Basic Pelvic Bone Anatomy Medicine Medicalstudent Anatomy Orthopaedics Biology

Anatomy Of The Pelvis Basics Orthopaedicprinciples Corona mortis. vascular anastomosis that connects the external iliac artery (or inferior epigastric artery) and obturator artery. encountered during anterior approaches to pelvis (ilioinguinal and modified stoppa) can result in brisk bleeding with rapid blood loss if not identified and ligated. posterior venous plexus. A basic overview of the bones of the pelvis.

Pelvis And Hip Bones With Major Anatomical Regions Labeled On A White Pelvis: anatomy. the pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. the pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column. Near the junction of the superior ischial ramus and body of ischium is a posterior medial projection of bone. this is a major bony landmark for many pelvic floor procedures. the sacrospinous ligament run where? ischial spine > posterior along the pelvic floor > insert on the lateral portions of the sacrum and coccyx. Thus, the immobility of the pelvis provides a strong foundation for the upper body as it rests on top of the mobile lower limbs. figure 8.4.1 8.4. 1: pelvis the pelvic girdle is formed by a single hip bone. the hip bone attaches the lower limb to the axial skeleton through its articulation with the sacrum. the right and left hip bones, plus the. The pelvis consists of the right and left hip bones, each formed by the union of the pubis, ischium, and ilium bones, together with the midline sacrum and coccyx. anteriorly, the hip bones meet to form the pubic symphysis. posteriorly, the hip bones unite with the sacrum to form the sacroiliac joints. together, this structure forms a basin shaped ring called the bony pelvis or pelvic girdle.
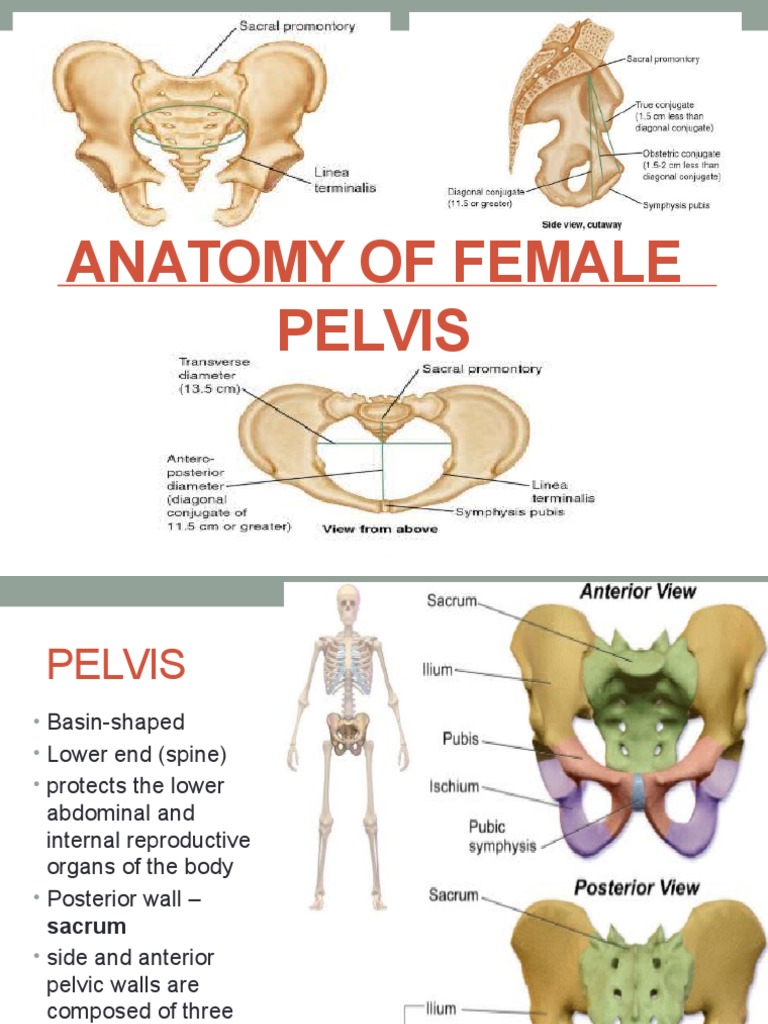
Anatomy Of A Woman S Pelvic Region Thus, the immobility of the pelvis provides a strong foundation for the upper body as it rests on top of the mobile lower limbs. figure 8.4.1 8.4. 1: pelvis the pelvic girdle is formed by a single hip bone. the hip bone attaches the lower limb to the axial skeleton through its articulation with the sacrum. the right and left hip bones, plus the. The pelvis consists of the right and left hip bones, each formed by the union of the pubis, ischium, and ilium bones, together with the midline sacrum and coccyx. anteriorly, the hip bones meet to form the pubic symphysis. posteriorly, the hip bones unite with the sacrum to form the sacroiliac joints. together, this structure forms a basin shaped ring called the bony pelvis or pelvic girdle. 1 4. synonyms: none. the perineum is the part of the pelvis which contains the external genitalia and anus. it is inferior to the pelvic diaphragm. regarding the surface anatomy, the perineal area is the region between the thighs, extending from the pubic symphysis anteriorly to the gluteal folds posteriorly. The pelvic spine consists of the coccyx and sacrum. the pubic bone, the ischial bone, and the iliac bone join together on each side and are called the innominate bones. thus there are 2 innominate bones, one on the right side and the other on the left side. the two part of the pelvis is forming a pelvic ring.

Comments are closed.