Are Wolves Secondary Consumers

Are Wolves Secondary Or Tertiary Consumers Outlife Expert Secondary consumers are typically carnivores or omnivores that feed on primary consumers. by this definition, wolves, with their carnivorous diet, might seem to fit the category of secondary consumers. however, the classification in the food chain is not always straightforward. wolves’ dietary habits differ from typical secondary consumers in. Wolves are tertiary consumers because they do eat some secondary consumers, while also eating a wide variety of primary consumers such as bison, elk and deer. wolves are threatened by human activity.

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Study Tertiary and apex consumers (carnivores) these carnivorous animals feed on primary and secondary consumers, like arctic wolves, snow leopards, wolverines, polar bears, and snowy owls. depending on the type of food chain, organisms in this group assume the role of a tertiary consumer or an apex consumer. Carnivorous mammals like lions, tigers, hyenas, wolves, leopards, and cheetahs are secondary consumers found in terrestrial ecosystems that prey on herbivores for survival. birds of prey or predatory birds such as eagles, vultures, falcons, hawks, and owls are secondary consumers that hunt other animals. Consumer hierarchy plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and functionality of ecosystems. each level, from primary to quaternary consumers, contributes uniquely to energy flow and nutrient cycling. grasping this hierarchical structure allows for deeper insights into ecological relationships and the overall health of natural habitats. Wolves, crows, and hawks are examples of secondary consumers that obtain their energy from primary consumers by scavenging. in light of the fact that other mammals could easily hunt humans, humans were classed as secondary consumers.
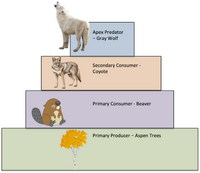
Answered Below Is A Simple Food Chain That Bartleby Consumer hierarchy plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and functionality of ecosystems. each level, from primary to quaternary consumers, contributes uniquely to energy flow and nutrient cycling. grasping this hierarchical structure allows for deeper insights into ecological relationships and the overall health of natural habitats. Wolves, crows, and hawks are examples of secondary consumers that obtain their energy from primary consumers by scavenging. in light of the fact that other mammals could easily hunt humans, humans were classed as secondary consumers. Consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consumer and decomposer are all trophic. levels that can be used to describe an organism's place in an ecosystem. roughly 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, thus preventing a large amounts of trophic levels. there must be higher amounts of biomass at the bottom of the. Secondary consumers, or carnivores, prey on herbivores and other smaller animals. they help regulate herbivore populations and maintain the balance of the ecosystem. examples of secondary consumers. predators such as wolves, foxes, and birds of prey are essential components of forest food webs as secondary consumers. 6. tertiary consumers: top.

Comments are closed.