Atopic Dermatitis Ad Encyclopedia Mdpi
Atopic Dermatitis Ad Encyclopedia Mdpi The global, regional, and national burden of atopic dermatitis in 195 countries and territories: an ecological study from the global burden of disease study. jaad int. 2020, 2, 12–18. valdman grinshpoun, y.; ben amitai, d.; zvulunov, a. barrier restoring therapies in atopic dermatitis: current approaches and future perspectives. dermatol. res. The manuscript provides a comprehensive overview of the evolving treatment landscape for atopic dermatitis (ad), highlighting the advancements in both topical and systemic therapies. the article is well written and the content provided were found to be satisfactory. however, there are few contents which might be included like. 1.
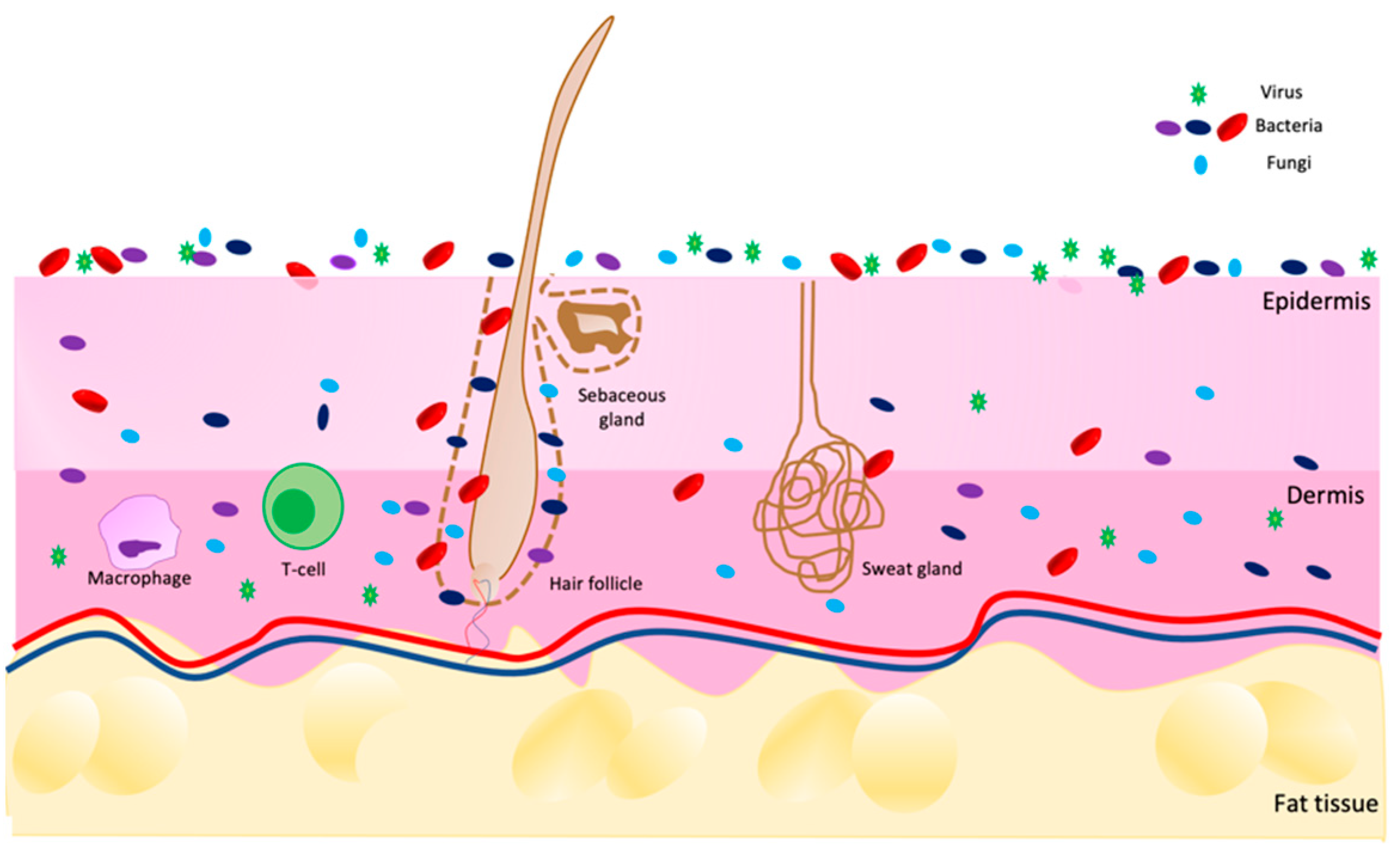
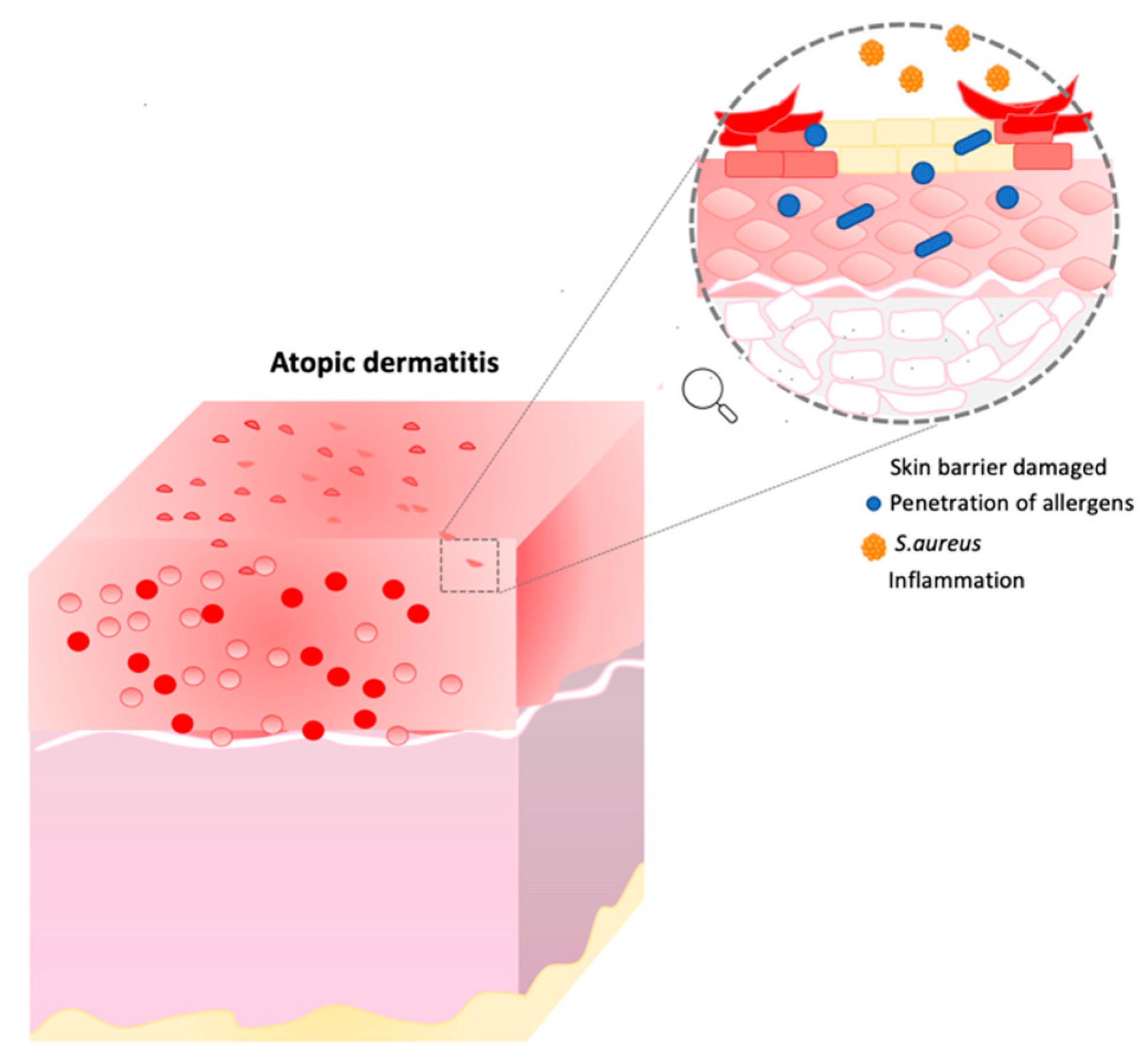
Atopic Dermatitis Ad Encyclopedia Mdpi Atopic dermatitis is one of the most common inflammatory skin diseases, with an increasing incidence among both