Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria How Do They Become Resistant Can They Still Be Killed
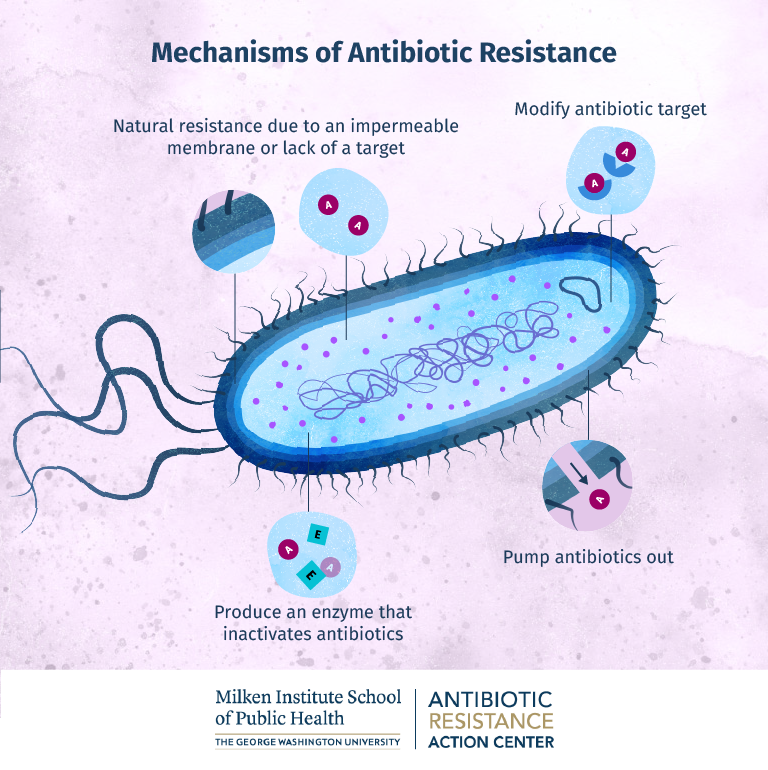
How Bacteria Build Resistance At The Cellular Level Online Public Health Antibiotic resistance is a type of antimicrobial resistance. fungi, parasites and viruses can also develop drug resistance. your body doesn’t develop antibiotic resistance — bacteria do. when antibiotic resistance happens, fewer antibiotics are effective against a particular bacterium. other antibiotics often help, but it’s important to. Once bacteria become antibiotic resistant, they can pass on their genes to other bacteria that also become resistant. antibiotic resistance limits the antibiotics available to treat serious infections. this can result in longer recovery time, increased risk of additional infections, and even death.

Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria How Do They Become Resistant Can They Resistance to a class of antibiotics known as fluoroquinolones (which includes ciprofloxacin) often occurs due to mutations of the enzyme targets. 4) destroy or modify the antibiotic. bacteria. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) is one of the top global public health and development threats. it is estimated that bacterial amr was directly responsible for 1.27 million global deaths in 2019 and contributed to 4.95 million deaths (1). the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials in humans, animals and plants are the main drivers in the. One bacterium can become more than 68 billion bacteria in 12 hours. however, bacteria don’t faithfully reproduce their genetic code, and mutations can slip in every generation. while most changes are bad, sometimes they can help the bacteria grow in the presence of an antibiotic. this “new and improved” population quickly takes over. Summary. antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria adapt or evolve to survive antibiotic treatment. this is a big issue as it can cause antibiotics to become less effective. bacteria are single.

What Is Antibiotic Resistance Facts Yourgenome Org One bacterium can become more than 68 billion bacteria in 12 hours. however, bacteria don’t faithfully reproduce their genetic code, and mutations can slip in every generation. while most changes are bad, sometimes they can help the bacteria grow in the presence of an antibiotic. this “new and improved” population quickly takes over. Summary. antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria adapt or evolve to survive antibiotic treatment. this is a big issue as it can cause antibiotics to become less effective. bacteria are single. There are a number of ways bacteria can resist antibiotics. 1) cell entry many antibiotics need to enter bacteria to kill them. they use special holes on the bacteria’s surface to do this but. Misuse or mismanagement of antibiotics and antifungals can also contribute to resistance. for example, people with tuberculosis (tb)—a disease caused by bacteria that are spread from person to person through the air—can die if they do not get proper treatment. drug resistant tb can occur when the drugs used to treat tb are used inappropriately.
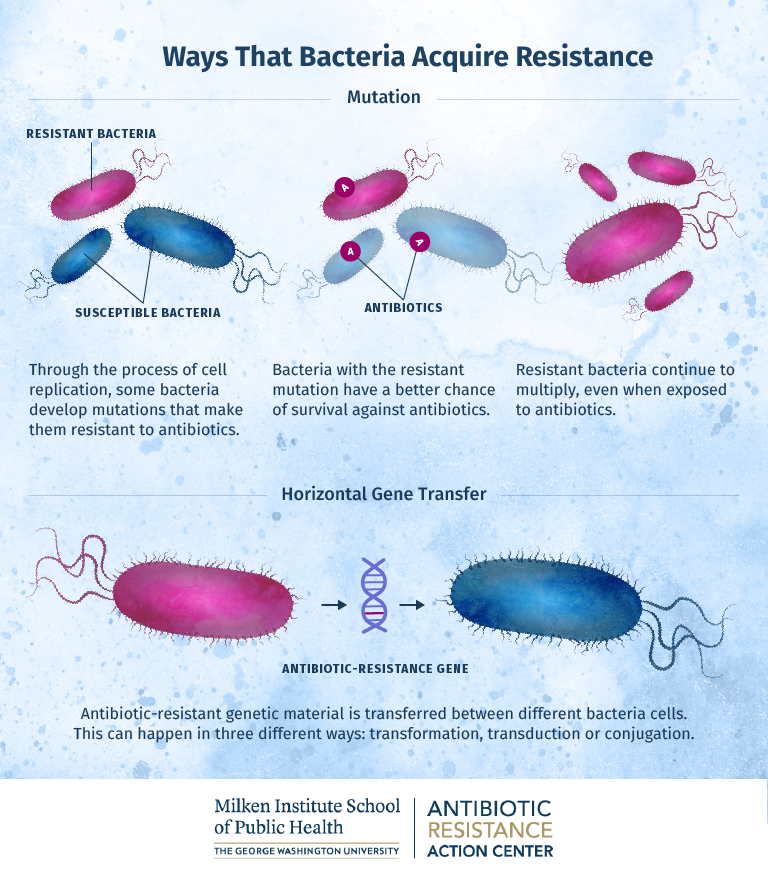
How Bacteria Build Resistance At The Cellular Level Online Public Health There are a number of ways bacteria can resist antibiotics. 1) cell entry many antibiotics need to enter bacteria to kill them. they use special holes on the bacteria’s surface to do this but. Misuse or mismanagement of antibiotics and antifungals can also contribute to resistance. for example, people with tuberculosis (tb)—a disease caused by bacteria that are spread from person to person through the air—can die if they do not get proper treatment. drug resistant tb can occur when the drugs used to treat tb are used inappropriately.

Comments are closed.