Ap Chem Unit 3 Notes Intermolecular Forces And Properties Unit

Chemistry Teaching Resources Gordon Watson Ap Chemistry Unit 3 Intermolecular forces shape the behavior of matter at the molecular level. these attractions between molecules influence properties like boiling point, viscosity, and solubility. understanding these forces helps explain phenomena from water's unique properties to a gecko's ability to climb walls. this unit explores different types of. Unit 3 intermolecular forces and properties. key topics: intermolecular forces, states of matter, boiling point, melting point, spectroscopy, ideal gas law, solutions. 📄️ intermolecular forces. ap chem guide's crash course on intermolecular forces. 📄️ properties of solids. ap chem guide's crash course on properties of solids.

Ap Chem Unit 3 Notes Intermolecular Forces And Properties Unit Ap chem guide learn blog contact. discord. introduction; unit 1 atomic structure and properties. unit 3 intermolecular forces and properties. intermolecular. Unit 1: atomic structure and properties; unit 2: molecular and ionic compound structure and properties; unit 3: intermolecular forces and properties; unit 4: chemical reactions; unit 5: kinetics; unit 6: thermodynamics; unit 7: equilibrium; unit 8: acids and bases; unit 9: applications of thermodynamics. B. dipole induced dipole interactions 1. the interaction between a polar molecule and a nonpolar molecule. when the polar molecule is near the nonpolar molecule, the negative end will repel electrons on the nonpolar molecule, inducing a dipole. Introduction. intermolecular forces (imfs) are the forces of attraction or repulsion between neighboring molecules, atoms, or ions, significantly influencing the physical properties of substances. these forces are distinct from intramolecular forces, which are the bonds within a molecule holding atoms together, such as covalent or ionic bonds.
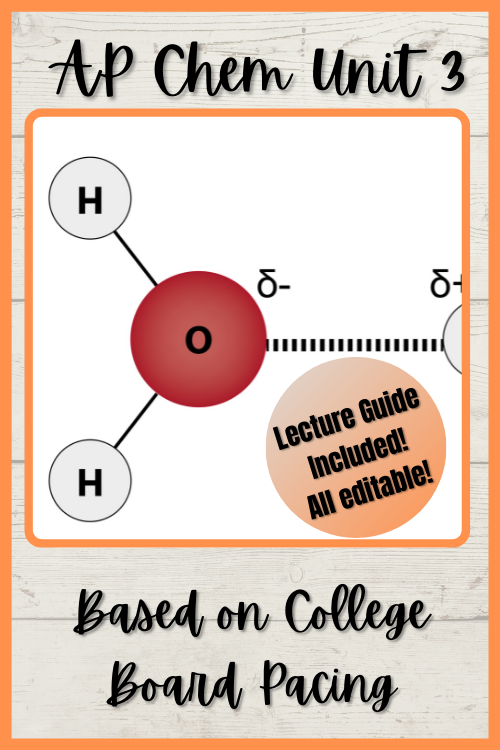
Ap Chemistry Unit 3 Intermolecular Forces Properties Powerpoint B. dipole induced dipole interactions 1. the interaction between a polar molecule and a nonpolar molecule. when the polar molecule is near the nonpolar molecule, the negative end will repel electrons on the nonpolar molecule, inducing a dipole. Introduction. intermolecular forces (imfs) are the forces of attraction or repulsion between neighboring molecules, atoms, or ions, significantly influencing the physical properties of substances. these forces are distinct from intramolecular forces, which are the bonds within a molecule holding atoms together, such as covalent or ionic bonds. Ap chem unit 3 notes intermolecular forces and properties unit outline. ap. 23 pages 2020 2021 100% (1). Unit 3.4: ideal gas law. unit 3.5: kinetic molecular theory. unit 3.6: deviation from the ideal gas law. unit 3.7: solutions & mixtures. unit 3.8: representations of solutions. unit 3.9: separation of solutions & mixtures chromatography. unit 3.10: solubility. unit 3.11: spectroscopy & the electromagnetic spectrum. unit 3.12: the photoelectric.

Comments are closed.