Advanced Ekgs Ventricular Tachycardia Classification Localization

Advanced Ekgs Ventricular Tachycardia Classification Localization How to classify vt based on duration, morphology, and mechanism. also how to localize scar based vt, as well as identify specific forms of idiopathic vt.rela. Dive deep into the classification and localization of ventricular tachycardia (vt) in this comprehensive 29 minute video. learn how to classify vt based on duration, morphology, and mechanism, and master the techniques for localizing scar based vt. explore specific forms of idiopathic vt and their identification.
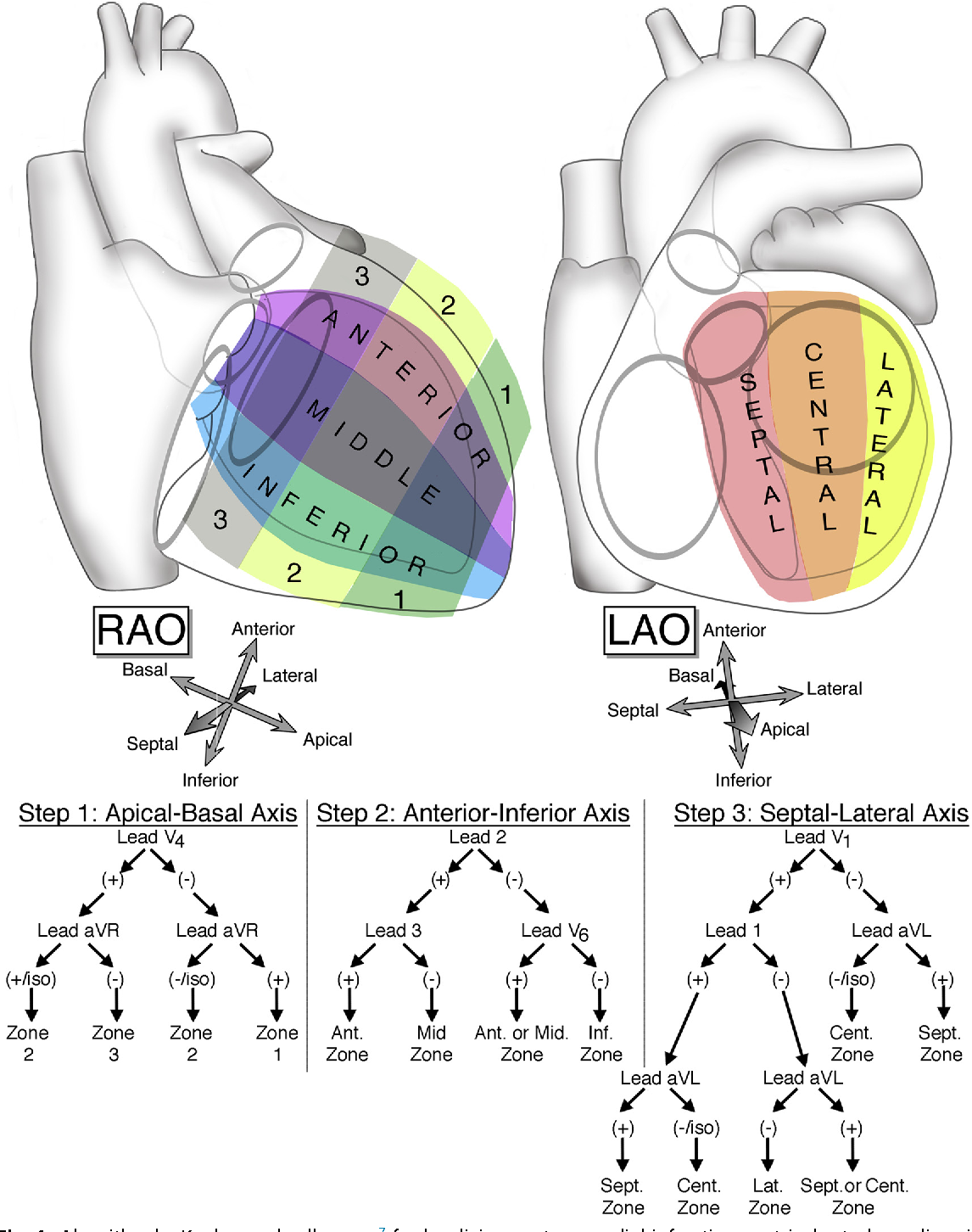
Electrocardiographic Localization Of Ventricular Tachycardia In Posterior lateral is located on the part between anterior and inferior. adapted from miller et al. [1] the localisation of the origin (or exit site) of a ventricular tachycardia can be helpful in understanding the cause of the vt and is very helpful when planning an ablation procedure to treat a ventricular tachycardia. Ventricular tachycardia (vt) is a broad complex tachycardia originating from the ventricles. there are several different forms of vt — the most common is monomorphic vt, which originates from a single focus within the ventricles. monomorphic vt can be difficult to differentiate from other causes of broad complex tachycardia. other ecg. Catheter ablation is an established therapeutic option for ventricular tachycardias (vts) or premature ventricular contractions (pvcs) in patients with structural heart disease (shd). 1 localizing the vt exit site or the pvc origin site can be critical for successful vt catheter ablation in these patients. 2 in 2012, yokokawa et al first demonstrated the feasibility of using a computerized. Fascicular ventricular tachycardia is an idiopathic form of vt. it is caused by re entry in the fascicles of the left bundle branch (i.e in the purkinje fibers). fascicular ventricular tachycardia occurs in people aged less than 50 years of age, and predominantly in males.
