Actin Definition Function Britannica

Actin Definition Function Britannica Actin, protein that is an important contributor to the contractile property of muscle and other cells. in muscle, two long strands of actin molecules are twisted together to form a thin filament, bundles of which alternate with bundles of myosin. the temporary fusion of actin and myosin results in muscle contraction. Actin is a globular protein that polymerizes (joins together many small molecules) to form long filaments. because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin filament is polar, with different ends, termed “barbed” and “pointed.”. an abundant protein in nearly all eukaryotic cells, actin has been extensively studied in.
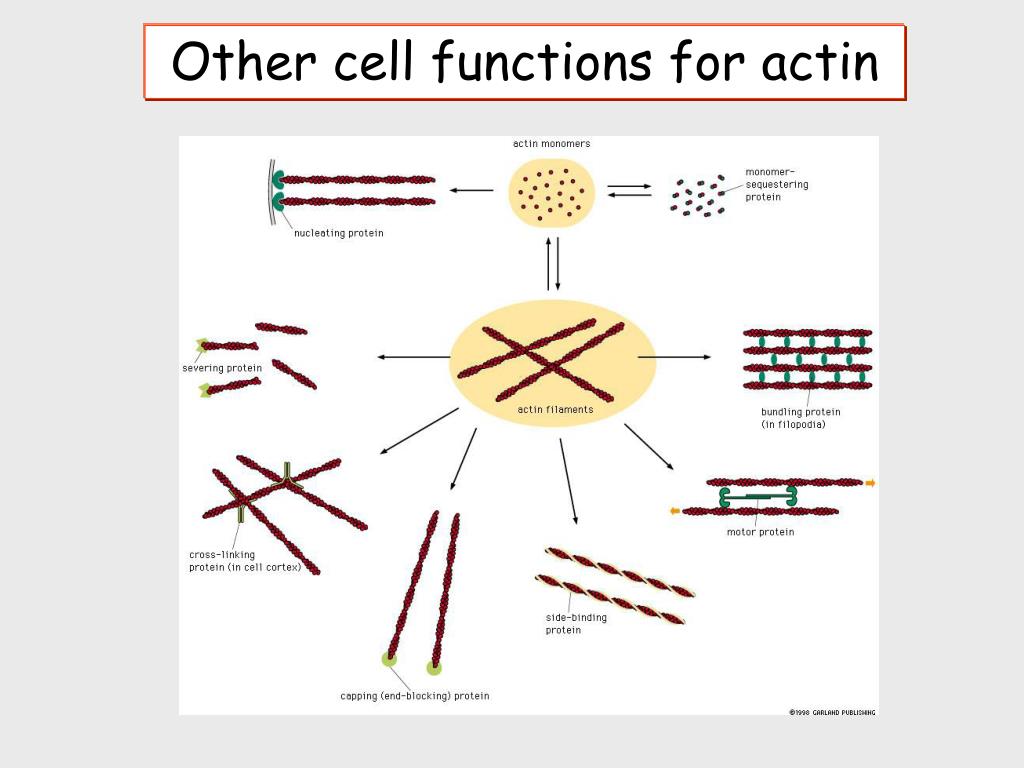
Ppt Other Cell Functions For Actin Powerpoint Presentation Free Intermediate filament. cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells (cells containing a nucleus). the cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell, maintains the cell’s shape, and is responsible for the locomotion of the cell itself and the movement of the various organelles. Actin filaments are particularly abundant beneath the plasma membrane, where they form a network that provides mechanical support, determines cell shape, and allows movement of the cell surface, thereby enabling cells to migrate, engulf particles, and divide.figure 11.1actin filamentselectron micrograph of actin filaments. The main functions of actin filaments include: forming a dynamic cytoskeleton to provide structural support to cells. supporting and allowing cell motility. supporting muscle contractions as actin filaments slide alongside myosin filaments. in muscle, actin molecules twist together to form a 'thin filament' which interdigitate with thick. Actin is the most abundant protein in most eukaryotic cells. it is highly conserved and participates in more protein protein interactions than any known protein. these properties, along with its ability to transition between monomeric (g actin) and filamentous (f actin) states under the control of nucleotide hydrolysis, ions, and a large number.
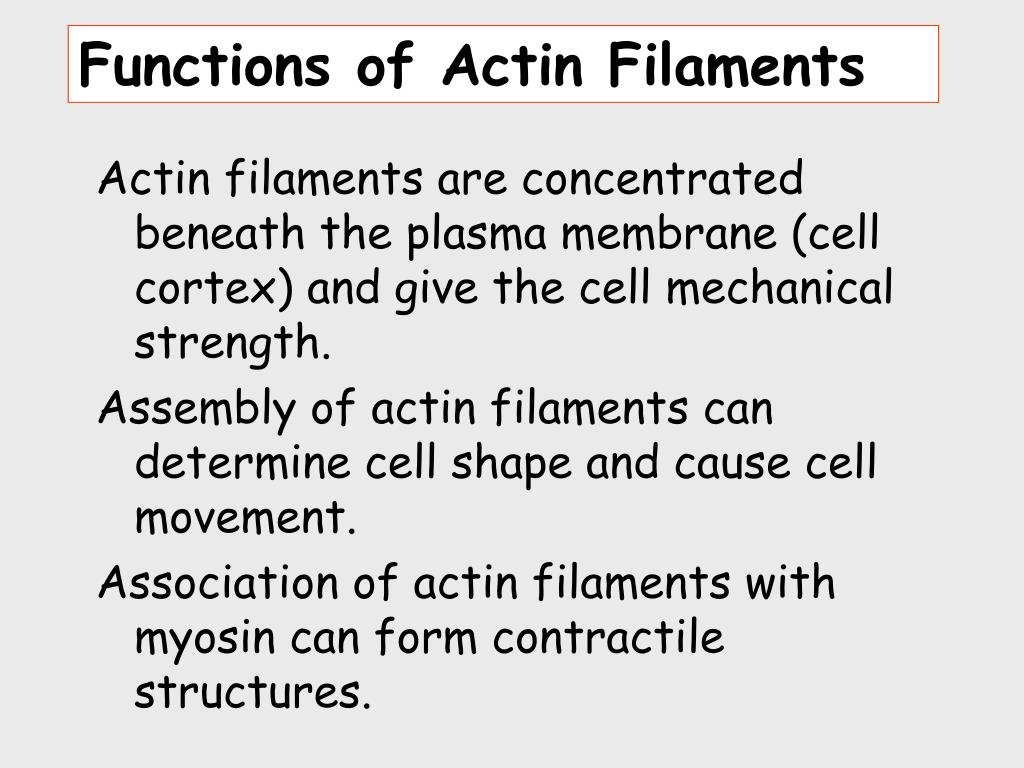
