Battling Bppv What You Need To Know About Benign Paroxysmal Positional

Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Bppv Physiotherapy The signs and symptoms of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) may include: dizziness. a sense that you or your surroundings are spinning or moving (vertigo) a loss of balance or unsteadiness. nausea. vomiting. the signs and symptoms of bppv can come and go and commonly last less than one minute. episodes of bppv can disappear for some. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) occurs when tiny canalith particles (otoconia) break loose and fall into the wrong part of the semicircular canals of the inner ear. the goal of the canalith repositioning procedure is to move the particles from the inner ear to a part of the ear where they won't cause problems (the utricle).
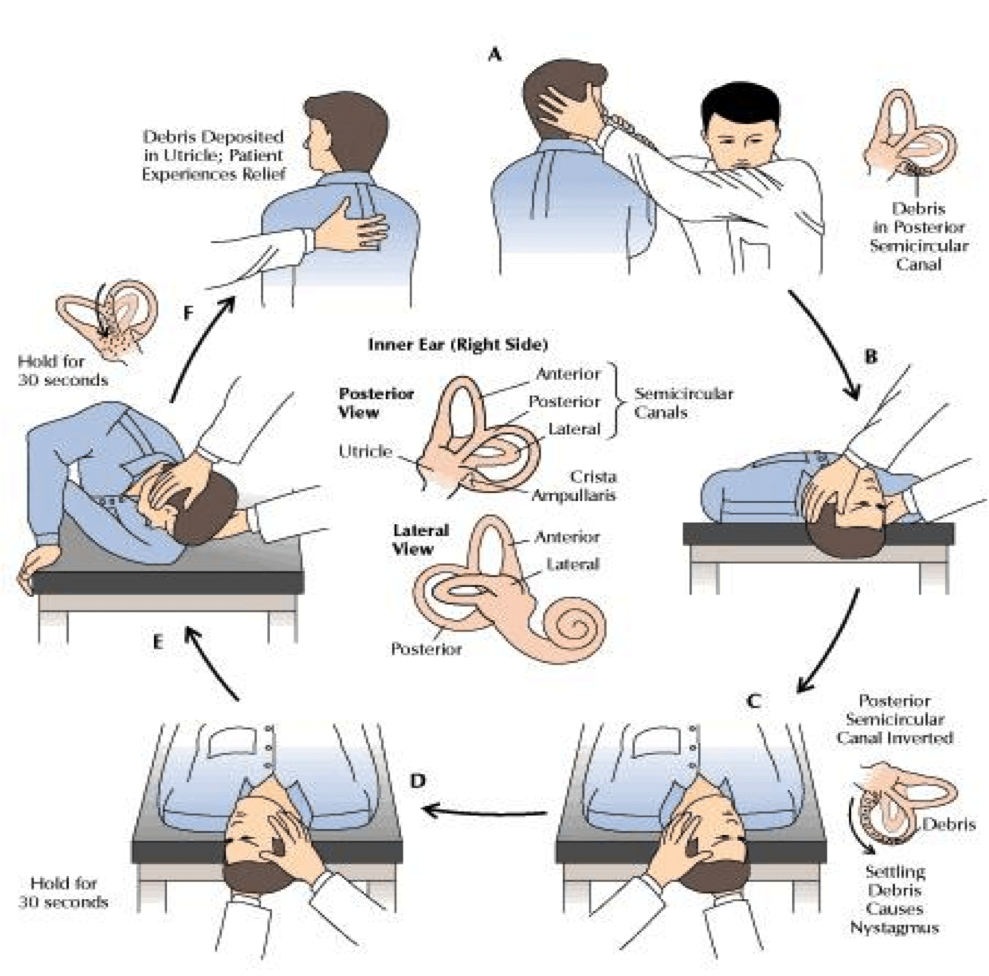
Best Positions For Vertigo At Gregory Holt Blog People with bppv can experience a spinning sensation — vertigo — any time there is a change in the position of the head. the symptoms can be very distressing. people can fall out of bed or lose their balance when they get up from bed and try to walk. if they tilt their head back or forward while walking, they may even fall, risking injury. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv), caused by wayward crystals (“rocks”) in the semicircular canals of the inner ear, is the most common cause of brief symptoms of vertigo secondary to head and body movements. diagnosing and treating it are simple to do in the medical office. this article reviews the differential diagnosis for patients presenting with dizziness and vertigo, the. What are the symptoms of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? vertigo is the main symptom of bppv. this vertigo sensation can range from mild to severe and may last seconds, or up to 1 minute. it may be accompanied by other benign paroxysmal positional vertigo symptoms, including: dizziness. lightheadedness. balance problems. nausea and vomiting. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) is a common form of vertigo, accounting for nearly one half of patients with peripheral vestibular dysfunction. it is most commonly attributed to calcium debris within the posterior semicircular canal, known as canalithiasis. while symptoms can be troublesome, the disorder usually responds to.
