Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Bppv What You Need To Know Mdmedicine Network
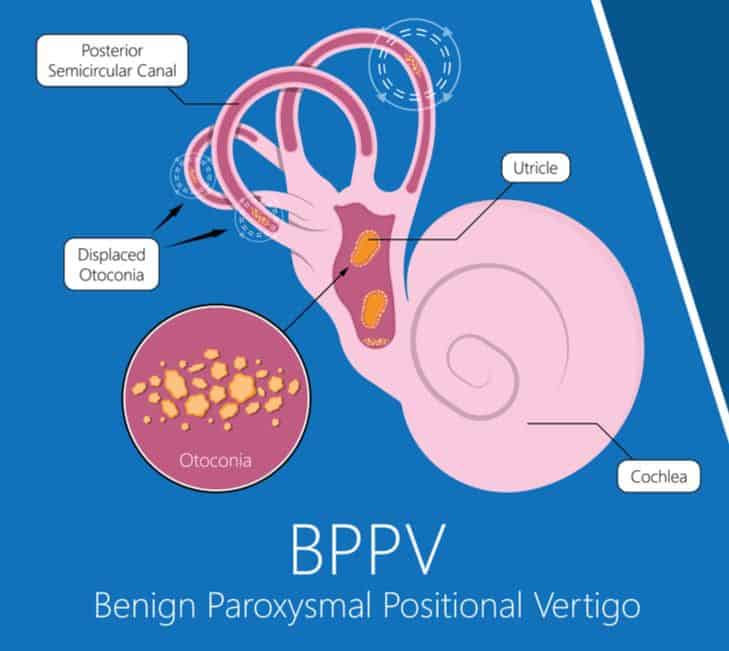
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Bppv Ear Science Institute The signs and symptoms of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) may include: dizziness. a sense that you or your surroundings are spinning or moving (vertigo) a loss of balance or unsteadiness. nausea. vomiting. the signs and symptoms of bppv can come and go and commonly last less than one minute. episodes of bppv can disappear for some. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) occurs when tiny canalith particles (otoconia) break loose and fall into the wrong part of the semicircular canals of the inner ear. the goal of the canalith repositioning procedure is to move the particles from the inner ear to a part of the ear where they won't cause problems (the utricle).

Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Shown Via Medical Animation Still And that is what makes you dizzy,” notes dr. cherian. the fact that your eyes continue to move in response to this false cue gives doctors another way to confirm that you have bppv. three. People with bppv can experience a spinning sensation — vertigo — any time there is a change in the position of the head. the symptoms can be very distressing. people can fall out of bed or lose their balance when they get up from bed and try to walk. if they tilt their head back or forward while walking, they may even fall, risking injury. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) is an inner ear disorder. a person with bppv experiences a sudden spinning sensation whenever they move their head. bppv isn’t a sign of a serious problem. if it doesn’t disappear on its own within six weeks, a simple in office procedure can help ease your symptoms. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (or bppv) is the most common cause of vertigo, which is a false sensation of spinning. 1. benign – it is not life threatening. paroxysmal – it comes in sudden, brief spells. positional – it gets triggered by certain head positions or movements. vertigo – a false sense of movement, often rotational.