children and adults. the recurrent nature, often with the persistence of symptoms, and the polymorphism of the response to current therapies have led to increased research in the therapeutic area dedicated to this condition. the understanding of pathophysiological pathways has. Atopic dermatitis (ad) is a common, chronic and recurring inflammatory skin disorder characterized by an intensely pruritic, eczematous dermatitis. the etiology of ad is thought to involve a combination of environmental, genetic, and immunologic factors. emerging research has investigated factors that may impact individual risk for developing ad, disease severity, and treatment response. one. Abstract. gut bacteria are closely associated with the development of atopic dermatitis (ad) due to their immunoregulatory function. indole derivatives, produced by gut bacteria metabolizing tryptophan, are ligands to activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (ahr), which plays a critical role in attenuating ad symptoms. Ceramide metabolism in keratinocytes. active pathways are marked with black arrows and inactive pathways are marked with white arrows. the objective of the ceramide metabolism centered therapeutic concept is to use appropriate compounds to maintain lysosomal nadh dependent redox chain, v atpase activity, and very long chain ceramide de novo synthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum to prevent.
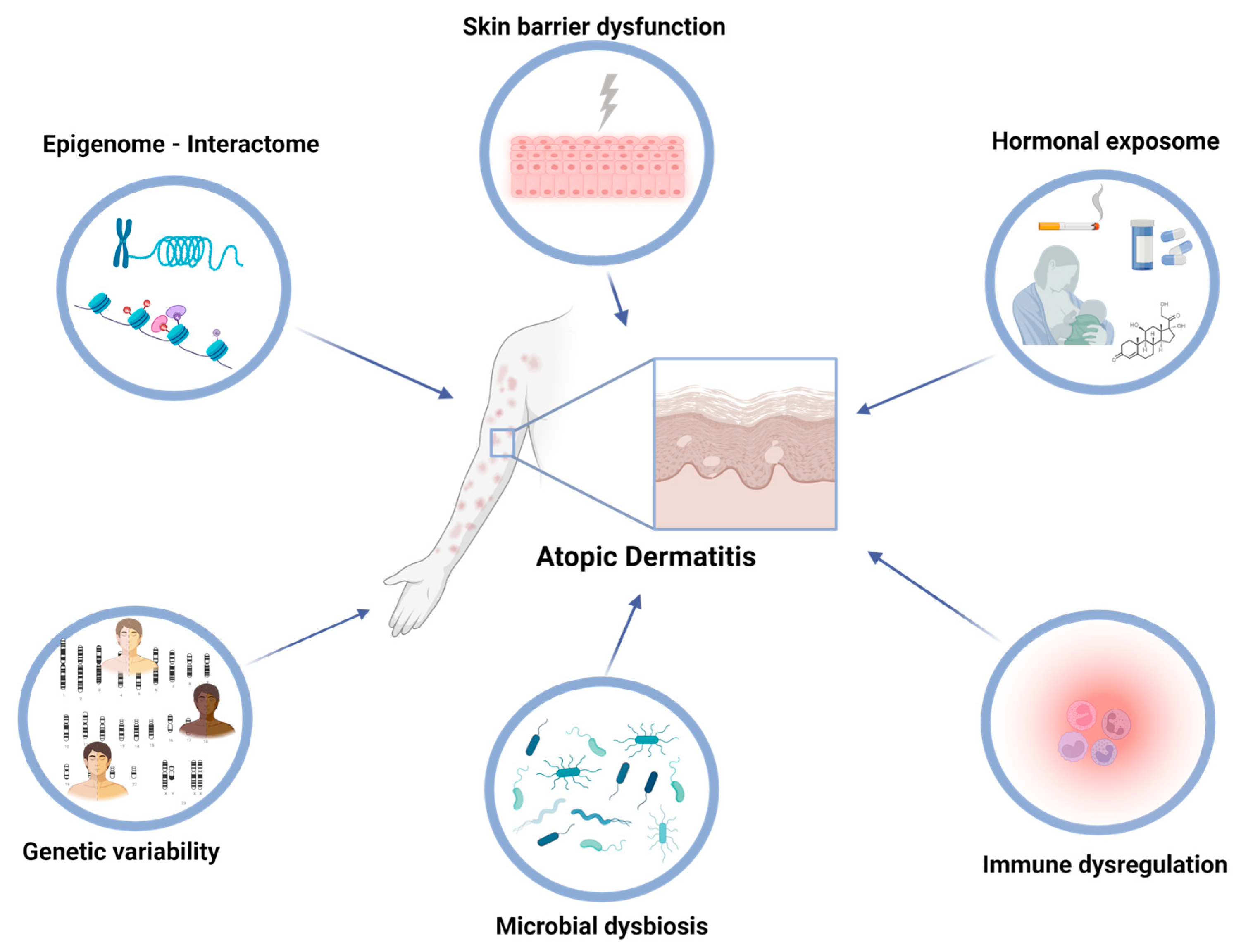
Factors Contributing To Atopic Dermatitis Development Encyclopedia Mdpi Abstract. gut bacteria are closely associated with the development of atopic dermatitis (ad) due to their immunoregulatory function. indole derivatives, produced by gut bacteria metabolizing tryptophan, are ligands to activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (ahr), which plays a critical role in attenuating ad symptoms. Ceramide metabolism in keratinocytes. active pathways are marked with black arrows and inactive