An Introduction To Pythagoras Theorem Syedlearns
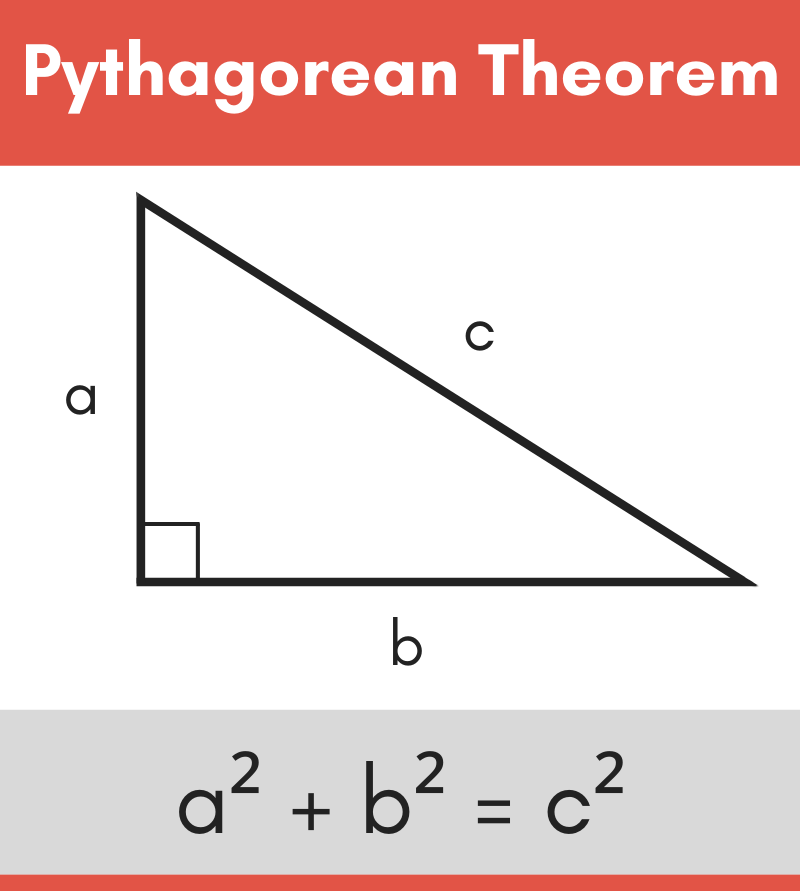
An Introduction To Pythagoras Theorem Syedlearns It is called "pythagoras' theorem" and can be written in one short equation: a 2 b 2 = c 2. note: c is the longest side of the triangle; a and b are the other two sides; definition. the longest side of the triangle is called the "hypotenuse", so the formal definition is:. According to the definition, the pythagoras theorem formula is given as: hypotenuse2 = perpendicular2 base2. c2 = a2 b2. the side opposite to the right angle (90°) is the longest side (known as hypotenuse) because the side opposite to the greatest angle is the longest. consider three squares of sides a, b, c mounted on the three sides of a.

Pythagoras Theorem Diagram The formula of pythagoras theorem is expressed as, hypotenuse 2 = base 2 height 2. this is also written as, c 2 = a 2 b 2; where 'c' is the hypotenuse and 'a' and 'b' are the two legs of the right angled triangle. using the pythagoras theorem formula, any unknown side of a right angled can be calculated if the other two sides are given. A great many different proofs and extensions of the pythagorean theorem have been invented. taking extensions first, euclid himself showed in a theorem praised in antiquity that any symmetrical regular figures drawn on the sides of a right triangle satisfy the pythagorean relationship: the figure drawn on the hypotenuse has an area equal to the sum of the areas of the figures drawn on the legs. What is the pythagorean theorem? the pythagorean theorem states that the square of the longest side of a right triangle (called the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. pythagorean theorem formula shown with triangle abc is: a^2 b^2=c^2 . side c is known as the hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the longest side of. The pythagoras theorem has a wide range of applications in mathematics, engineering, and architecture. it is widely used to calculate the lengths of the sides of a right triangle, as well as the distances between two points. it is also used to calculate the area of a triangle and the volume of a pyramid or cone.

Introduction To Pythagoras Theorem Teaching Resources What is the pythagorean theorem? the pythagorean theorem states that the square of the longest side of a right triangle (called the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. pythagorean theorem formula shown with triangle abc is: a^2 b^2=c^2 . side c is known as the hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the longest side of. The pythagoras theorem has a wide range of applications in mathematics, engineering, and architecture. it is widely used to calculate the lengths of the sides of a right triangle, as well as the distances between two points. it is also used to calculate the area of a triangle and the volume of a pyramid or cone. The longest side in a right angled triangle is called the hypotenuse. the hypotenuse will always be the side opposite the right angle. if we label the hypotenuse c, and label the other two sides a and b then pythagoras’ theorem tells us that: a2 b2 = c2. where a, b, and c are the lengths of the three sides. The corbettmaths practice questions on pythagoras. next: direct and inverse proportion practice questions.

Comments are closed.