Atrial Septal Defect Acha

Atrial Septal Defect Acha The atrial septum is the wall that separates the left and right atria. if there is a hole in the atrial septum, it is called an atrial septal defect (asd). some of the blood that should flow into the left ventricle (or lower pumping chamber) from the left atrium now flows into the right atrium through the asd. There are four types of asds. the most common is the secundum asd (75%). others are primum (20%), sinus venosus (4%) and coronary sinus (<1%) asd. each is unique not only in its location and size but in how it “acts” and how it is treated. when the asd or shunt is small, only a little blood flows from one atrium to the other.

Atrial Septal Defect Causes Symptoms Types Diagnosis Treatment For example, an 80 year old patient who has a small atrial septal defect (asd), but whose symptoms are related to diastolic hf, chronic kidney disease caused by hypertension and diabetes mellitus, and moderate aortic stenosis is well suited to be followed according to existing guidelines for those diseases, rather than according to the achd ap. Transposition of the great arteries after arterial switch or rastelli procedure. transposition of the great arteries (tga or d tga) is a complex congenital heart defect. the two main arteries, the pulmonary artery and aorta, are reversed. Sinus venosus atrial septal defects. the superior form of the sinus venosus asd constitutes 5% to 10% of all asds. its posterior aspect is the right atrial free wall, and its superior border is often absent because of an overriding superior vena cava (svc; figure 2 a). anomalous connection of some or all of the right pulmonary veins to the svc. Atrial septal defect (asd) is one of the more commonly recognized congenital cardiac anomalies presenting in adulthood. atrial septal defect is characterized by a defect in the interatrial septum allowing pulmonary venous return from the left atrium to pass directly to the right atrium.
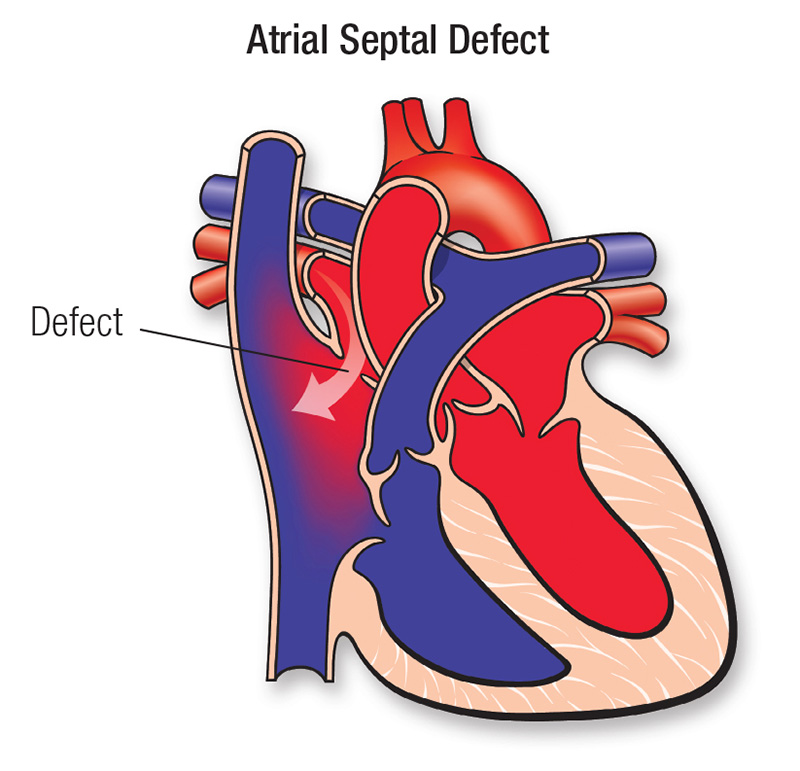
Atrial Septal Defect Asd American Heart Association Sinus venosus atrial septal defects. the superior form of the sinus venosus asd constitutes 5% to 10% of all asds. its posterior aspect is the right atrial free wall, and its superior border is often absent because of an overriding superior vena cava (svc; figure 2 a). anomalous connection of some or all of the right pulmonary veins to the svc. Atrial septal defect (asd) is one of the more commonly recognized congenital cardiac anomalies presenting in adulthood. atrial septal defect is characterized by a defect in the interatrial septum allowing pulmonary venous return from the left atrium to pass directly to the right atrium. Atrial septal defect (asd) is one of the most common types of congenital heart defects, occurring in about 25% of children.[1] an atrial septal defect occurs when there is a failure to close the communication between the right and left atria. it encompasses defects involving both the true septal membrane and other defects that allow for communication between both atria. there are five types of. An opening or hole (defect) in the wall (septum) that separates the top two chambers of the heart (atria). this defect allows oxygen rich blood to leak into the oxygen poor blood chambers in the heart. asd is a defect in the septum between the heart's two upper chambers. the septum is a wall that separates the heart's left and right sides.

Comments are closed.