pathways are marked with white arrows. the objective of the ceramide metabolism centered therapeutic concept is to use appropriate compounds to maintain lysosomal nadh dependent redox chain, v atpase activity, and very long chain ceramide de novo synthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum to prevent. Atopic dermatitis (ad) is a highly heterogeneous inflammatory disease regarding both its pathophysiology and clinical manifestations. however, it is treated according to the “one size fits all” approach, which may restrict response to treatment. thus, there is an unmet need for the stratification of patients with ad into distinct endotypes. Atopic dermatitis (ad) is a common, relapsing inflammatory skin condition characterized by pruritic, erythematous plaques and papules typically affecting the body’s flexural surfaces. while ad is known to emerge due to barrier dysfunction, aberrant immune activation, and genetic predisposition, a clear understanding of the pathogenesis of its.
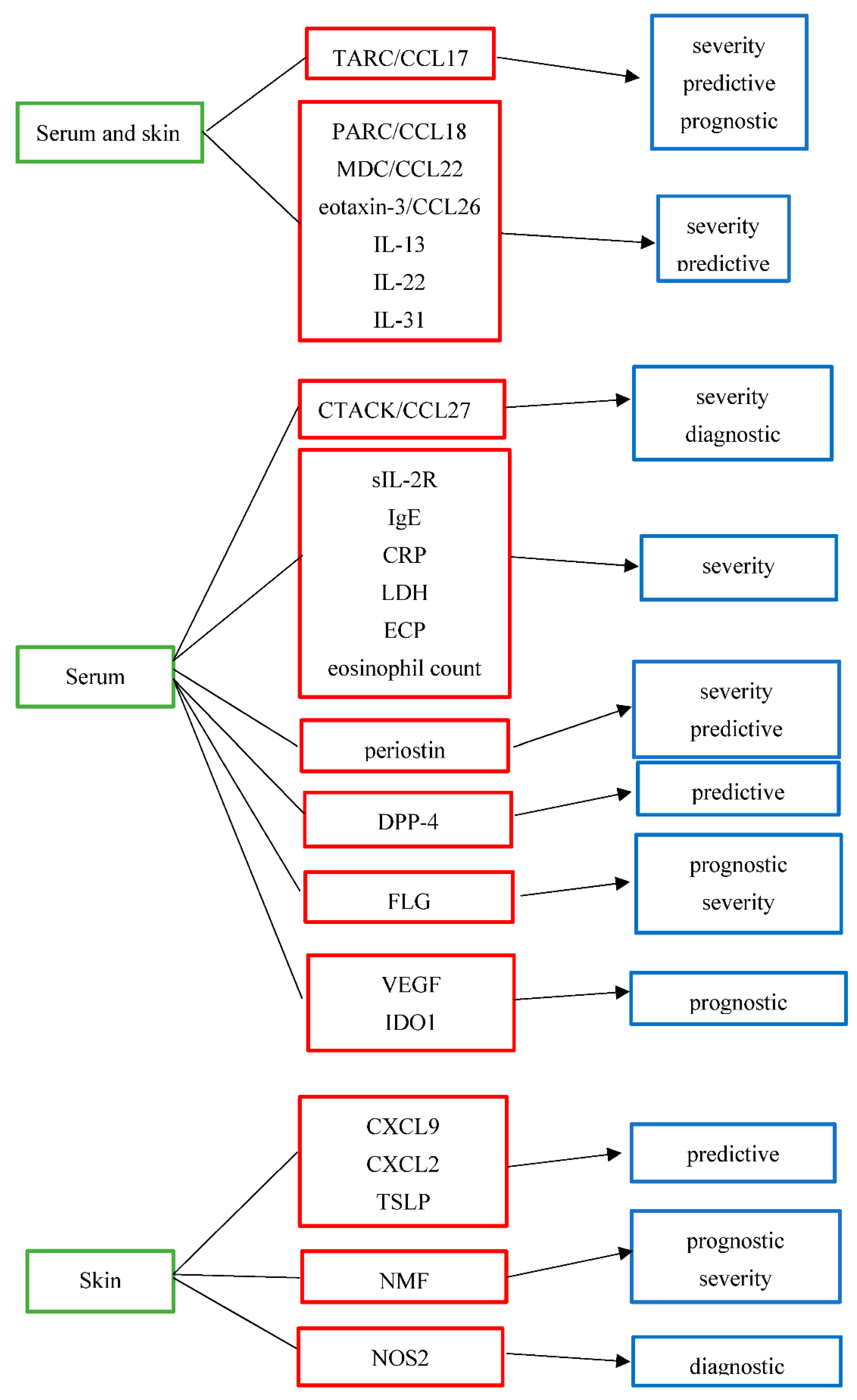
Biomarkers In Atopic Dermatitis Encyclopedia Mdpi Atopic dermatitis (ad) is a highly heterogeneous inflammatory disease regarding both its pathophysiology and clinical manifestations. however, it is treated according to the “one size fits all” approach, which may restrict response to treatment. thus, there is an unmet need for the stratification of patients with ad into distinct endotypes. Atopic dermatitis (ad) is a common, relapsing inflammatory skin condition characterized by pruritic, erythematous plaques and papules typically affecting the body’s flexural surfaces. while ad is known to emerge due to barrier dysfunction, aberrant immune activation, and genetic predisposition, a clear understanding of the pathogenesis of its.

Manipulating Microbiota To Treat Atopic Dermatitis Encyclopedia Mdpi
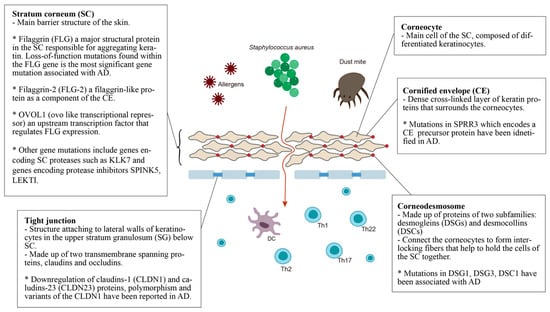
Genes Associated With Atopic Dermatitis Encyclopedia Mdpi

Comments are closed.