Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary
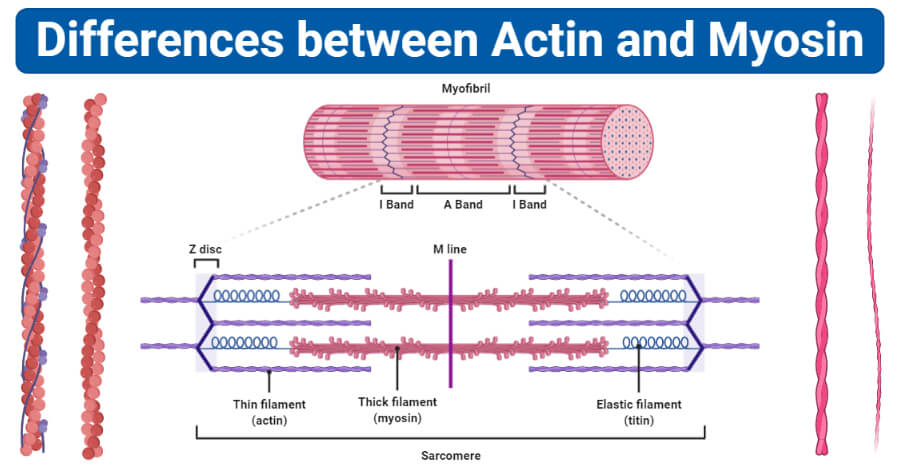
Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary 48 Off Actin and myosin are both proteins that are found in all types of muscle tissue. myosin forms thick filaments (15 nm in diameter) and actin forms thinner filaments (7nm in diameter). actin and myosin filaments work together to generate force. this force produces the muscle cell contractions that facilitate the movement of the muscles and. Muscle cell definition. a muscle cell, known technically as a myocyte, is a specialized animal cell which can shorten its length using a series of motor proteins specially arranged within the cell. while several associated proteins help, actin and myosin form thick and thin filaments which slide past each other to contract small units of a.

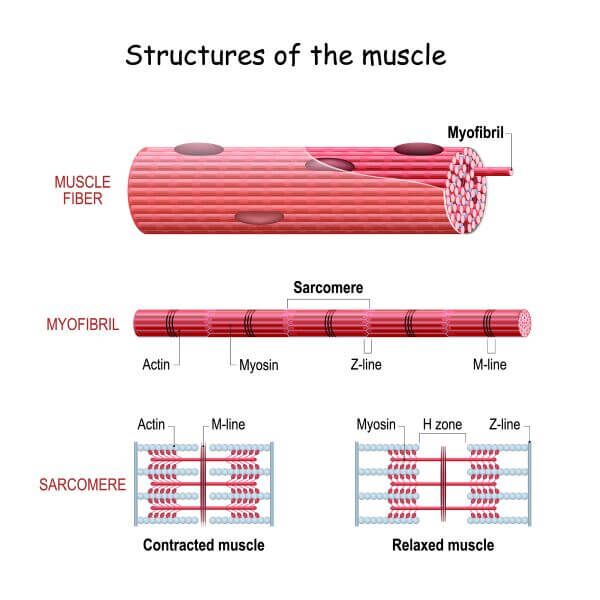
Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary Beyond their well known roles in muscle contraction, myosin and actin are integral to a variety of cellular functions. these proteins are crucial for maintaining cell integrity, facilitating intracellular transport, and enabling cellular motility. myosin and actin’s collaboration is evident in processes such as endocytosis, where cells. Smooth muscle definition. smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. these cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. In figure 12.7.11 12.7. 11, you can see that a sarcomere is constructed so that the stationary myosin fibers are located centrally, with two parallel sets of actin fibers interspersed between the myosin fibers, to the left and the right of the center. note that the actin fibers do not cross the center line, and that at the center, the myosin. Myosin. definition. noun, plural: myosins. a family of motor atpases that interact with f actin filaments. supplement. myosins belong to a family of motor proteins in muscle s to enable muscle contraction. they may also be present in other cells such as amoeba e and macrophages as a motor protein involved in different motility processes.

Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary In figure 12.7.11 12.7. 11, you can see that a sarcomere is constructed so that the stationary myosin fibers are located centrally, with two parallel sets of actin fibers interspersed between the myosin fibers, to the left and the right of the center. note that the actin fibers do not cross the center line, and that at the center, the myosin. Myosin. definition. noun, plural: myosins. a family of motor atpases that interact with f actin filaments. supplement. myosins belong to a family of motor proteins in muscle s to enable muscle contraction. they may also be present in other cells such as amoeba e and macrophages as a motor protein involved in different motility processes. The cross bridge cycle is a fundamental process that underpins muscle contraction, facilitating the interaction between actin and myosin to generate force. this cycle begins when calcium ions, released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, bind to regulatory proteins on the actin filament. this binding induces a conformational change that exposes. Actin filaments, usually in association with myosin, are responsible for many types of cell movements. myosin is the prototype of a molecular motor —a protein that converts chemical energy in the form of atp to mechanical energy, thus generating force and movement. the most striking variety of such movement is muscle contraction, which has.
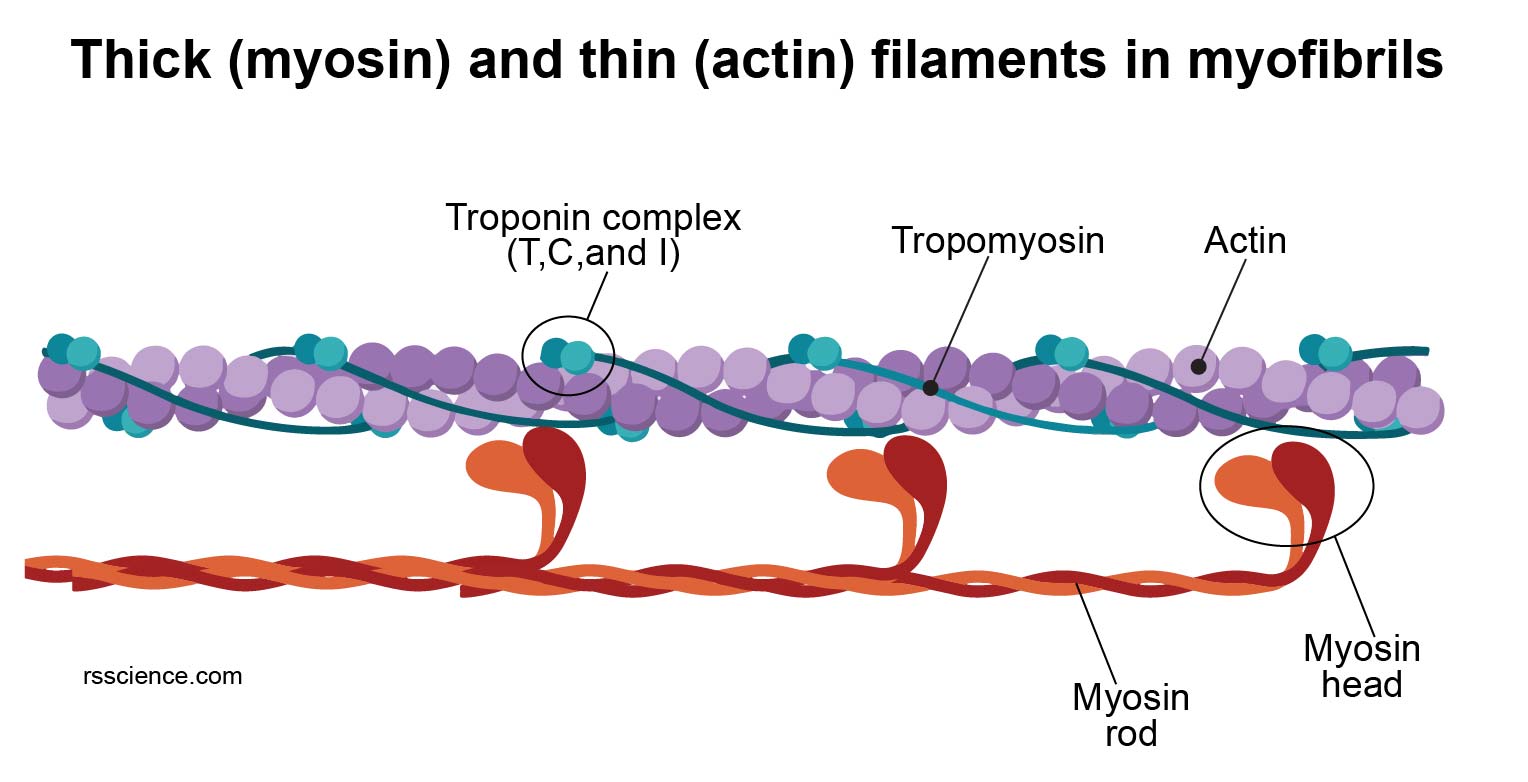
Cytoskeleton The Muscle And The Bone Of A Cell Definition The cross bridge cycle is a fundamental process that underpins muscle contraction, facilitating the interaction between actin and myosin to generate force. this cycle begins when calcium ions, released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, bind to regulatory proteins on the actin filament. this binding induces a conformational change that exposes. Actin filaments, usually in association with myosin, are responsible for many types of cell movements. myosin is the prototype of a molecular motor —a protein that converts chemical energy in the form of atp to mechanical energy, thus generating force and movement. the most striking variety of such movement is muscle contraction, which has.

Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary
Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary

Comments are closed.