Benefits Of Lecanemab A New Alzheimer S Drug Unclear For Patients Of

Benefits Of Lecanemab A New Alzheimer S Drug Unclear For Patients Of A new drug for alzheimer's disease, called lecanemab, got a lot of attention earlier this year for getting fast tracked approval based on a clinical trial that included nearly 1,800 people. it was. Aarp interviewed six leading alzheimer’s specialists to get answers to 15 questions about the new alzheimer’s drugs. alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia, afflicting an estimated 6.9 million americans older than 65, according to 2020 data from the centers for disease control and prevention.
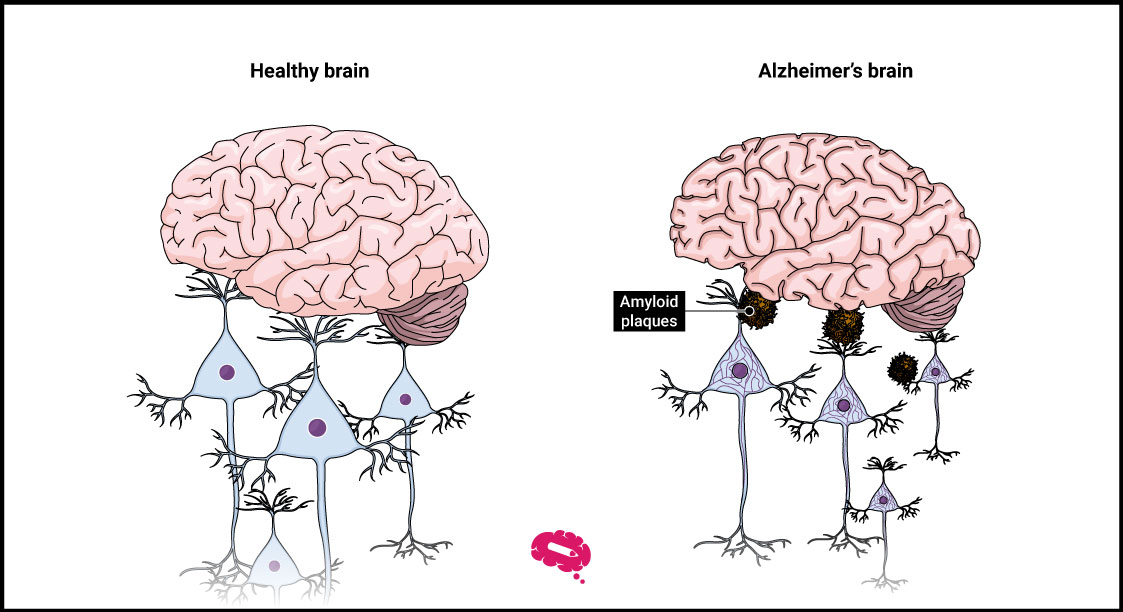
What Is Lecanemab The New Treatment For Alzheimer S The food and drug administration (fda) recently granted full approval to a new alzheimer’s treatment called lecanemab, which has been shown to moderately slow cognitive and functional decline in early stage cases of the disease. alzheimer’s disease is a progressive disorder that damages and destroys nerve cells in the brain. over time, the. Samuel gandy, a leading alzheimer’s physician and researcher at the icahn school of medicine at mount sinai, has an understanding of lecanemab’s unique molecular targets: he works with his. After plaque removal, dual acting lecanemab continues to positively impact biomarkers over the course of treatment. the key ad fluid biomarkers aβ42 40, ptau181, ptau217, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (***gfap) are more sensitive indicators of amyloid and tau development than amyloid pet and have been shown to re accumulate at a faster rate when treatment is discontinued. Lecanemab (leqembi®) is an antibody intravenous (iv) infusion therapy that targets and removes beta amyloid from the brain. it has received traditional approval from the u.s. food and drug administration (fda) to treat early alzheimer's disease, including people living with mild cognitive impairment (mci) or mild dementia due to alzheimer's disease who have confirmation of elevated beta.
