Accuracy Vs Precision Explained With Examples

Accuracy Vs Precision Explained With Examples Accuracy assesses whether a series of measurements are correct on average. for example, if a part has an accepted length of 5mm, a series of accurate data will have an average right around 5mm. in statistical terms, accuracy is an absence of bias. in other words, measurements are not systematically too high or too low. Both accuracy and precision are the goal of any measurement. variations in accuracy and precision are largely controllable. in target shooting, you improve accuracy by moving closer to the target, or using an aiming aid like a scope or laser pointer. you improve precision by mounting your gun to a table or bench or shooting indoors out of the wind.

Accuracy Vs Precision Explained With Examples R Leanstartup More examples. while accuracy is “how close to the mark,” precision is “how close measurements are together.”. if you measure once and get the true value, you’re accurate. if you consistently measure the true value over repeated measurements, you are precise. accurate and precise: if a weather thermometer reads 75 o f outside and it. Examples . you can think of the difference between accuracy and precision in terms of a basketball player. if the player always makes a basket, even though she strikes different portions of the rim, she has a high degree of accuracy. if she doesn't make many baskets but always strikes the same portion of the rim, she has a high degree of precision. Accuracy and precision in practice. accuracy and precision are crucial in various fields, including science, engineering, medicine, and manufacturing. let's explore some practical examples to understand their significance: scientific research. in scientific research, accuracy and precision play a vital role in obtaining reliable and valid results. While it is possible for a statement to be both accurate and precise, it is often the case that the statement is one or the other. if i was given the sum 2 2 2 2 and were to provide the answer "between 0 0 and 10 10," my answer would be accurate, and it is certainly correct. however, the statement is not precise as my answer has a range of 10 10.
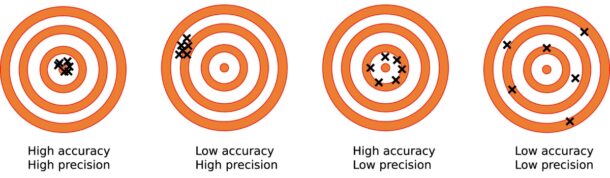
Accuracy Vs Precision In Measurement Explained Eley Metrology Accuracy and precision in practice. accuracy and precision are crucial in various fields, including science, engineering, medicine, and manufacturing. let's explore some practical examples to understand their significance: scientific research. in scientific research, accuracy and precision play a vital role in obtaining reliable and valid results. While it is possible for a statement to be both accurate and precise, it is often the case that the statement is one or the other. if i was given the sum 2 2 2 2 and were to provide the answer "between 0 0 and 10 10," my answer would be accurate, and it is certainly correct. however, the statement is not precise as my answer has a range of 10 10. High accuracy, low precision: the darts spread out in this scenario. their average position is close to the bullseye (true value). the darts do not group consistently. however, the overall result is close to the target. you have good accuracy but poor precision. high precision, low accuracy: the darts are closely grouped, but they are far from. The measure precision at k, for example, is a measure of precision looking only at the top ten (k=10) search results. more sophisticated metrics, such as discounted cumulative gain , take into account each individual ranking, and are more commonly used where this is important.

Precision Vs Accuracy Examples High accuracy, low precision: the darts spread out in this scenario. their average position is close to the bullseye (true value). the darts do not group consistently. however, the overall result is close to the target. you have good accuracy but poor precision. high precision, low accuracy: the darts are closely grouped, but they are far from. The measure precision at k, for example, is a measure of precision looking only at the top ten (k=10) search results. more sophisticated metrics, such as discounted cumulative gain , take into account each individual ranking, and are more commonly used where this is important.

Comments are closed.