Antiepileptics Seizure Pharmacology
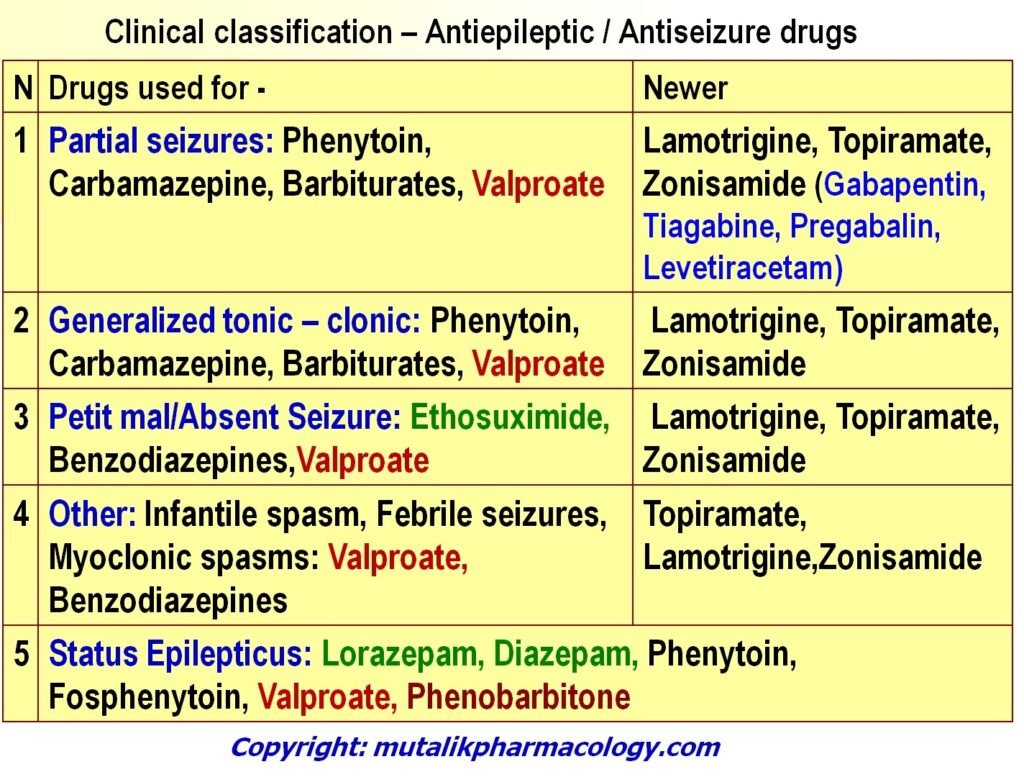
Anti Seizure Drugs Anti Epileptics Mutalik Pharmacology Epilepsy is the tendency to have recurrent seizures unprovoked by systemic or acute neurologic insults. (slide 2) antiepileptic drugs (aeds) are those which decrease the frequency and or severity of seizures in people with epilepsy. the older term, anticonvulsant drug, is still sometimes used as a synonym for aed, but is less accurate because many seizures do not involve convulsive movements. Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological diseases; its first line treatment is the administration of antiepileptic drugs (aeds). these are divided into first , second , and third generation aeds. 1) the commonly used first generation aeds are phenytoin (pht), phenobarbital (pb), carbamazepine (cbz), valproic acid (vpa), zonisamide (zns.

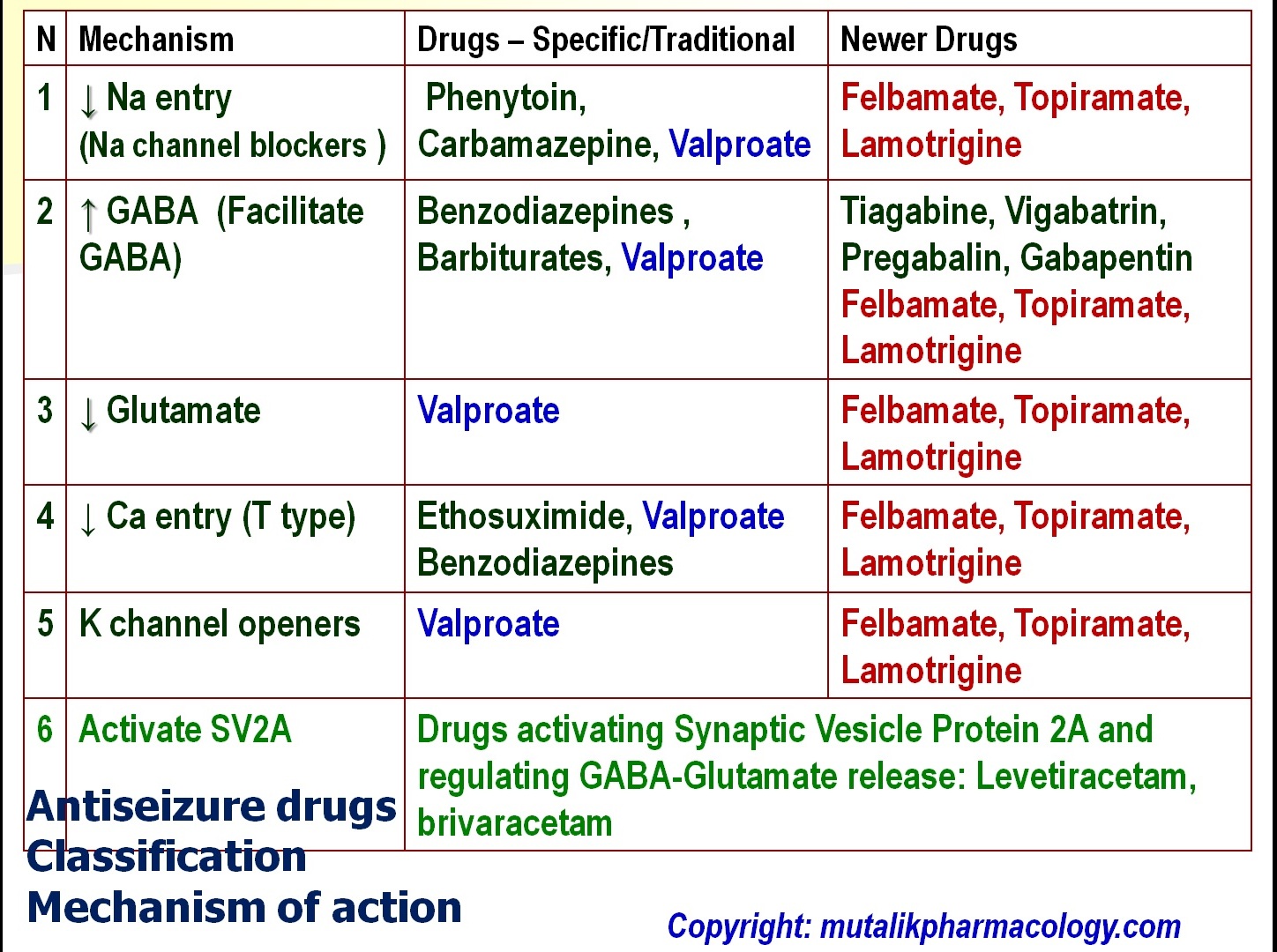
Antiepileptics Seizure Pharmacology Youtube The mainstay treatment strategy for seizures is medication management. however, much like the prescription of any other pharmaceutical agent, a clinician must balance efficacy with adverse events, and provide consideration for cost, drug interactions, patient preference, and availability. this activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, methods of administration, important adverse. Mechanisms of action — antiseizure medications are typically grouped by their principal mode of action, although for many drugs, the precise mechanism of action is not known or multiple actions are suspected (table 1). to some degree, the cellular effects of antiseizure medications are linked with the types of seizures against which they are. Four randomized controlled trials compared intravenous (iv) lorazepam and iv diazepam. 