Angles In Parallel Lines Gcse Maths Steps Examples
Angles In Parallel Lines Gcse Maths Steps Examples Show step. co interior angles add up to 180^o 180o. here 180 110=70^o 180 − 110 = 70o. state the alternate angle, co interior angle or corresponding angle fact to find a missing angle in the diagram. show step. θ θ is corresponding to 70 35 70 35 so θ = 70 35 = 105^o θ = 70 35 = 105o. Next: angles in polygons practice questions gcse revision cards. 5 a day workbooks.
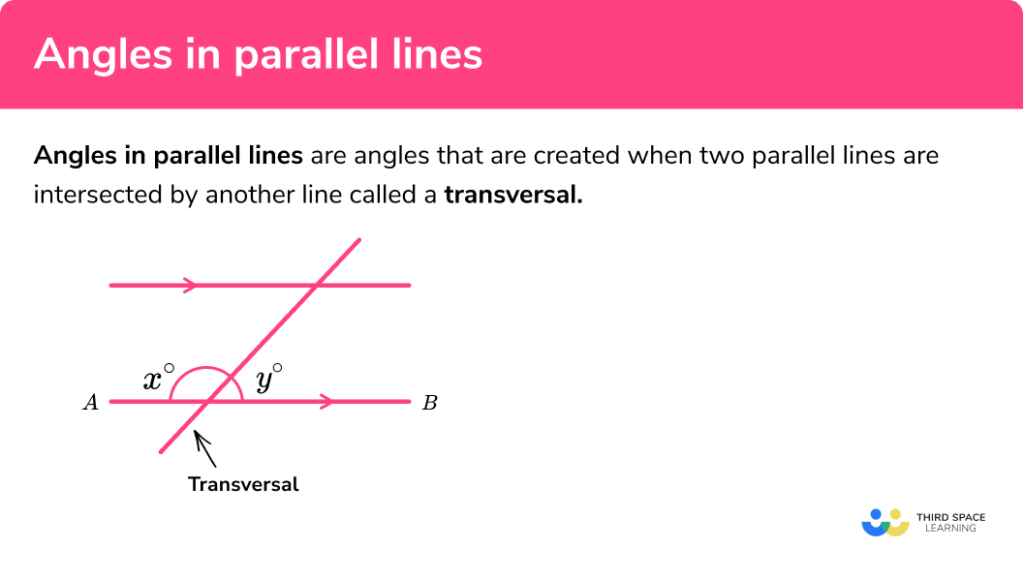
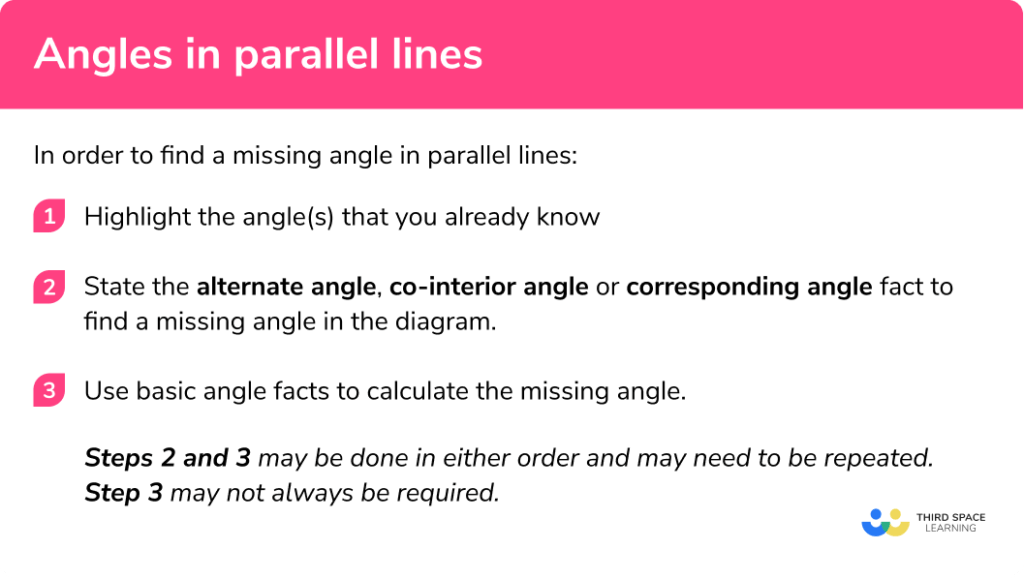
Angles In Parallel Lines Gcse Maths Steps Examples When we intersect a pair of parallel lines with a transversal, alternate angles occur on opposite sides of the transversal line. they are either both obtuse or both acute. co interior angles; the sum of two co interior angles is \bf{180^{o}} . co interior angles occur in between two parallel lines when they are intersected by a transversal. the. Identify any matching angles and any angles that add up to 180°. step 1: identify where the parallel lines are on the diagram. they will be marked with arrows or will be in a 2d shape that contains parallel lines. you may need to identify them from other reasons, such as vectors. step 2: identify the transverse. Learn about and revise angles, lines and multi sided shapes and their properties with this bbc bitesize gcse maths edexcel study guide. This means we will need multiple steps. firstly, we will use the fact that angles on a straight line add to 180 degrees. specifically, \angle efc and \angle cfg add to make 180\degree. which means we can do the following: \angle cfg = 180\degree 32\degree = 148\degree. now, looking at the diagram we can see that angle \angle cfg and the.

Angles In Parallel Lines Gcse Maths Mr Mathematics Youtube Learn about and revise angles, lines and multi sided shapes and their properties with this bbc bitesize gcse maths edexcel study guide. This means we will need multiple steps. firstly, we will use the fact that angles on a straight line add to 180 degrees. specifically, \angle efc and \angle cfg add to make 180\degree. which means we can do the following: \angle cfg = 180\degree 32\degree = 148\degree. now, looking at the diagram we can see that angle \angle cfg and the. Edexcel gcse. mathematics (linear) – 1ma0. allel linesmaterials required for examination ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetre. , protractor, compasses, p. tracing paper may be used. ructionsitems included with que. on papersniluse black ink or ball point pen. fill in the boxes at the top of this page wi. Parallel lines continue in the same direction as each other, forever, without touching. therefore, they remain the same distance apart from each other at all times. there are 4 main rules for angles in parallel lines which we can use to solve geometrical problems. an angle around a point on a parallel line is 95\degree 95°.
Angles In Parallel Lines Gcse Maths Steps Examples Edexcel gcse. mathematics (linear) – 1ma0. allel linesmaterials required for examination ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetre. , protractor, compasses, p. tracing paper may be used. ructionsitems included with que. on papersniluse black ink or ball point pen. fill in the boxes at the top of this page wi. Parallel lines continue in the same direction as each other, forever, without touching. therefore, they remain the same distance apart from each other at all times. there are 4 main rules for angles in parallel lines which we can use to solve geometrical problems. an angle around a point on a parallel line is 95\degree 95°.

Fillable Online Angles In Parallel Lines Gcse Maths Steps
Angles In Parallel Lines Gcse Maths Steps Examples

Comments are closed.