Anatomy Concussions
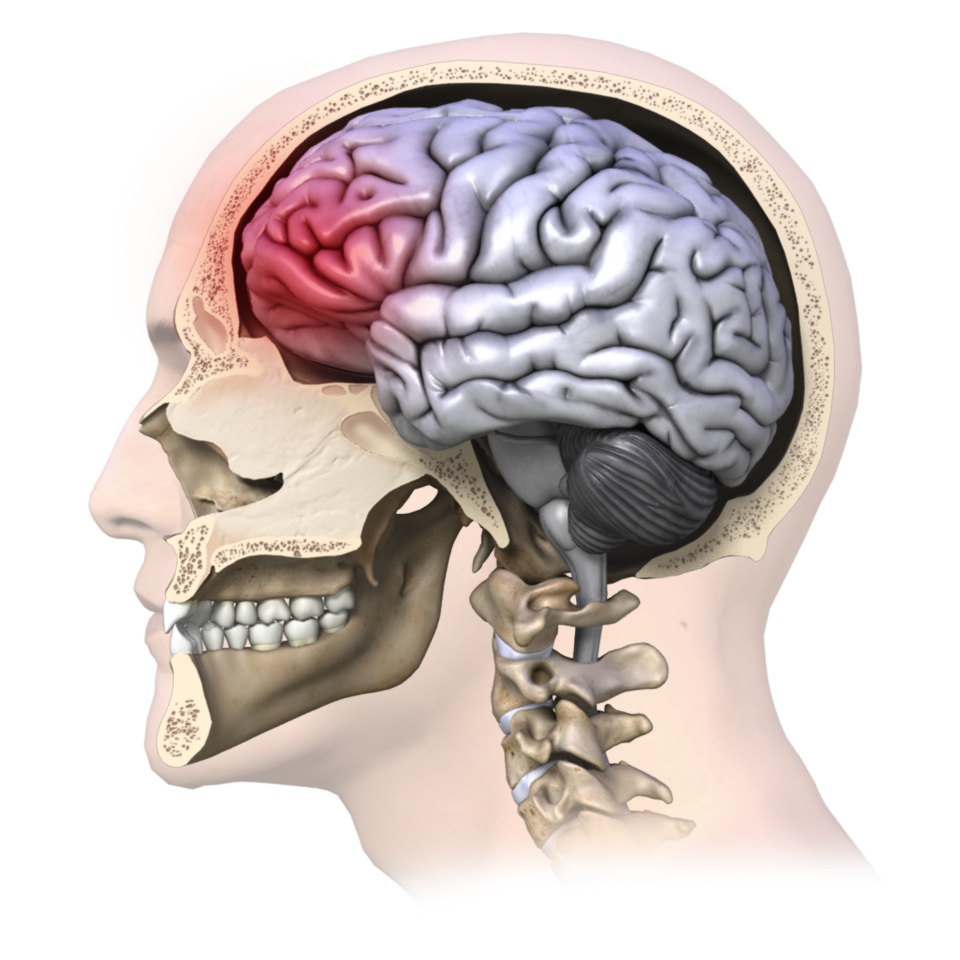
Concussion Rehab My Patient The anatomy of brain trauma, concussion, and coma. trauma to the head can produce many problems because so many components may be injured. brain tissue is surrounded both by the skull and by a tough membrane called the dura, which is right next to the brain. within, and surrounding, the brain tissue and dura are many arteries, veins, and. A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury (tbi) that results in temporary impairment of mental function. concussions are sometimes referred to as mild traumatic brain injuries (mtbi) to distinguish them from more serious types of brain injuries. concussions occur when a sudden movement causes the brain to bounce against or around the.

Concussion Definition Symptoms Treatment Study A concussion is a “traumatically induced transient disturbance of brain function.”[1] concussions are a subset of the neurologic injuries known as traumatic brain injuries. traumatic brain injuries have varying severity, ranging from mild, transient symptoms to extended periods of altered consciousness. given the usually self limited nature of symptoms associated with a concussion, the. The concussion public health burden has increased alongside our knowledge of the pathophysiology of mild traumatic brain injury (mtbi). the purpose of this review is to summarize our current understanding of mtbi pathophysiology and biomechanics and how these underlying principles correlate with clinical manifestations of mtbi. A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury that affects brain function. effects are often short term and can include headaches and trouble with concentration, memory, balance, mood and sleep. concussions usually are caused by an impact to the head or body that is associated with a change in brain function. not everyone who experiences a blow. Concussion. acceleration (g forces) can exert rotational forces in the brain, especially the midbrain and diencephalon. a concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mtbi), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. [9] symptoms may include loss of consciousness; memory loss; headaches; difficulty with thinking.

Anatomy Of A Concussion Concussions Tramatic Brain Injury Medical A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury that affects brain function. effects are often short term and can include headaches and trouble with concentration, memory, balance, mood and sleep. concussions usually are caused by an impact to the head or body that is associated with a change in brain function. not everyone who experiences a blow. Concussion. acceleration (g forces) can exert rotational forces in the brain, especially the midbrain and diencephalon. a concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mtbi), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. [9] symptoms may include loss of consciousness; memory loss; headaches; difficulty with thinking. 1.6 3.8 million sports related concussions per year. increasing over the past decade, though possibly due to increased awareness. substantial rise in youth athletes is concerning. 5 9% of all sports injuries. demographics. traumatic brain injury (tbi) is the leading cause of sport related death. A concussion, which is a form of mild traumatic brain injury, occurs after a blow to the head. the brain is surrounded by fluid and protective membranes called meninges, which usually cushion the brain. during an impact, the brain is pushed against the inside of the skull and can be bruised. in addition, different parts of the brain can move at.

Comments are closed.