Amygdala And Emotion Neuroplasticity Neuroscience School Psychology

Amygdala And Emotion Neuroplasticity Neuroscience School Psychology Emotions arise from activations of specialized neuronal populations in several parts of the cerebral cortex, notably the anterior cingulate, insula, ventromedial prefrontal, and subcortical structures, such as the amygdala, ventral striatum, putamen, caudate nucleus, and ventral tegmental area. feelings are conscious, emotional experiences of. Front. behav. neurosci. 9:178. doi: 10.3389 fnbeh.2015.00178. it has long been known that the amygdala, a bilateral structure from the medial temporal lobe, is related to emotion, particularly in processing of aversive information (e.g., ledoux, 1996). however, accumulating evidence suggests that amygdala activation is also involved in.

Exploring The Amygdala The Emotional Center Of The Brain Neural dynamics in response to affective stimuli are linked to momentary emotional experiences. the amygdala, in particular, is involved in subjective emotional experience and assigning value to neutral stimuli. because amygdala activity persistence following aversive events varies across individuals, some may evaluate subsequent neutral stimuli more negatively than others. this may lead to. The overnight neuronal plasticity that is important for emotional resolution includes strengthening of some memory circuit components and targeted weakening of others. and amygdala are. Laviolette, s. r. & grace, a. a. cannabinoids potentiate emotional learning plasticity in neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex through basolateral amygdala inputs. j. neurosci. 26 , 6458–6468. This review describes how both negative and positive social factors, ranging from stress to meditation, affect brain structure and functioning. experiential factors shape the neural circuits.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amygdala-anatomy-373211_FINAL2-53b5c8e385fe490e95afef2f03f2e475.png)