14, 15, 17, 20 one of these trials showed the superiority of lorazepam at 0.05–0.1 mg kg in seizure control over diazepam at 0.3–0.4 mg kg. 15 while the other trials also appeared to favor lorazepam (4, 2, and 0.1 mg kg, respectively) over diazepam (10, 5. Valproate (vpa) was licensed in europe in 1960 and in the united states in 1978, and now is widely available throughout the world. it became the drug of choice in primary generalized epilepsies and in the mid 1990s was approved for treatment of partial seizures. these anticonvulsants were the mainstays of seizure treatment until the 1990s, when.
Anti Seizure Drugs Anti Epileptics Mutalik Pharmacology Four randomized controlled trials compared intravenous (iv) lorazepam and iv diazepam. 14, 15, 17, 20 one of these trials showed the superiority of lorazepam at 0.05–0.1 mg kg in seizure control over diazepam at 0.3–0.4 mg kg. 15 while the other trials also appeared to favor lorazepam (4, 2, and 0.1 mg kg, respectively) over diazepam (10, 5. Valproate (vpa) was licensed in europe in 1960 and in the united states in 1978, and now is widely available throughout the world. it became the drug of choice in primary generalized epilepsies and in the mid 1990s was approved for treatment of partial seizures. these anticonvulsants were the mainstays of seizure treatment until the 1990s, when. 1. introduction. epilepsy is a group of chronic non communicable neurological disorders categorized by spontaneous recurrent seizures [1, 2]. these seizures result from episodes of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. the process by which epilepsy develops in an otherwise normal brain is called epileptogenesis. Epilepsy syndromes are disorders in which epilepsy is a predominant feature, and there is sufficient evidence to suggest a common underlying mechanism. 1 three main epilepsy syndromes have been classified; one is associated with partial seizures (mesial temporal lobe epilepsy syndrome) and the others are associated with generalized seizures (juvenile myoclonic epilepsy syndrome and lennox.

Comments are closed.