A Draw A Graph For A Monopoly With Demand Marginal Revenue And

Draw The Graph For A Monopoly With Demand Marginal Revenue And Equation 10.1. q = 10 −p q = 10 − p. this demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in figure 10.4 “demand, elasticity, and total revenue”. total revenue for each quantity equals the quantity times the price at which that quantity is demanded. the monopoly firm’s total revenue curve is given in panel (b). Short answer. step by step solution. chapter 9: q32. (page 233) draw the demand curve, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves from figure 9.6, and identify the quantity of output the monopoly wishes to supply and the price it will charge. suppose the demand for the monopoly’s product increases dramatically.

A Draw A Graph For A Monopoly With Demand Marginal Revenue And Economics questions and answers. draw the graph for a monopoly with demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves. identify the profit maximizing output level (qm) and price (pm). suppose the monopolist sells qm units of output at the regular price and then puts the product on sale at a lower price, ps. show the new price and quantity. Because of the lower price on all units sold, the marginal revenue of selling a unit is less than the price of that unit—and the marginal revenue curve is below the demand curve. tip: for a straight line demand curve, the marginal revenue curve equals price at the lowest level of output. (graphically, mr and demand have the same vertical axis.). Once we have determined the monopoly firm’s price and output, we can determine its economic profit by adding the firm’s average total cost curve to the graph showing demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost, as shown in figure 10.7. the average total cost (atc) at an output of qm units is atcm. Assume that a monopolist has a demand curve with the price elasticity of demand equal to negative two: ed = − 2. when this is substituted into equation 3.3.3, the result is: p– mc p = 0.5. multiply both sides of this equation by price (p): (p– mc) = 0.5p, or 0.5p = mc, which yields: p = 2mc.
Solved Draw A Monopolist S Demand Curve Marginal Revenue And Once we have determined the monopoly firm’s price and output, we can determine its economic profit by adding the firm’s average total cost curve to the graph showing demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost, as shown in figure 10.7. the average total cost (atc) at an output of qm units is atcm. Assume that a monopolist has a demand curve with the price elasticity of demand equal to negative two: ed = − 2. when this is substituted into equation 3.3.3, the result is: p– mc p = 0.5. multiply both sides of this equation by price (p): (p– mc) = 0.5p, or 0.5p = mc, which yields: p = 2mc. The firm can use the points on the demand curve d to calculate total revenue, and then, based on total revenue, calculate its marginal revenue curve. the profit maximizing quantity will occur where mr = mc—or at the last possible point before marginal costs start exceeding marginal revenue. on figure 9.6, mr = mc occurs at an output of 5. Draw the demand curve, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves from figure 4, and identify the quantity of output the monopoly wishes to supply and the price it will charge. suppose demand for the monopoly’s product increases dramatically. draw the new demand curve. what happens to the marginal revenue as a result of the increase in demand?.
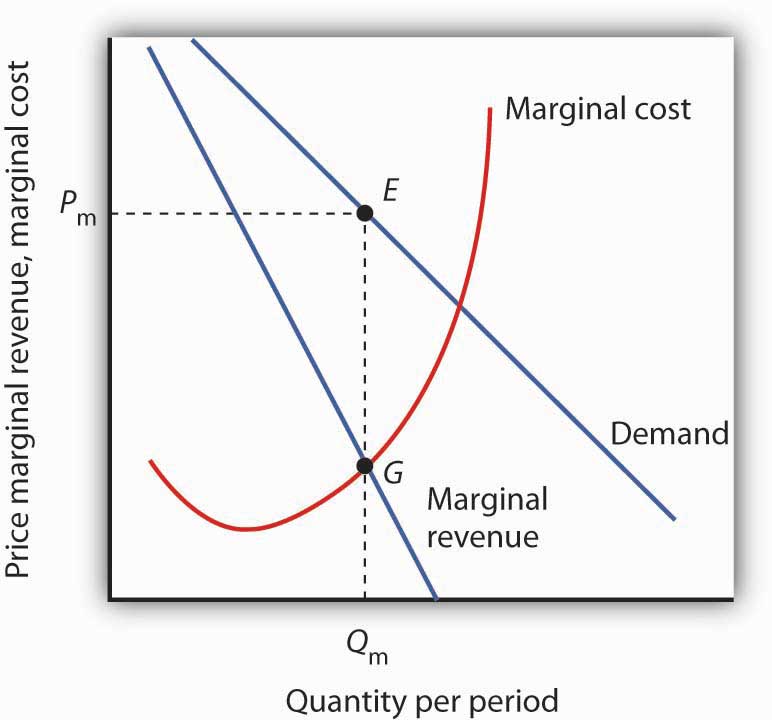
10 2 The Monopoly Model Principles Of Economics The firm can use the points on the demand curve d to calculate total revenue, and then, based on total revenue, calculate its marginal revenue curve. the profit maximizing quantity will occur where mr = mc—or at the last possible point before marginal costs start exceeding marginal revenue. on figure 9.6, mr = mc occurs at an output of 5. Draw the demand curve, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves from figure 4, and identify the quantity of output the monopoly wishes to supply and the price it will charge. suppose demand for the monopoly’s product increases dramatically. draw the new demand curve. what happens to the marginal revenue as a result of the increase in demand?.

