Animal Tissue Structure And Types Of Animal Tissue
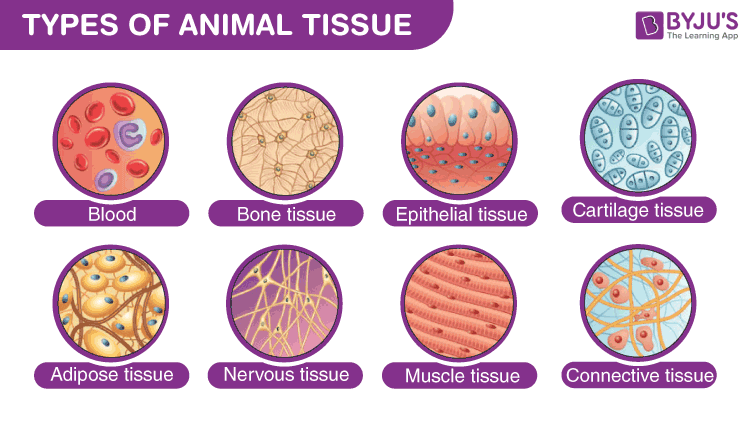
Animal Tissues Grade 9 Notes The animal cells are grouped together to form animal tissues. these tissues vary in their structure, function, and origin. the animal tissues are divided into epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissues. let us have a glimpse of each type of animal tissue in detail. table of contents. epithelial tissue. connective tissue. muscle tissue. What is animal tissues ? animal tissues are groups of specialized cells that work together to perform specific functions in the body of animals. these tissues are essential for the organism’s growth, survival, and reproduction, forming the basis of the complex structures and functions found within animals. types of animal tissues.

Classification Of Animal Tissues Pcsstudies Biology Describe nervous tissue. multicellular, complex animals have four primary types of tissue: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. recall that tissues are groups of similar cells carrying out related functions. these tissues combine to form organs—like the skin or kidney—that have specific, specialized functions within the body. There are four basic types of animal tissue: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. epithelial tissue is made up of thin layers of cells that perform mostly. These are organized into tissues; the tissues into organs. groups of organs make up the various systems — digestive, excretory, etc. — of the body (figure 3.13.1 and table 3.13.1). figure 3.13.1: animal tissues. the actual number of differentiated cell types is surely much larger than 100. Bone tissue forms the internal skeleton of vertebrate animals, providing structure to the animal and points of attachment for tendons. figure 1.4.9 1.4. 9: (a) compact bone is a dense matrix on the outer surface of bone. spongy bone, inside the compact bone, is porous with web like trabeculae.
3 Main Animal Tissues With Structure And Functions These are organized into tissues; the tissues into organs. groups of organs make up the various systems — digestive, excretory, etc. — of the body (figure 3.13.1 and table 3.13.1). figure 3.13.1: animal tissues. the actual number of differentiated cell types is surely much larger than 100. Bone tissue forms the internal skeleton of vertebrate animals, providing structure to the animal and points of attachment for tendons. figure 1.4.9 1.4. 9: (a) compact bone is a dense matrix on the outer surface of bone. spongy bone, inside the compact bone, is porous with web like trabeculae. Discuss the tissue structures found in animals. the tissues of multicellular, complex animals are four primary types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. recall that tissues are groups of similar cells carrying out related functions. these tissues combine to form organs—like the skin or kidney—that have specific, specialized. Tissue definition. tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and act together to perform a specific function. the word tissue comes from a form of an old french verb meaning “to weave”. there are four different types of tissues in animals: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. in plants, tissues are divided into three.

Animal Tissue Structure And Types Of Animal Tissue Discuss the tissue structures found in animals. the tissues of multicellular, complex animals are four primary types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. recall that tissues are groups of similar cells carrying out related functions. these tissues combine to form organs—like the skin or kidney—that have specific, specialized. Tissue definition. tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and act together to perform a specific function. the word tissue comes from a form of an old french verb meaning “to weave”. there are four different types of tissues in animals: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. in plants, tissues are divided into three.

Comments are closed.