Anesthesia Lumbar Puncture Spinal Anesthesia Central Coast

Anesthesia Lumbar Puncture Spinal Anesthesia Central Coast Anesthesia (lumbar puncture, spinal anesthesia) this numbing medication is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid through a fine needle placed near the nerve roots of the lower spine. it can be used to numb the abdomen, groin, legs and feet. it does not put the patient to sleep, but blocks painful sensations during or after a medical procedure. Lumbar puncture (lp) with examination of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) is an important diagnostic tool for a variety of infectious and noninfectious neurologic conditions. the indications, contraindications, technique, and complications of lp in adults will be reviewed here. techniques of lp in children and of spinal and other types of neuraxial.
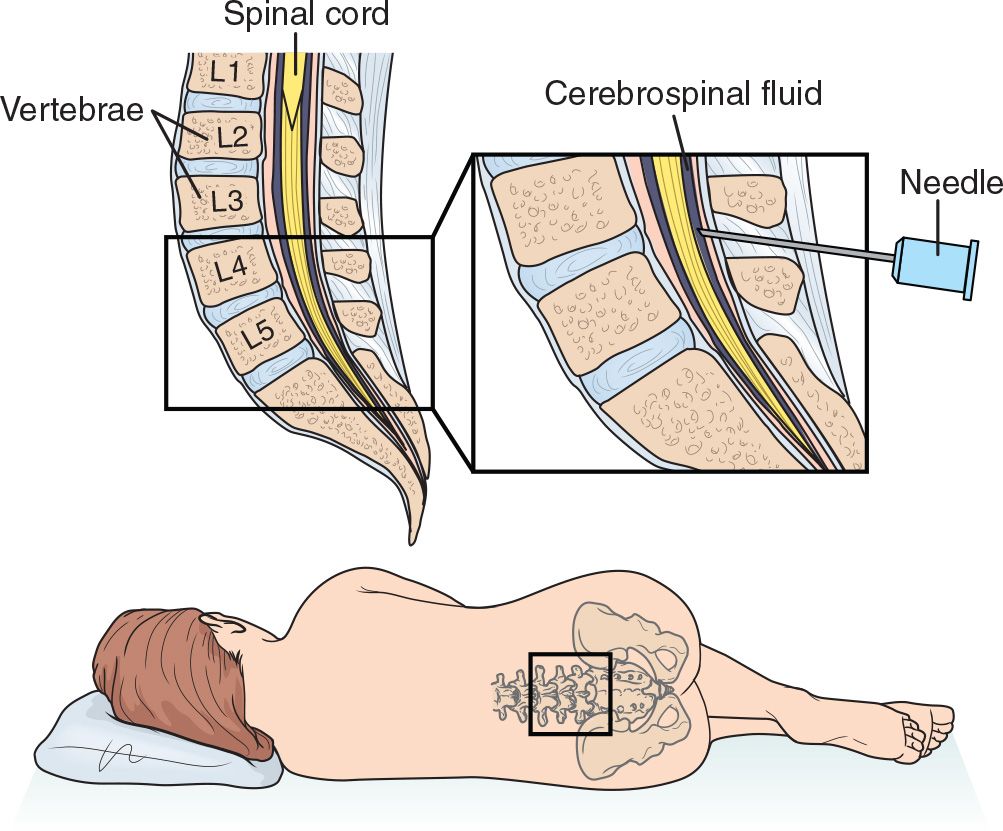
Lumbar Puncture Anesthesia Key Anesthesia (lumbar puncture, spinal anesthesia) this numbing medication is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid through a fine needle placed near the nerve roots of the lower spine. it can be used to numb the abdomen, groin, legs and feet. it does not put the patient to sleep, but blocks painful sensations during or after a medical procedure. Neuraxial anesthesia (na) is most commonly used for lower abdominal and lower extremity surgery (table 1). the sensory level required for a specific surgery is determined by the dermatome level of the skin incision and by the level required for surgical manipulation; these two requirements may be very different. The development of regional anesthesia started with the isolation of local anesthetics, the first being cocaine (the only naturally occurring local anesthetic). the first regional anesthetic technique performed was spinal anesthesia, and the first operation under spinal anesthesia was in 1898 in germany by august bier. before this, the only local anesthetic techniques were topical anesthesia. Post lumbar puncture headache. bleeding into the epidural space (spinal hematoma) lower back discomfort or pain that may radiate to the posterior legs (self limited) epidermoid tumor, which occurs years after lumbar puncture; risk is increased if the spinal needle is inserted or withdrawn with the stylet absent (very rare) brain herniation (rare).

Lumbar Puncture Lp Almostadoctor The development of regional anesthesia started with the isolation of local anesthetics, the first being cocaine (the only naturally occurring local anesthetic). the first regional anesthetic technique performed was spinal anesthesia, and the first operation under spinal anesthesia was in 1898 in germany by august bier. before this, the only local anesthetic techniques were topical anesthesia. Post lumbar puncture headache. bleeding into the epidural space (spinal hematoma) lower back discomfort or pain that may radiate to the posterior legs (self limited) epidermoid tumor, which occurs years after lumbar puncture; risk is increased if the spinal needle is inserted or withdrawn with the stylet absent (very rare) brain herniation (rare). The anesthesia injection will be given in the lumbar spine, below the level at which the spinal cord tapers off and the nerve roots continue down to the lower extremities. the needle will not come into contact with the spinal cord. the anesthesia provider first numbs the skin of the insertion site. a fine needle is placed into this numbed. A retrospective analysis of almost 5000 spinal anesthetics by horlocker and colleagues reported inadequate anesthesia in less than 2% of cases, and failure rates of under 1% have been described. yet, the “failed spinal” demonstrates remarkable interinstitutional variation, and in some published reports, it may be much higher.
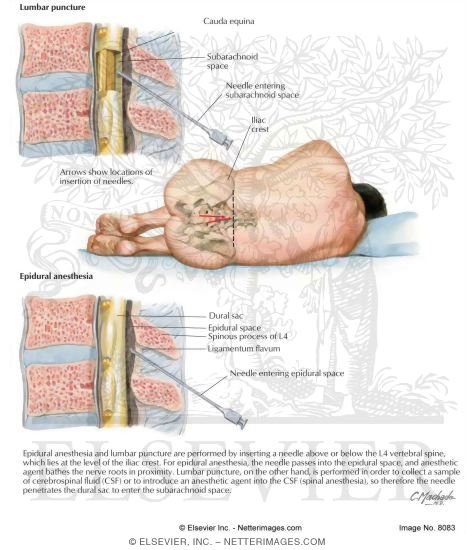
Lumbar Puncture And Epidural Anesthesia The anesthesia injection will be given in the lumbar spine, below the level at which the spinal cord tapers off and the nerve roots continue down to the lower extremities. the needle will not come into contact with the spinal cord. the anesthesia provider first numbs the skin of the insertion site. a fine needle is placed into this numbed. A retrospective analysis of almost 5000 spinal anesthetics by horlocker and colleagues reported inadequate anesthesia in less than 2% of cases, and failure rates of under 1% have been described. yet, the “failed spinal” demonstrates remarkable interinstitutional variation, and in some published reports, it may be much higher.

Comments are closed.