Autism Spectrum Disorder Dsm Criteria
Autism Spectrum Disorder Dsm Criteria Autism spectrum disorder dsm 5 diagnostic criteria: full text. a. persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by the following, currently or by history (examples are illustrative, not exhaustive, see text):. Intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder frequently co occur; to make comorbid diagnoses of autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability, social communication should be below that expected for general developmental level. note: individuals with a well established dsm iv diagnosis of autistic disorder, asperger’s disorder, or.

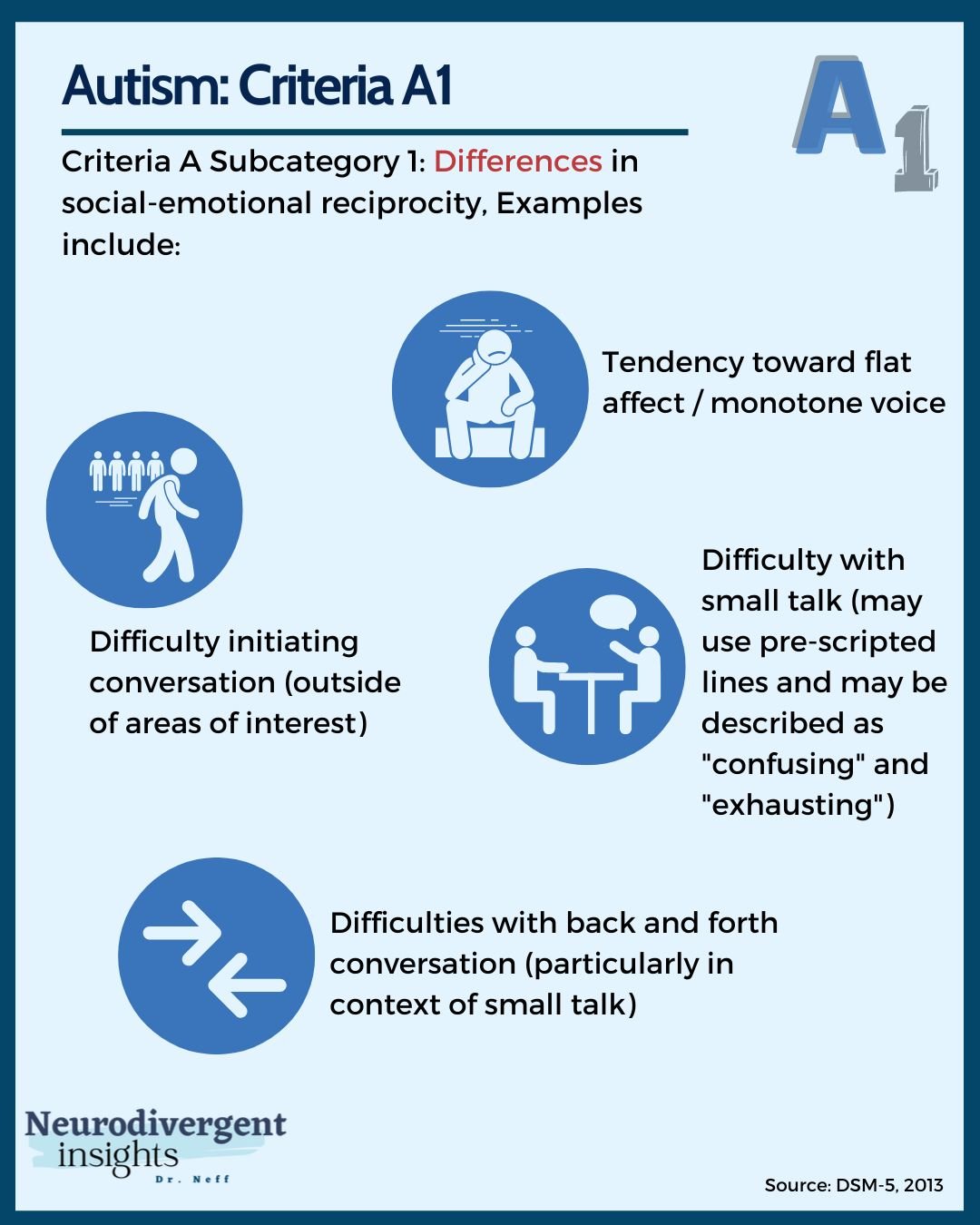
Autism Spectrum Disorder Dsm Criteria Diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (asd) usually relies on two main sources of information: parents' or caregivers' descriptions of their child's development and a professional's observation of the child's behavior. the american psychiatric association's diagnostic and statistical manual, fifth edition (dsm 5) provides standardized criteria to. Autism spectrum disorder. diagnostic criteria 299.00 (f84.0) deficits in social emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back and forth conversation; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect; to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions. Dsm 5 criteria overview. the fifth edition of the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (dsm 5), released by the american psychiatric association (apa) in 2013, redefined the criteria for diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (asd). an autism diagnosis requires persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction. The diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches of autism spectrum disorders (asd) have changed greatly over the years. currently, diagnosis is conducted mainly by observational screening tools that measure a child’s social and cognitive abilities. the two main tools used in the diagnosis of asd are dsm 5 and m chat, which examine persistent deficits in interaction and social communication.
