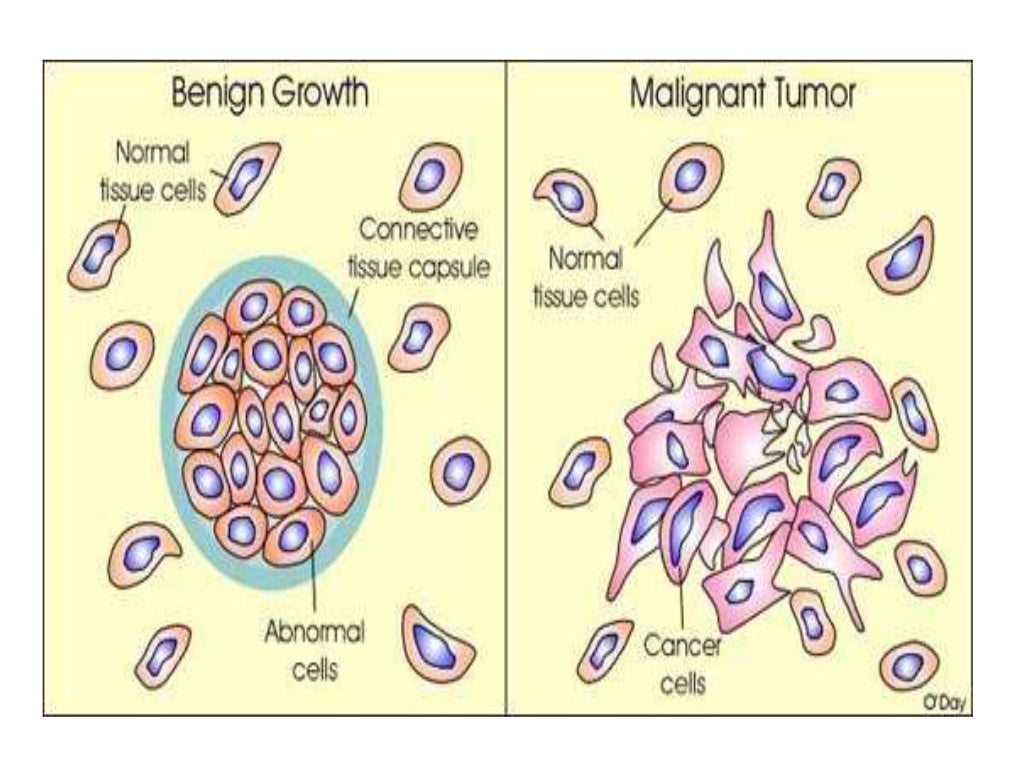
Benign And Malignant Tumor Comparison

Comments are closed.