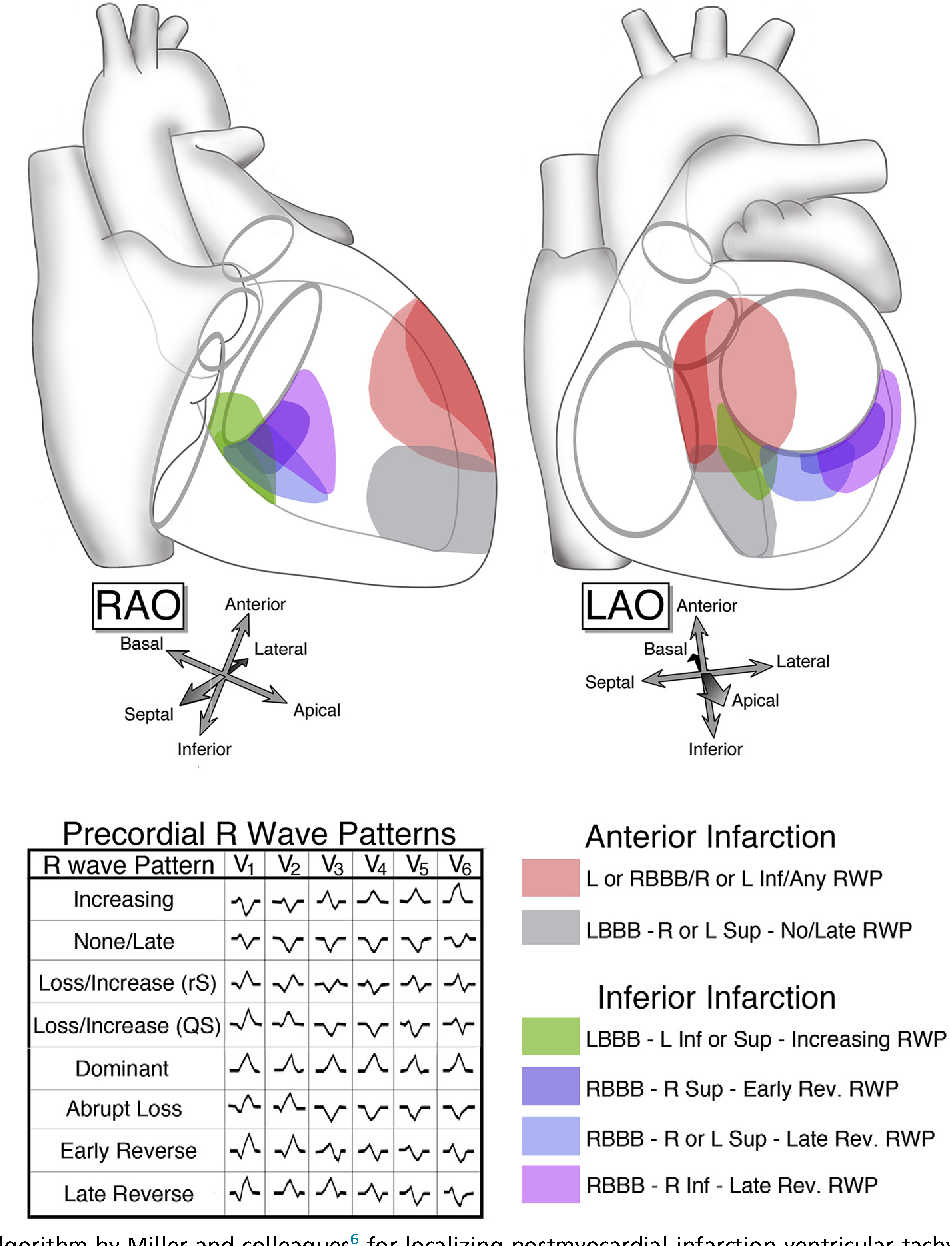
Electrocardiographic Localization Of Ventricular Tachycardia In Catheter ablation is an established therapeutic option for ventricular tachycardias (vts) or premature ventricular contractions (pvcs) in patients with structural heart disease (shd). 1 localizing the vt exit site or the pvc origin site can be critical for successful vt catheter ablation in these patients. 2 in 2012, yokokawa et al first demonstrated the feasibility of using a computerized. Fascicular ventricular tachycardia is an idiopathic form of vt. it is caused by re entry in the fascicles of the left bundle branch (i.e in the purkinje fibers). fascicular ventricular tachycardia occurs in people aged less than 50 years of age, and predominantly in males. Ventricular tachycardia is defined as a sequence of three or more ventricular beats. the frequency must by higher than 100 bpm, mostly it is 110 250 bpm. ventricular tachycardias often origin around old scar tissue in the heart, e.g. after myocardial infarction. also electrolyte disturbances and ischemia can cause ventricular tachycardias. Mean localization errors (a) are reported in millimeters with corresponding standard deviations for ecg based (blue) and egm based (red) testing. an example of how ventricular tachycardia (vt) focal origins compare to uvc based localized sources is shown in (b); diamonds represent the ground truths, whereas the circles are the cnn outputs. the.

Comments are closed.