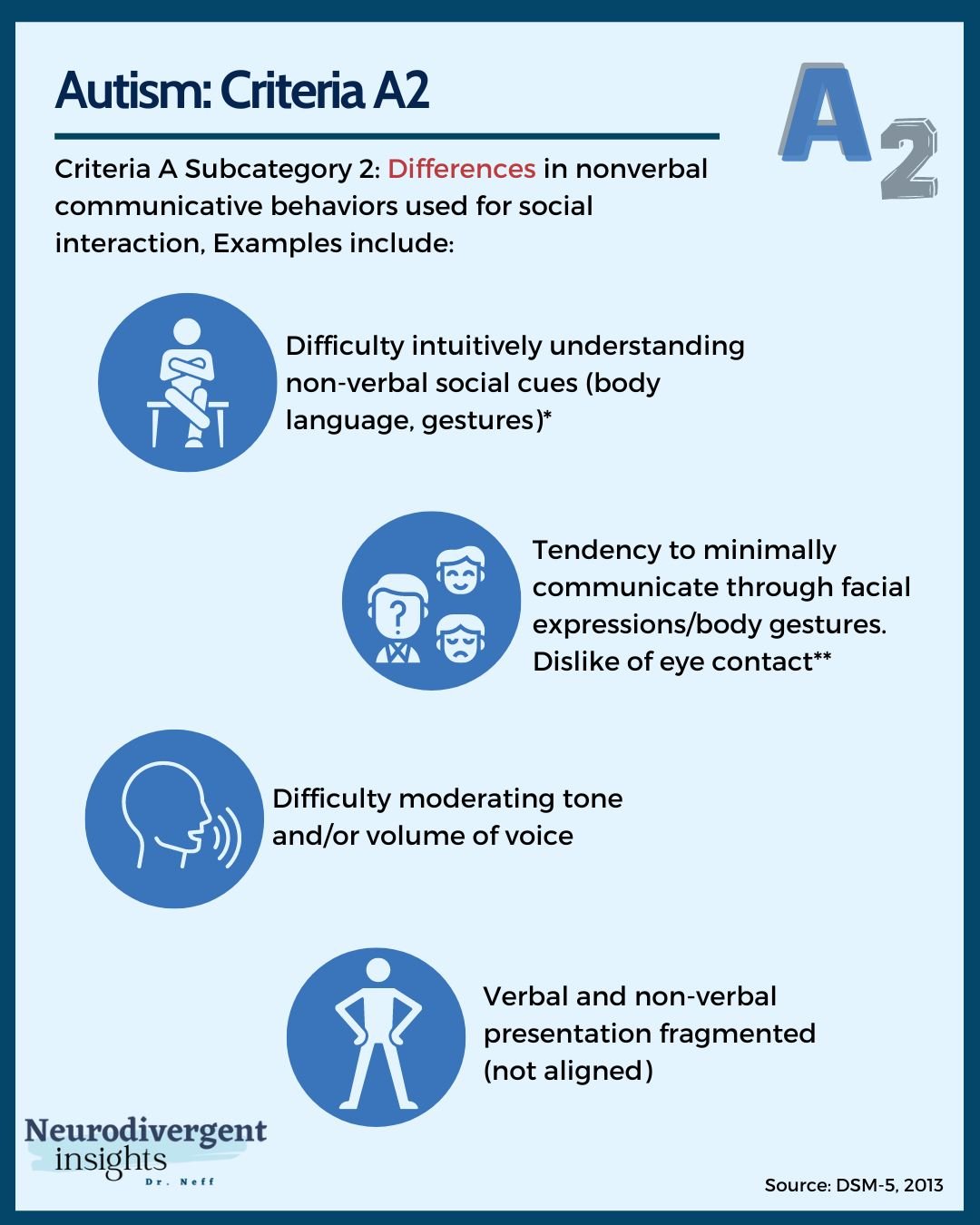
Dsm 5 Criteria For Autism Dsm 5 criteria overview. the fifth edition of the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (dsm 5), released by the american psychiatric association (apa) in 2013, redefined the criteria for diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (asd). an autism diagnosis requires persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction. The diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches of autism spectrum disorders (asd) have changed greatly over the years. currently, diagnosis is conducted mainly by observational screening tools that measure a child’s social and cognitive abilities. the two main tools used in the diagnosis of asd are dsm 5 and m chat, which examine persistent deficits in interaction and social communication. Read the full text of the dsm 5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder. how will these dsm 5 changes affect people already diagnosed with asperger syndrome, pdd nos or other previous autism categories? the dsm 5 states, “individuals with a well established dsm iv diagnoses of autistic disorder, asperger’s disorder or pervasive developmental. Disorders (dsm 5 tr), the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder is revised from the dsm 5 diagnosis. in addition to text changes throughout the disorder’s description, which reflect updated literature and advances in knowledge, the most noticeable change is to the diagnostic criteria, specifically criterion a. rationale for change.

Comments are closed.