Draw A Graph For A Monopoly With Demand Marginal Revenue And Marginal
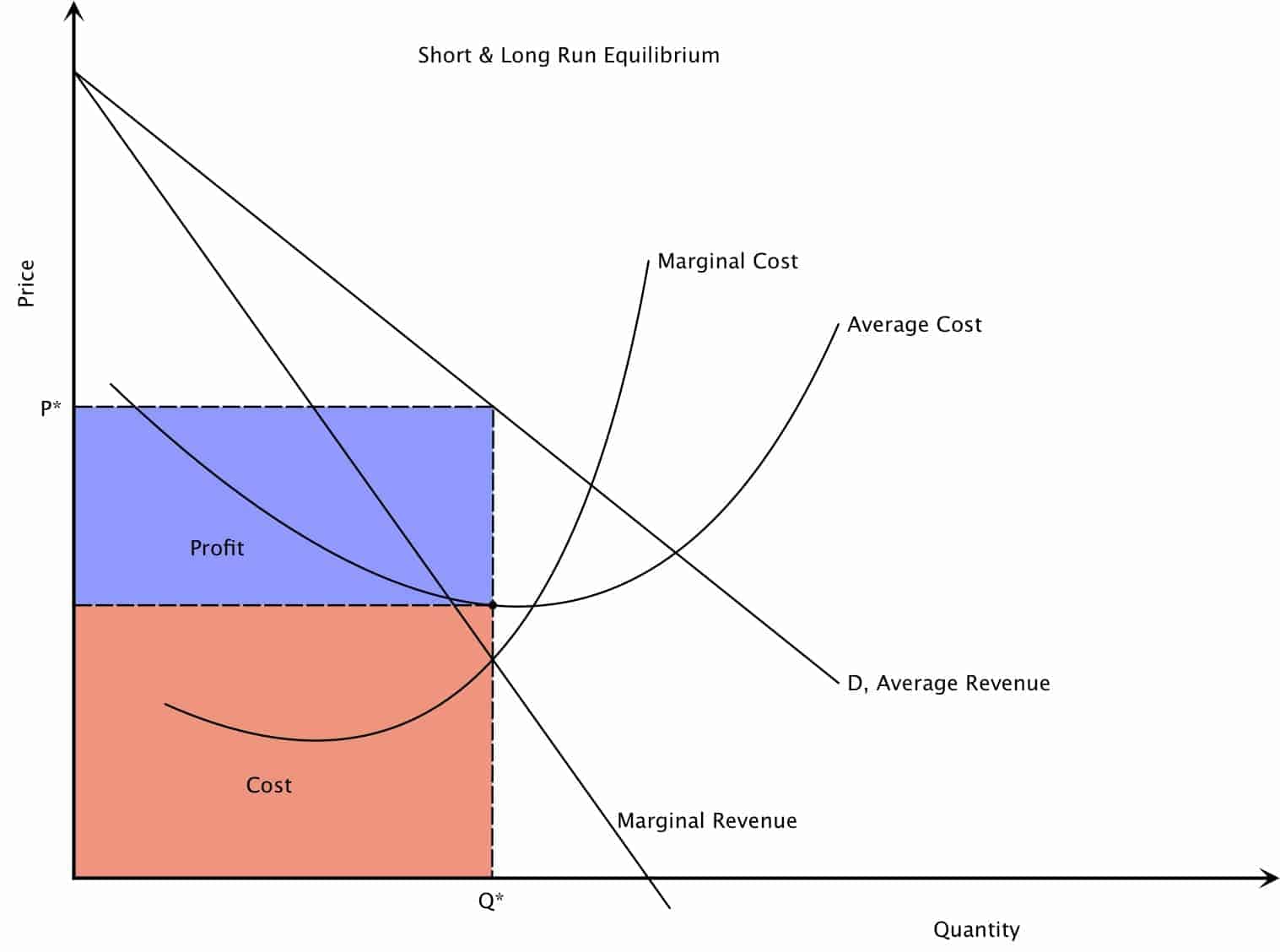
Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist

Comments are closed.