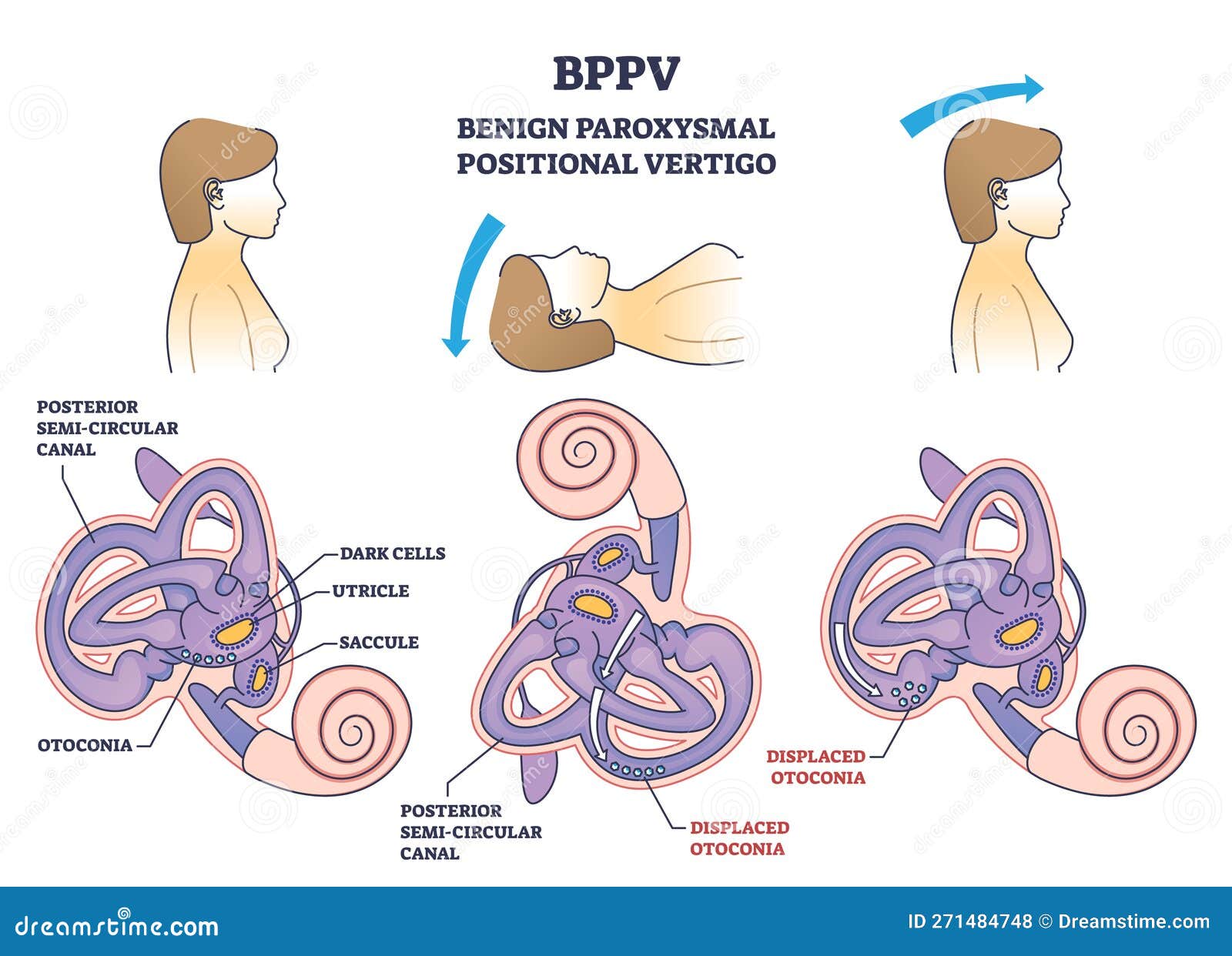
Bppv Or Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Syndrome Outline Diagram Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) is an inner ear disorder. a person with bppv experiences a sudden spinning sensation whenever they move their head. bppv isn’t a sign of a serious problem. if it doesn’t disappear on its own within six weeks, a simple in office procedure can help ease your symptoms. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (or bppv) is the most common cause of vertigo, which is a false sensation of spinning. 1. benign – it is not life threatening. paroxysmal – it comes in sudden, brief spells. positional – it gets triggered by certain head positions or movements. vertigo – a false sense of movement, often rotational. Paroxysmal means that it hits suddenly, lasts a short time, and comes and goes. positional means you trigger the vertigo with certain postures or movements of your head. bppv is common and usually. The clinical problem. benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) is by far the most common type of vertigo, with a reported prevalence between 10.7 and 64.0 cases per 100,000 population and a.

Comments are closed.