Analytical Geometry Grd 10 E G 3

Grade 10 Mathematics Workbook Analytical Geometry Watch on. free lessons, worksheets, and video tutorials for students and teachers. topics in this unit include: midpoint and length of a line segment, medians, right bisectors, altitude, equation of a circle, and applications of formulas. this follows chapter 2 of the principles of math grade 10 mcgraw hill textbook. First find the distance of ‘ ’ from the two coordinates – e.g. ; . ∴ ; and. next find the distance of ‘ ’ from the two coordinates: ∴. then substitute it into the original pythagoras equation: ∴. so the distance formula for any point is: example: find the distance from the point a( 2; 3) to point b (3; 2) .

Grade 10 Mathematics Term 3 Analytical Geometry E Classroom 26.9 km. write an expression for the length of a line with the endpoints (x,3y) and (3x, 2y) d=square root of (4x^2 25y^2) study with quizlet and memorise flashcards containing terms like what is the slope of the line y = 5 6 (x 4), what is the midpoint of a line with endpoints of ( 5, 3) and (8, 5), find the coordinates of the midpoint with. Gr 10 analytical geometry page 4 of 29 gradient of a horizontal line 𝑚 e f= 3−3 −4−2 𝑚 e f= 0 −6 𝑚 e f= 0 this will be the same for all horizontal lines – the gradient will always be 0. gradient of a vertical line 𝑚 e g= 3−1 −4−(−4) 𝑚 e g= 2 0 𝑚 e g= undefined undefined because you may not divide by 0. Question 2. the diagram below shows quadrilateral akbc, with a ( 4;1) and b (4;5). c is on the. axis and k is the fourth vertex of the quadrilateral. the gradient of the line segment bc is 2. is the angle of inclination of bc. (a) determine the coordinates of the midpoint of ab. (2) (b) calculate the value of . (2). This video was created to assist our grade 10 learners with analytical geometry.

Grade 10 Mathematics Term 3 Analytical Geometry E Classroom Question 2. the diagram below shows quadrilateral akbc, with a ( 4;1) and b (4;5). c is on the. axis and k is the fourth vertex of the quadrilateral. the gradient of the line segment bc is 2. is the angle of inclination of bc. (a) determine the coordinates of the midpoint of ab. (2) (b) calculate the value of . (2). This video was created to assist our grade 10 learners with analytical geometry. In the diagram below, 3), b(—5; — determine the equations of the lines through band c a and b state the gradient of any line parallel to bc. prove that : bcd = 900 1) and — 8): (3) (2) write down the coordinates of e, if aecb is a parallelogram. calculate the length of diagonal db. Analytic geometry grade 10. first calculate the midpoint of the opposite line segment. next calculate the slope of the line segment using the slope formula. use the vertex and the slope of the opposite line segment to find the y intercept.
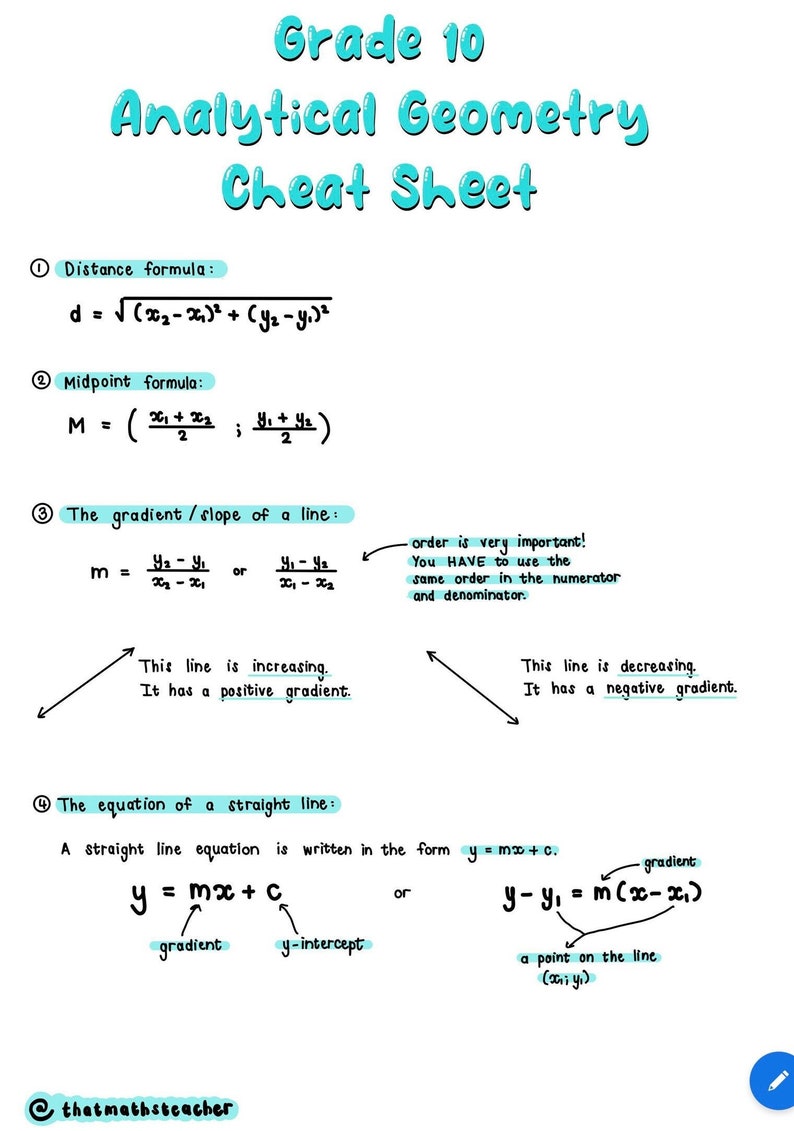
Grade 10 Analytical Geometry Cheat Sheet Etsy Uk In the diagram below, 3), b(—5; — determine the equations of the lines through band c a and b state the gradient of any line parallel to bc. prove that : bcd = 900 1) and — 8): (3) (2) write down the coordinates of e, if aecb is a parallelogram. calculate the length of diagonal db. Analytic geometry grade 10. first calculate the midpoint of the opposite line segment. next calculate the slope of the line segment using the slope formula. use the vertex and the slope of the opposite line segment to find the y intercept.

Comments are closed.