Amygdala S Location And Function Laviolette, s. r. & grace, a. a. cannabinoids potentiate emotional learning plasticity in neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex through basolateral amygdala inputs. j. neurosci. 26 , 6458–6468. This review describes how both negative and positive social factors, ranging from stress to meditation, affect brain structure and functioning. experiential factors shape the neural circuits. The authors present an overview of the neural bases of emotion. they underscore the role of the prefrontal cortex (pfc) and amygdala in 2 broad approach and withdrawal related emotion systems. components and measures of affective style are identified. emphasis is given to affective chronometry and a role for the pfc in this process is proposed. plasticity in the central circuitry of emotion. Abstract: emotions arise from activations of specialized neuronal populations in several parts of. the cerebral cortex, notably the anterior cingulate, insula, ventromedial prefrontal, and.
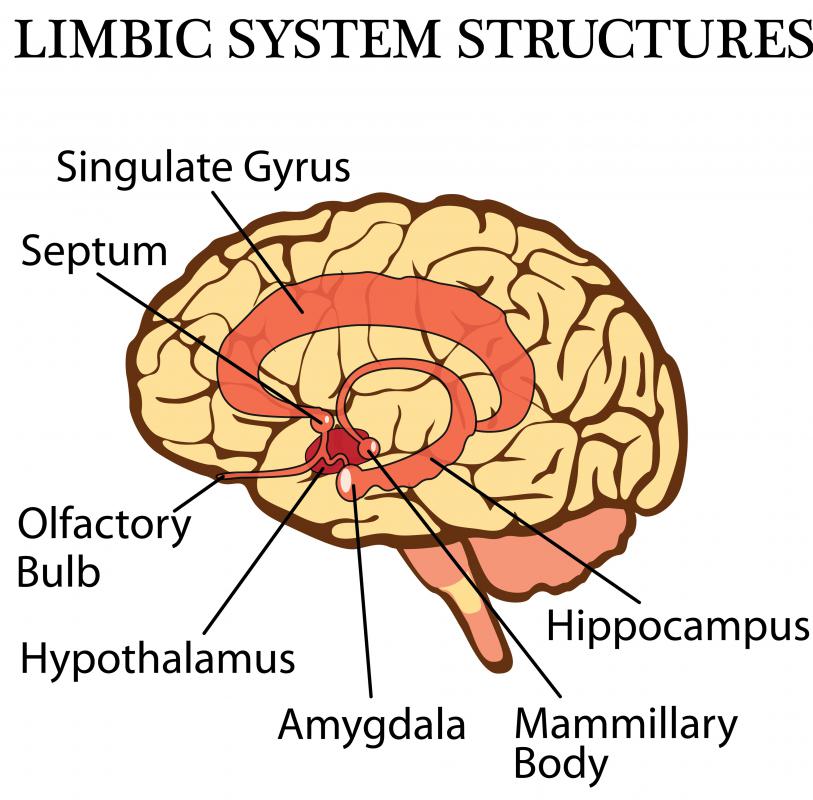
What Is The Amygdala With Pictures The authors present an overview of the neural bases of emotion. they underscore the role of the prefrontal cortex (pfc) and amygdala in 2 broad approach and withdrawal related emotion systems. components and measures of affective style are identified. emphasis is given to affective chronometry and a role for the pfc in this process is proposed. plasticity in the central circuitry of emotion. Abstract: emotions arise from activations of specialized neuronal populations in several parts of. the cerebral cortex, notably the anterior cingulate, insula, ventromedial prefrontal, and.
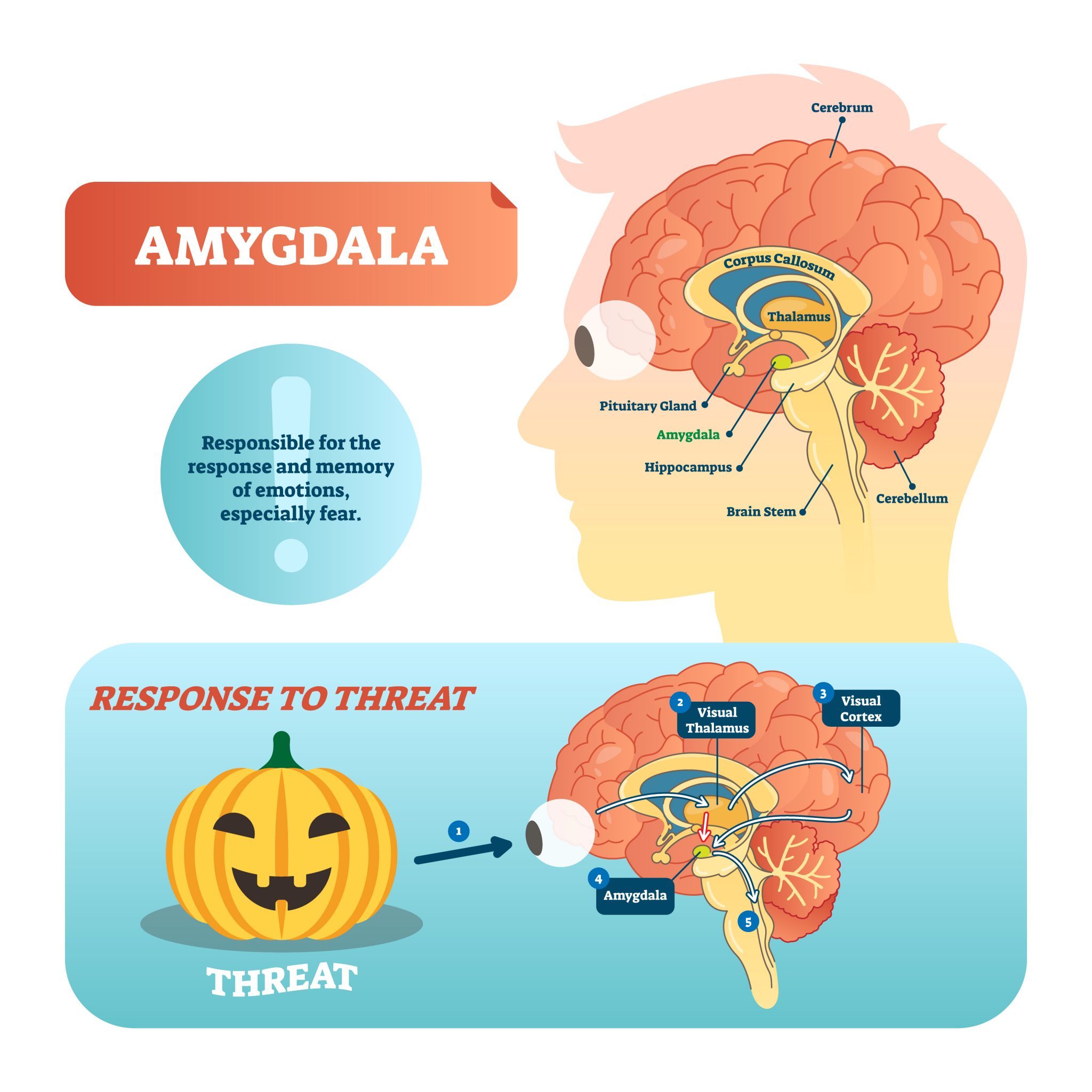
Amygdala The Powerhouse Of Emotions Cognifit Blog Brain Health News

Comments are closed.