Ppt Other Cell Functions For Actin Powerpoint Presentation Free The main functions of actin filaments include: forming a dynamic cytoskeleton to provide structural support to cells. supporting and allowing cell motility. supporting muscle contractions as actin filaments slide alongside myosin filaments. in muscle, actin molecules twist together to form a 'thin filament' which interdigitate with thick. Actin is the most abundant protein in most eukaryotic cells. it is highly conserved and participates in more protein protein interactions than any known protein. these properties, along with its ability to transition between monomeric (g actin) and filamentous (f actin) states under the control of nucleotide hydrolysis, ions, and a large number. Actin is the most abundant protein in most eukaryotic cells. it is highly conserved and participates in more protein protein interactions than any known protein. these properties, along with its ability to transition between monomeric (g actin) and filamentous (f actin) states under the control of nucleotide hydrolysis, ions, and a large number. Actin is interesting. we state this not just because actin is so plentiful that it is the single most abundant protein in many eukaryotic cells. actin is interesting not only because it is so highly conserved that between humans and chickens there have been no amino acid changes in the 375 residues present in the skeletal muscle isoform (1). we think that actin remains interesting because.

Function Of Actin Filaments Actin is the most abundant protein in most eukaryotic cells. it is highly conserved and participates in more protein protein interactions than any known protein. these properties, along with its ability to transition between monomeric (g actin) and filamentous (f actin) states under the control of nucleotide hydrolysis, ions, and a large number. Actin is interesting. we state this not just because actin is so plentiful that it is the single most abundant protein in many eukaryotic cells. actin is interesting not only because it is so highly conserved that between humans and chickens there have been no amino acid changes in the 375 residues present in the skeletal muscle isoform (1). we think that actin remains interesting because.
.PNG)
Actin And Myosin Presentation Biology

Comments are closed.