A Polynomial Equation And Roots Of Unity Cheenta Academy

A Polynomial Equation And Roots Of Unity Cheenta Academy The given equation means that l a t e x z ( − 3 ± 4 z − 3 2) are also zeroes of l a t e x p . claim one of the two numbers l a t e x | − 3 ± 4 z − 3 2 | is greater than 1. proof suppose that they are both l a t e x ≤ 1. then we have l a t e x 2 ≥ | − 3 4 z − 3 | l a t e x 2 ≥ | − 3 − 4 z − 3 | adding these two. Try this beautiful problem on algebra based on roots of polynomial from amc 10 a, 2019. you may use sequential hints to solve the problem. algebra amc 10a, 2019 problem 24.
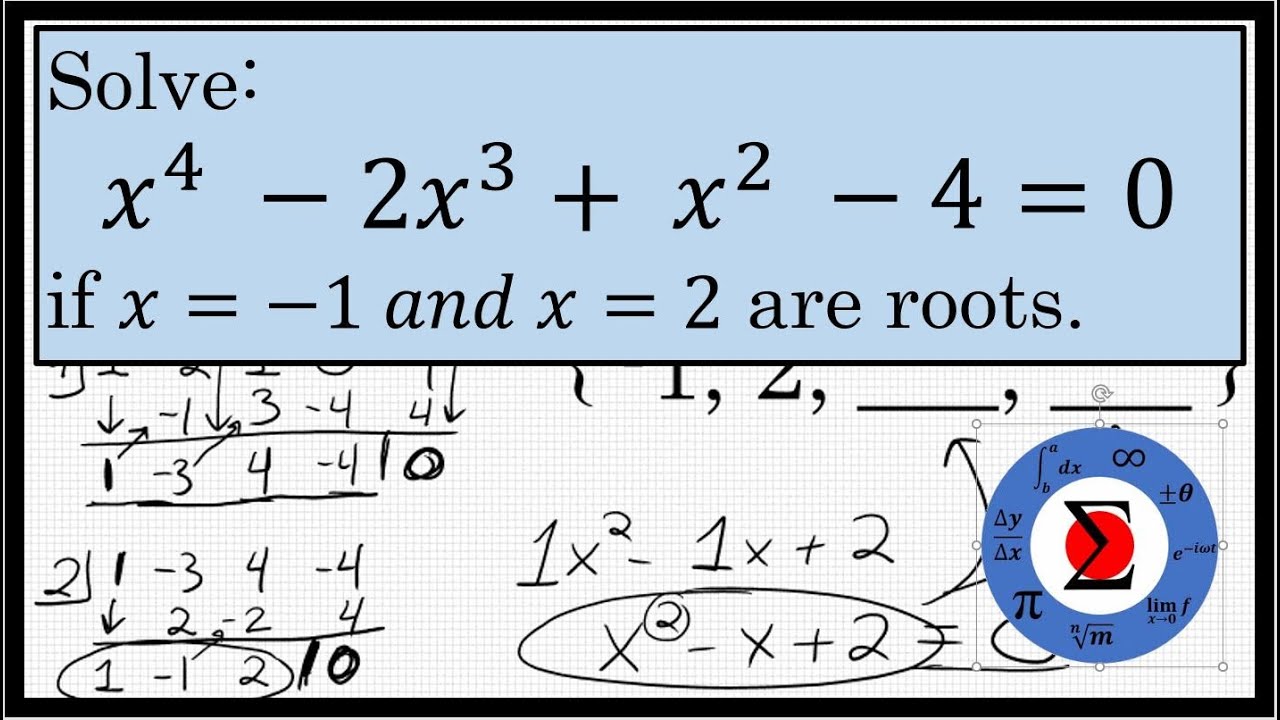
Solving A Polynomial Equation Given Roots Youtube I did it using the theory of equation. sum of roots of the given polynomial x^7 x^2 1 = 0 if option one is true then it must be multiplied to x^2 x 1 as the sum of roots of the polynomial in option one is 1. multiplying x^5 x^4 x^2 x 1 with x^2 x 1 yields us the required polynomial. i was lucky that the first option itself was. For , the sum of the nth roots of unity is 0. more generally, if is a primitive nth root of unity (i.e. for ), then . this is an immediate result of vieta's formulas on the polynomial and newton sums. if is a primitive nth root of unity, then the roots of unity can be expressed as . also, don't overlook the most obvious property of all!. Since x4 and 1 are both perfect squares, you can use the difference of squares formula here as well: x4 – 1 = (x2) 2 – 1 2 = (x2 – 1) (x2 1). this turns the equation x4 – 1 = 0 into. (x2 – 1) (x2 1)=0. the x2 – 1 should look familiar: we factored that when we found the square roots of unity. this gives us. A root of unity is a complex number that, when raised to a positive integer power, results in 1 1. roots of unity have connections to many areas of mathematics, including the geometry of regular polygons, group theory, and number theory. the following problem, although not seemingly related to complex numbers, is a good demonstration of how.

How To Determine Roots Of A Polynomial Since x4 and 1 are both perfect squares, you can use the difference of squares formula here as well: x4 – 1 = (x2) 2 – 1 2 = (x2 – 1) (x2 1). this turns the equation x4 – 1 = 0 into. (x2 – 1) (x2 1)=0. the x2 – 1 should look familiar: we factored that when we found the square roots of unity. this gives us. A root of unity is a complex number that, when raised to a positive integer power, results in 1 1. roots of unity have connections to many areas of mathematics, including the geometry of regular polygons, group theory, and number theory. the following problem, although not seemingly related to complex numbers, is a good demonstration of how. The solution is the polynomial ∏m − 1i = 0 f(τix) where now τ is a primitive m th root of unity. this process might spread out the roots. in the case m = 2 one has (with q repeated application) α2q i and the dandelin–graeffe method for finding the roots of a univariate polynomial. splitting f into its even and odd parts speeds up the. Raising complex numbers to powers is accomplished by raising the modulus to the power and then multiplying the angle. roots of unity. roots or unity refer to roots or zeros of the polynomial . any such root of unity would be a solution to the equation , which is why they are called roots of unity. for instance, the square roots of unity are the.

Cyclotomic Polynomials And Primitive Roots Of Unity Youtube The solution is the polynomial ∏m − 1i = 0 f(τix) where now τ is a primitive m th root of unity. this process might spread out the roots. in the case m = 2 one has (with q repeated application) α2q i and the dandelin–graeffe method for finding the roots of a univariate polynomial. splitting f into its even and odd parts speeds up the. Raising complex numbers to powers is accomplished by raising the modulus to the power and then multiplying the angle. roots of unity. roots or unity refer to roots or zeros of the polynomial . any such root of unity would be a solution to the equation , which is why they are called roots of unity. for instance, the square roots of unity are the.

Let O 1 Be A Seventh Root Of Unity Write Down A Polynomial Equation Of

Algebra 2 5 5 Theorems About Roots Of Polynomial Equations Youtube

Comments are closed.