A Consumer Chooses An Optimal Consumption Point Where The

A Consumer Chooses An Optimal Consumption Point Where The Brainly Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a consumer chooses an optimal consumption point where the select one: a. marginal rate of substitution exceeds the relative price ratio. b. slope of the indifference curve equals the slope of the budget constraint. c. ratio of the prices equals one. d. all of the above are correct., a consumer likes two goods: books and movies. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a consumer chooses an optimal consumption point where the a. slope of the indifference curve equals the slope of the budget constraint. b. marginal rate of substitution exceeds the relative price ratio. c. ratio of the prices equals one. d. all other answers are correct., the consumer's optimum is where a. mux muy = py px b. no.

Answered A Consumer Chooses An Optimal Bartleby A consumer chooses an optimal consumption point where the ratios of all the marginal utilities are equal. marginal rate of substitution equals the relative price ratio. all of the above are correct. slope of the indifference curve exceeds the slope of the budget constraint. figure 21 18 refer to figure 21 18. The theory of consumer choice assumes consumers wish to maximise their utility through the optimal combination of goods given their limited budget. to illustrate how consumers choose between different combinations of goods we can use equi marginal principle and indifference curves and budget lines. consumer equilibrium equimarginal. The slope of the budget constraint line is rise run or –8 4=–2. the specific choices along the budget constraint line show the combinations of affordable t shirts and movies. figure 6.2 a choice between consumption goods josé has income of $56. movies cost $7 and t shirts cost $14. the points on the budget constraint line show the. The second part of the consumer choice problem, the budget constraint, as we are on the budget line or the “subject to” part, is straightforward: p aa p bb = i p a a p b b = i (4.7) at this point, solving the problem is a matter of simple algebra. we have two equations with two unknowns, good a a and good b b.
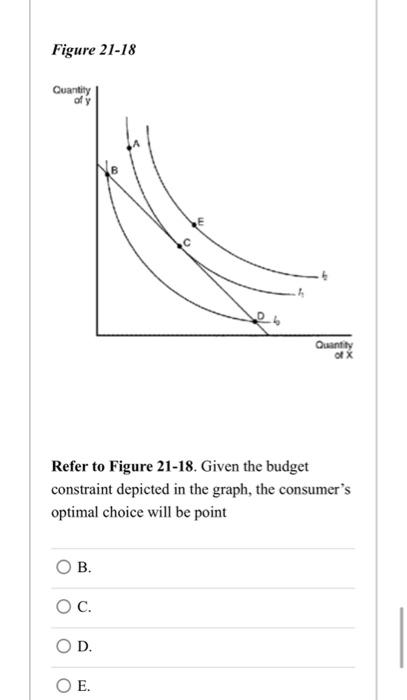
Solved A Consumer Chooses An Optimal Consumption Point Where Chegg The slope of the budget constraint line is rise run or –8 4=–2. the specific choices along the budget constraint line show the combinations of affordable t shirts and movies. figure 6.2 a choice between consumption goods josé has income of $56. movies cost $7 and t shirts cost $14. the points on the budget constraint line show the. The second part of the consumer choice problem, the budget constraint, as we are on the budget line or the “subject to” part, is straightforward: p aa p bb = i p a a p b b = i (4.7) at this point, solving the problem is a matter of simple algebra. we have two equations with two unknowns, good a a and good b b. Economics. economics questions and answers. question 6 a consumer chooses an optimal consumption point where the a. marginal rate of substitution equals the relative price ratio. o b. slope of the indifference curve exceeds the slope of the budget constraint o c. ratios of all the marginal utilities are equal o d. all of the above are correct. 7.6 the consumer's optimal choice. as before, this “gravitational pull” holds in every possible case. in some cases, the optimum will be characterized by the tangency condition mrs = p 1 p 2 m rs = p1 p2. let’s think about what this means intiuitively, mathematically, and visually. intuitively, when this is the case, the “bang for the.

Solved A Consumer Chooses An Optimal Consumption Point Where Chegg Economics. economics questions and answers. question 6 a consumer chooses an optimal consumption point where the a. marginal rate of substitution equals the relative price ratio. o b. slope of the indifference curve exceeds the slope of the budget constraint o c. ratios of all the marginal utilities are equal o d. all of the above are correct. 7.6 the consumer's optimal choice. as before, this “gravitational pull” holds in every possible case. in some cases, the optimum will be characterized by the tangency condition mrs = p 1 p 2 m rs = p1 p2. let’s think about what this means intiuitively, mathematically, and visually. intuitively, when this is the case, the “bang for the.

Comments are closed.