Angle Bisectors Of A Triangle
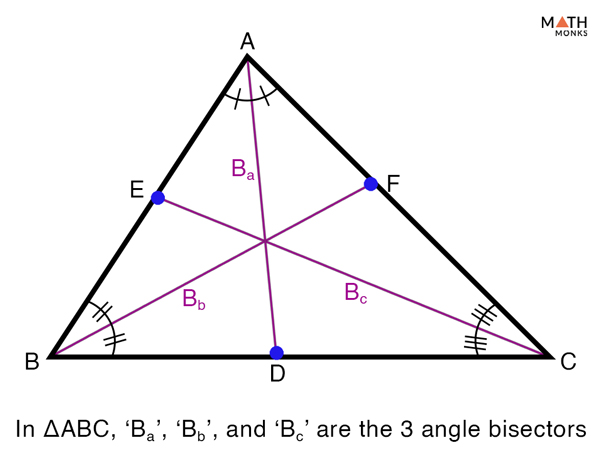
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle Definition Theorem Examples Learn what an angle bisector is and how to construct it in geometry. find out the properties and examples of angle bisectors of angles and triangles, and the angle bisector theorem. The angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side into two parts proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. converse of internal angle bisector theorem: in a triangle, if the interior point is equidistant from the two sides of a triangle, then that point lies on the angle bisector of the angle formed by the two line segments.

Angle Bisector Definition Examples Cuemath Angle bisector theorem. an angle bisector cuts an angle exactly in half. one important property of angle bisectors is that if a point is on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle. this is called the angle bisector theorem. in other words, if → bd bisects ∠abc, → ba ⊥ fd ¯ ab, and, → bc ⊥. An angle bisector of a triangle is a line segment that bisects a vertex angle of a triangle and meets the opposite side of the triangle when extended. they are also called the internal bisector of an angle. shown below is a Δabc, with angle bisector ad of ∠bac. angle bisector of a triangle. how many angle bisectors does a triangle have. The angle bisector theorem states that an angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. thus, when an angle bisector is drawn from one vertex of a triangle, and it falls on one side of such a triangle, it divides that side in the same ratio as the ratio of. The angle bisector theorem tells us that the ratio between the sides that aren't this bisector so when i put this angle bisector here, it created two smaller triangles out of that larger one. the angle bisector theorem tells us the ratios between the other sides of these two triangles that we've now created are going to be the same.
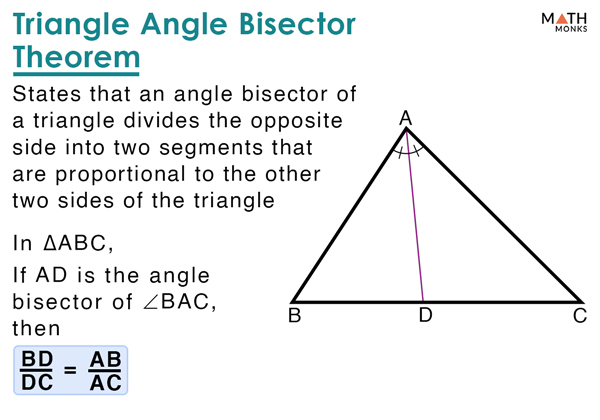
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle Definition Theorem Examples The angle bisector theorem states that an angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. thus, when an angle bisector is drawn from one vertex of a triangle, and it falls on one side of such a triangle, it divides that side in the same ratio as the ratio of. The angle bisector theorem tells us that the ratio between the sides that aren't this bisector so when i put this angle bisector here, it created two smaller triangles out of that larger one. the angle bisector theorem tells us the ratios between the other sides of these two triangles that we've now created are going to be the same. The angle bisector of an angle of a triangle is a straight line that divides the angle into two congruent angles. the three angle bisectors of the angles of a triangle meet in a single point, called the incenter . here, i is the incenter of Δ p q r . the incenter is equidistant from the sides of the triangle. that is, p i = q i = r i . For a triangle, like the one in the diagram below, if the bisector of angle a intersects side bc at point d, the ratio of the lengths of ab to ac equals the ratio of the length bd to dc. this can be written as: .
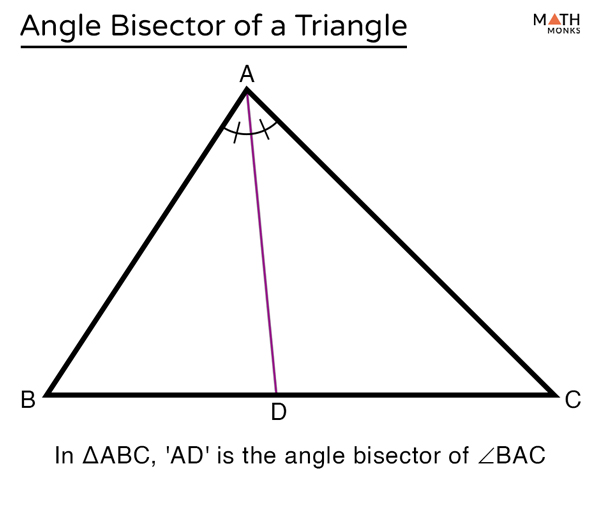
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle Definition Theorem Examples The angle bisector of an angle of a triangle is a straight line that divides the angle into two congruent angles. the three angle bisectors of the angles of a triangle meet in a single point, called the incenter . here, i is the incenter of Δ p q r . the incenter is equidistant from the sides of the triangle. that is, p i = q i = r i . For a triangle, like the one in the diagram below, if the bisector of angle a intersects side bc at point d, the ratio of the lengths of ab to ac equals the ratio of the length bd to dc. this can be written as: .
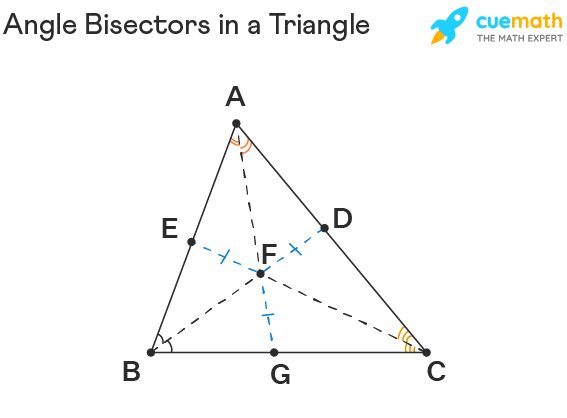
Angle Bisector Definition Construction Properties Examples

Angle Bisectors Of A Triangle

Comments are closed.