Australian Court Hierarchy Structure Pyramid Hierarchy Structure
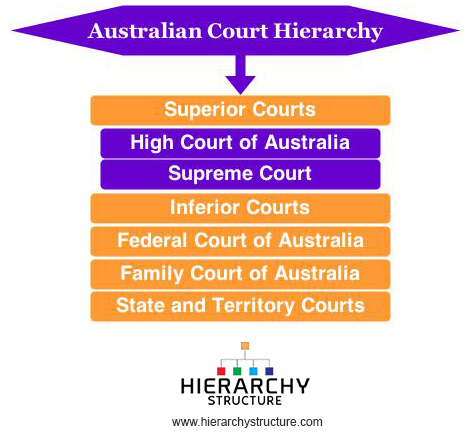
Australian Court Hierarchy Structure Pyramid Hierarchy Structure High court of australia. the apex of the appellate system in australia is the high court. all decisions made in the high court are final and binding on all lower courts across all geographical jurisdictions in australia. there are no intermediate courts in the australian capital territory or northern territory. Under the australian constitution, courts are independent of the other arms of government. therefore, judicial officers can act without political interference. the constitution itself creates only the high court of australia. however, it gives parliament the power to create other federal courts and to give power to state and territory courts.
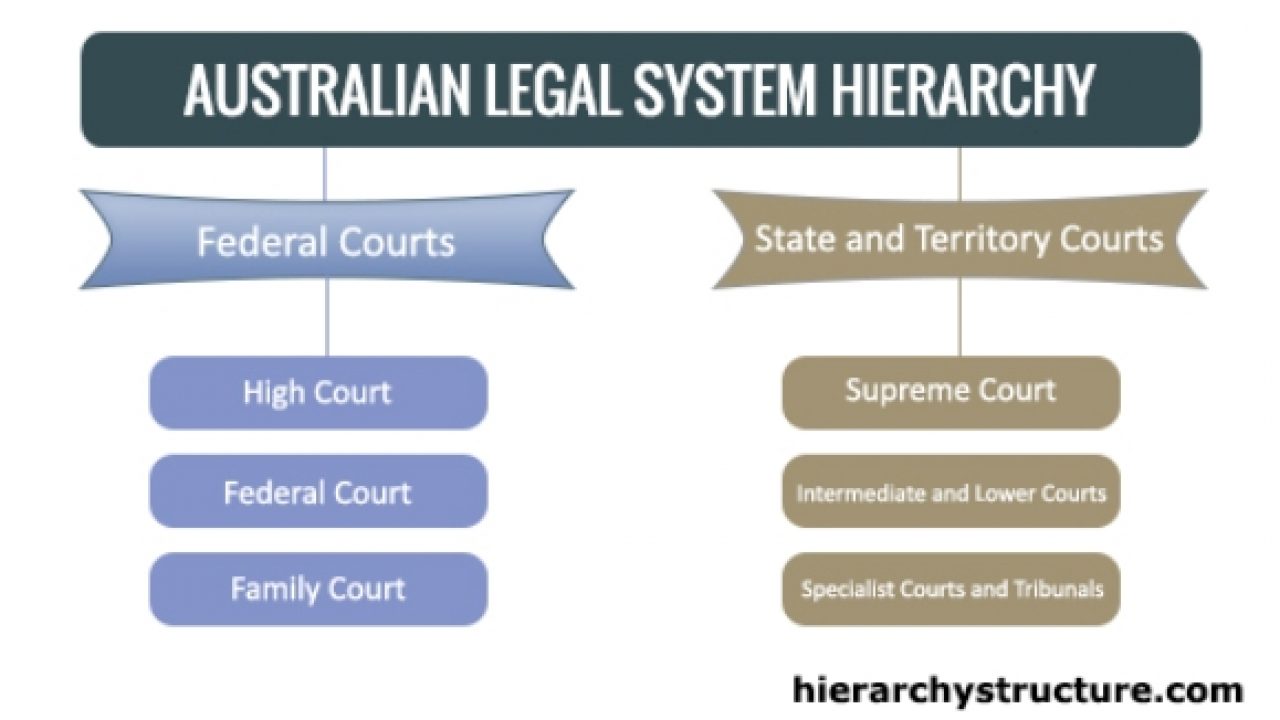
Australian Court Hierarchy Structure Pyramid Hierarchy Structure Vlr Federal court of australia. the federal court mainly hears those matters which are related to trade practices, bankruptcy, customs, industrial relations, immigrations, corporations and other areas of federal law. this is a superior court of limited jurisdiction but halls below the high court in the hierarchy structure. Figure 6: sex ratio of judicial officers by level of court hierarchy, 2000–2012. source: australasian institute of judicial administration. there have been improvements in gender balance at all levels of the court hierarchy, but there are also sizable differences in sex ratios by court level (figure 6). The judiciary of australia comprises judges who sit in federal courts and courts of the states and territories of australia. the high court of australia sits at the apex of the australian court hierarchy as the ultimate court of appeal on matters of both federal and state law. the large number of courts in australia have different procedural. Court hierarchy. parliamentary education office. parliament and the courts are independent of each other. for example: the parliament can only create law; it cannot judge if the law has been broken. the australian parliament has the right to make, change or repeal – remove – any law within the limits of the constitution.

Overview Of Australia S Court System Mccullough Robertson The judiciary of australia comprises judges who sit in federal courts and courts of the states and territories of australia. the high court of australia sits at the apex of the australian court hierarchy as the ultimate court of appeal on matters of both federal and state law. the large number of courts in australia have different procedural. Court hierarchy. parliamentary education office. parliament and the courts are independent of each other. for example: the parliament can only create law; it cannot judge if the law has been broken. the australian parliament has the right to make, change or repeal – remove – any law within the limits of the constitution. Commonwealth of australia constitution act (‘the constitution’) and came into existence in 1903. the high court is the highest court in australia and is the final court of appeal. access to the high court is very limited. 1.2 the jurisdiction of the high court is derived from sections 75 and 76 of the constitution. The supreme court is comprised of a chief justice, four resident judges and an associate judge. the supreme court hears criminal cases involving indictable offences, meaning crimes that carry a maximum penalty of at least two years' imprisonment. criminal trials in the supreme court usually involve a jury, although an accused person can choose.
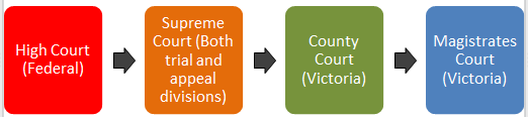
Australian Court Hierarchy Structure Pyramid Hierarchy Structure Vlr Commonwealth of australia constitution act (‘the constitution’) and came into existence in 1903. the high court is the highest court in australia and is the final court of appeal. access to the high court is very limited. 1.2 the jurisdiction of the high court is derived from sections 75 and 76 of the constitution. The supreme court is comprised of a chief justice, four resident judges and an associate judge. the supreme court hears criminal cases involving indictable offences, meaning crimes that carry a maximum penalty of at least two years' imprisonment. criminal trials in the supreme court usually involve a jury, although an accused person can choose.

Australian Court Hierarchy Rule Of Law Education Centre

Australian Court Structure Diagram Quizlet

Comments are closed.