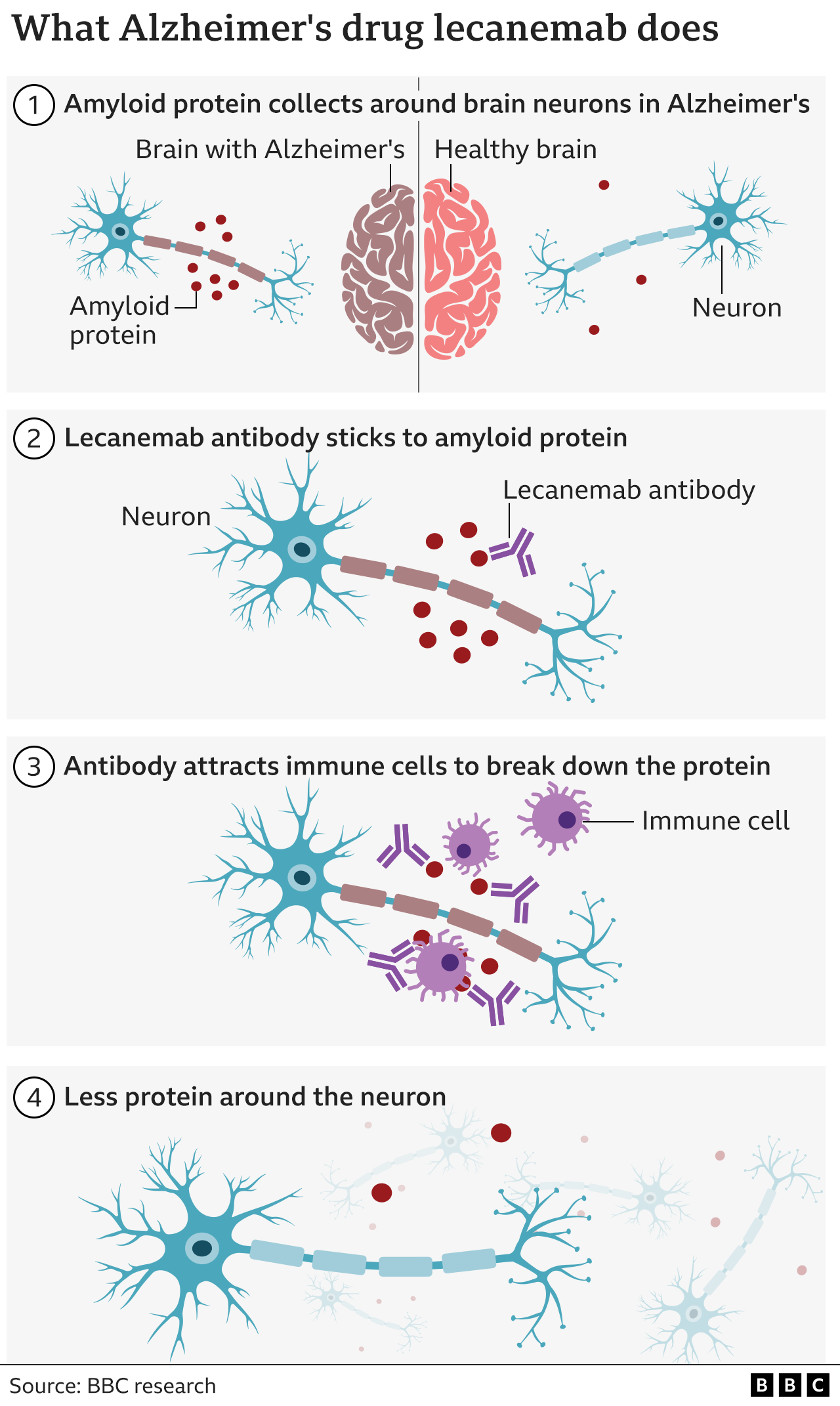
Alzheimer S Drug Lecanemab Hailed As Momentous Breakthrough Bbc News After plaque removal, dual acting lecanemab continues to positively impact biomarkers over the course of treatment. the key ad fluid biomarkers aβ42 40, ptau181, ptau217, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (***gfap) are more sensitive indicators of amyloid and tau development than amyloid pet and have been shown to re accumulate at a faster rate when treatment is discontinued. Lecanemab (leqembi®) is an antibody intravenous (iv) infusion therapy that targets and removes beta amyloid from the brain. it has received traditional approval from the u.s. food and drug administration (fda) to treat early alzheimer's disease, including people living with mild cognitive impairment (mci) or mild dementia due to alzheimer's disease who have confirmation of elevated beta. Lecanemab's approval came with the fda's strongest safety warning, so it's not surprising that the drug's potential side effects are in the spotlight. the most common are headaches and infusion related reactions — nausea, changes in blood pressure, flu like symptoms. "however, in about 15% of patients, amyloid related imaging abnormalities. Recently, the institute for clinical and economic review (icer) evaluated the cost effectiveness and health and economic outcomes of lecanemab for patients with early ad, and concluded in a 12 3 vote “the current evidence is inadequate to demonstrate that the net health benefit of lecanemab added to supportive care is superior to that.

Comments are closed.