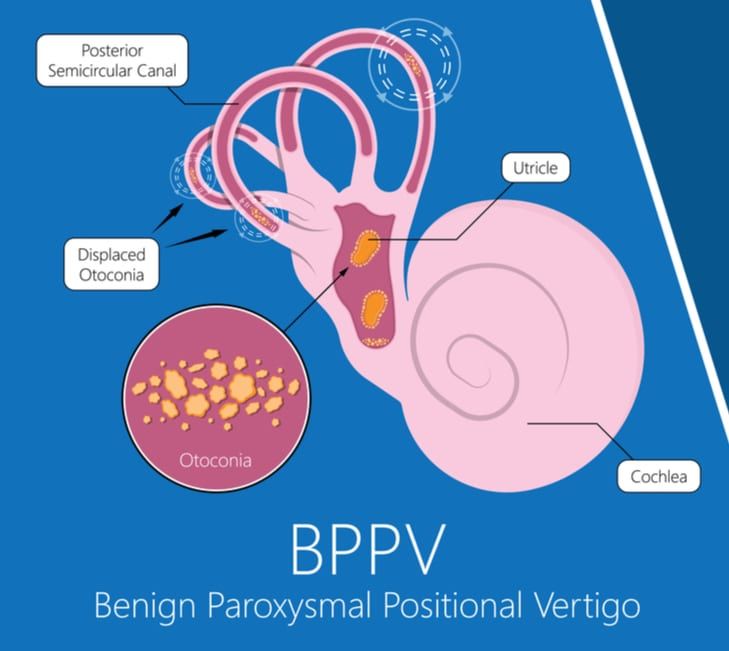
What To Do If You Have Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo At What are the symptoms of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? vertigo is the main symptom of bppv. this vertigo sensation can range from mild to severe and may last seconds, or up to 1 minute. it may be accompanied by other benign paroxysmal positional vertigo symptoms, including: dizziness. lightheadedness. balance problems. nausea and vomiting. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) is a common form of vertigo, accounting for nearly one half of patients with peripheral vestibular dysfunction. it is most commonly attributed to calcium debris within the posterior semicircular canal, known as canalithiasis. while symptoms can be troublesome, the disorder usually responds to. The primary purpose of the update to the 2008 clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is to improve quality of care and outcomes for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) by improving the accurate and efficient diagnosis of bppv, reducing the inappropriate use of vestibular suppressant medications, decreasing the. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (or bppv) is the most common cause of vertigo, which is a false sensation of spinning. 1. benign – it is not life threatening. paroxysmal – it comes in sudden, brief spells. positional – it gets triggered by certain head positions or movements. vertigo – a false sense of movement, often rotational.

Battling Bppv What You Need To Know About Benign Paroxysmal Positional The primary purpose of the update to the 2008 clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is to improve quality of care and outcomes for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (bppv) by improving the accurate and efficient diagnosis of bppv, reducing the inappropriate use of vestibular suppressant medications, decreasing the. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (or bppv) is the most common cause of vertigo, which is a false sensation of spinning. 1. benign – it is not life threatening. paroxysmal – it comes in sudden, brief spells. positional – it gets triggered by certain head positions or movements. vertigo – a false sense of movement, often rotational.

Comments are closed.