Acute Ischemic Stroke Matrix Metalloproteinases And Blood Brain
Frontiers Matrix Metalloproteinases And Blood Brain Barrier Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (gelatinase b), first described in neutrophils in 1974 (sopata and dancewicz, 1974), is expressed as a 92 kda proenzyme, which can be activated to the 83 kda mature enzyme (klein and bischoff, 2011). among mmps, mmp 9 is the most widely studied enzyme in acute ischemic stroke. Abstract. matrix metalloproteinases are versatile endopeptidases with many different functions in the body in health and disease. in the brain, matrix metalloproteinases are critical for tissue formation, neuronal network remodeling, and blood brain barrier integrity. many reviews have been published on matrix metalloproteinases before, most of.

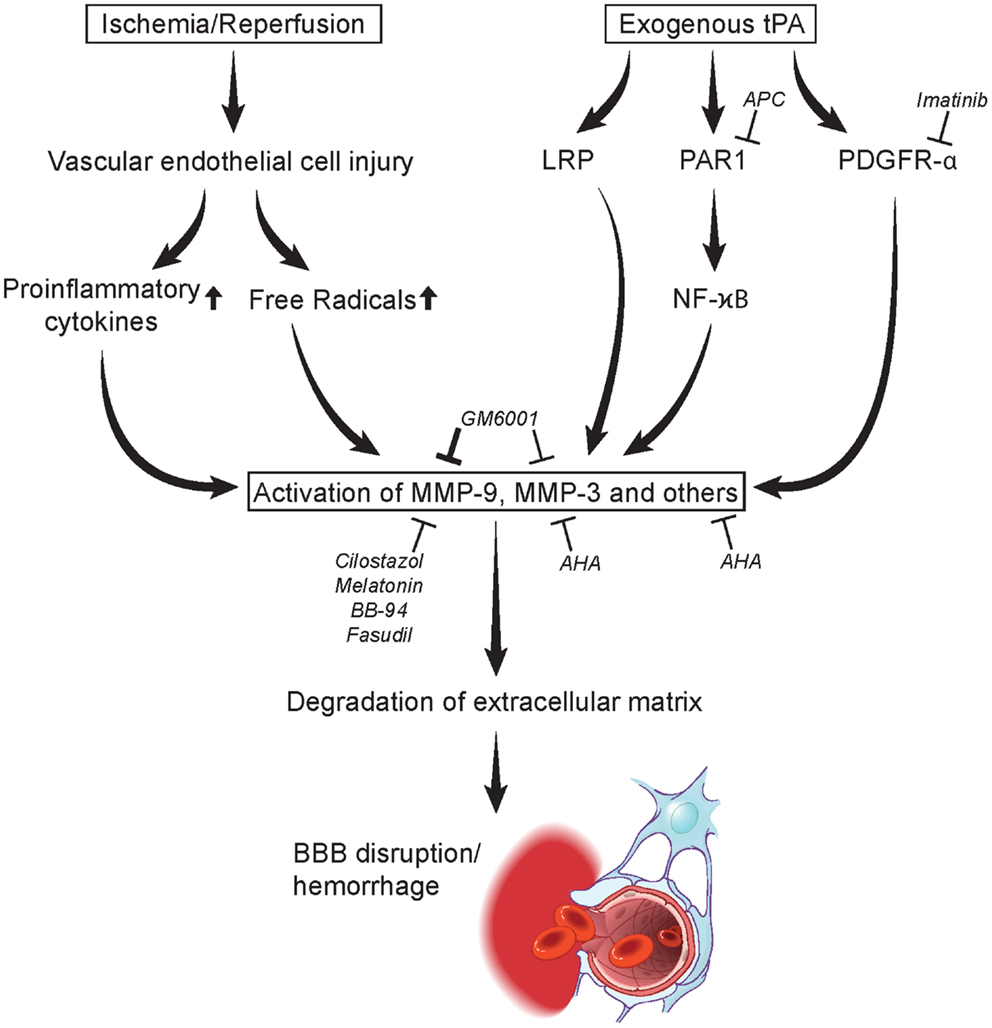
Acute Ischemic Stroke Matrix Metalloproteinases And Blood Brain Blood brain barrier (bbb) disruption, mediated through matrix metalloproteinases (mmps) and other mechanisms, is a critical event during ischemic stroke. tissue plasminogen activator (tpa) is the only fda approved thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke, but the efficacy and safety of its therapeutic application is limited by narrow. Fig. 2.postischemic inflammation, blood brain barrier (bbb) disruption, and neuronal injury in stroke. activation of microglia and astrocytes following ischemia results in an increase in the production of cytokines, chemokines, matrix metalloproteinases (mmps), and vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf) in the ischemic brain tissue. It affects the extracellular matrix around the blood arteries in addition to neurons after a stroke, promoting the death of brain cells. in the initial stages after cerebral ischemia, mmp 9. Stroke outcome can be predicted by clinical features, biochemical parameters, and some risk factors. matrix metalloproteinase 9 (mmp 9) is involved in various stages of stroke pathology. mmp 9 inhibitors are potential stroke therapeutic agents. little is known about the relation between mmp 9—after the acute stage—and clinical recovery.

Acute Ischemic Stroke Matrix Metalloproteinases And Blood Brain It affects the extracellular matrix around the blood arteries in addition to neurons after a stroke, promoting the death of brain cells. in the initial stages after cerebral ischemia, mmp 9. Stroke outcome can be predicted by clinical features, biochemical parameters, and some risk factors. matrix metalloproteinase 9 (mmp 9) is involved in various stages of stroke pathology. mmp 9 inhibitors are potential stroke therapeutic agents. little is known about the relation between mmp 9—after the acute stage—and clinical recovery. The role of matrix metalloproteinases (mmps) in blood brain barrier (bbb) disruption as a consequence of ischemic stroke is discussed and mmp 9 in particular appears to play an important role in tpa associated hemorrhagic complications. ischemic stroke continues to be one of the most challenging diseases in translational neurology. tissue plasminogen activator (tpa) remains the only approved. Neuronal cell death during ischemic stroke triggers an immune response leading to inflammatory cell activa tion and infiltration. these activated inflammatory cells release cytotoxic agents, including matrix metalloproteinases (mmps), which may induce further cell damage and disruption of the blood–brain barrier. proenzyme acti.

Comments are closed.