A Brief About Non Invasive Prenatal Testing
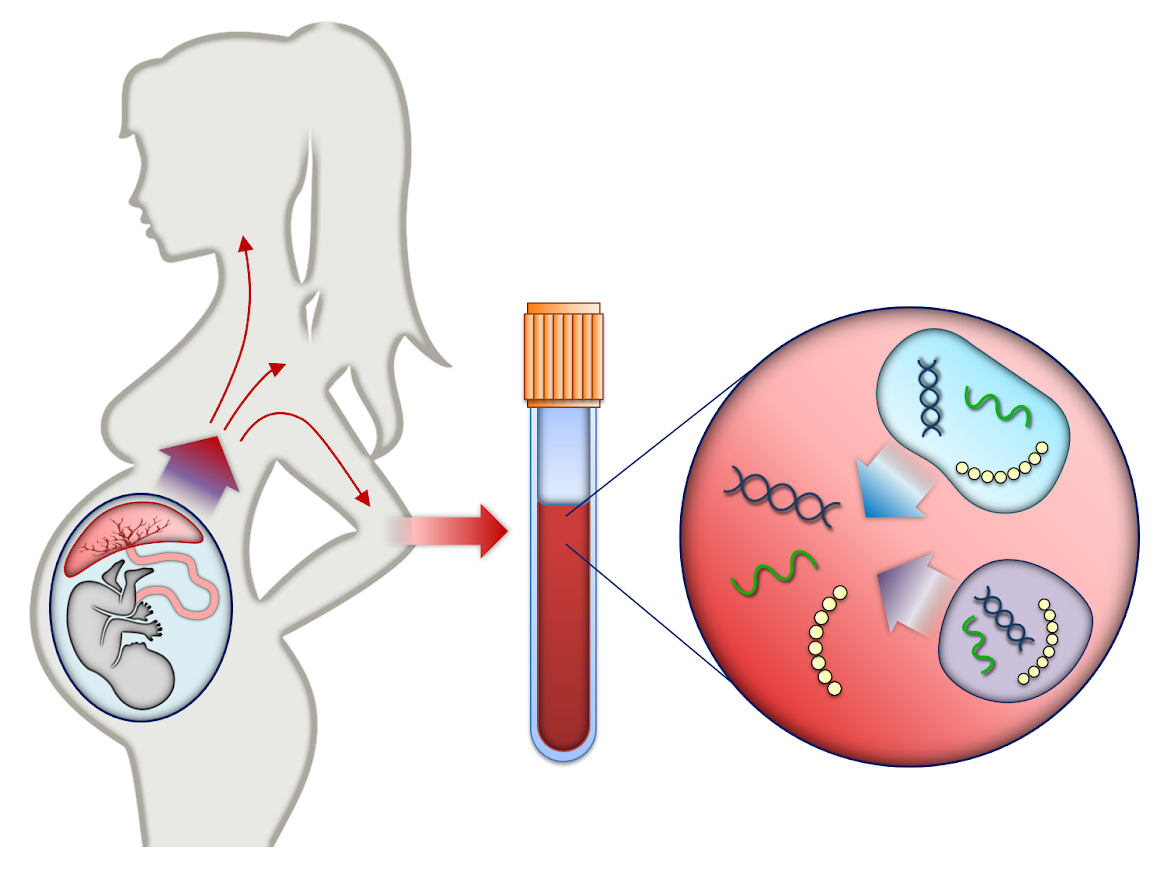
Non Invasive Prenatal Testing Nipt Pregnancy Birth And Baby Nipt tests (noninvasive prenatal testing test) use a pregnant person’s blood to detect congenital abnormalities in the fetus’s dna. the dna is examined for genetic conditions, such as down syndrome. nipt tests don’t diagnose conditions. they tell your provider how likely it is that a condition exists. this test can be done beginning at 10. Non invasive prenatal testing for aneuploidy and beyond: challenges of responsible innovation in prenatal screening. summary and recommendations. eur j hum genet. 2015 apr 1. doi: 10.1038 ejhg.2015.56. [epub ahead of print] pubmed: 25828867. goldwaser t, klugman s. cell free dna for the detection of fetal aneuploidy.
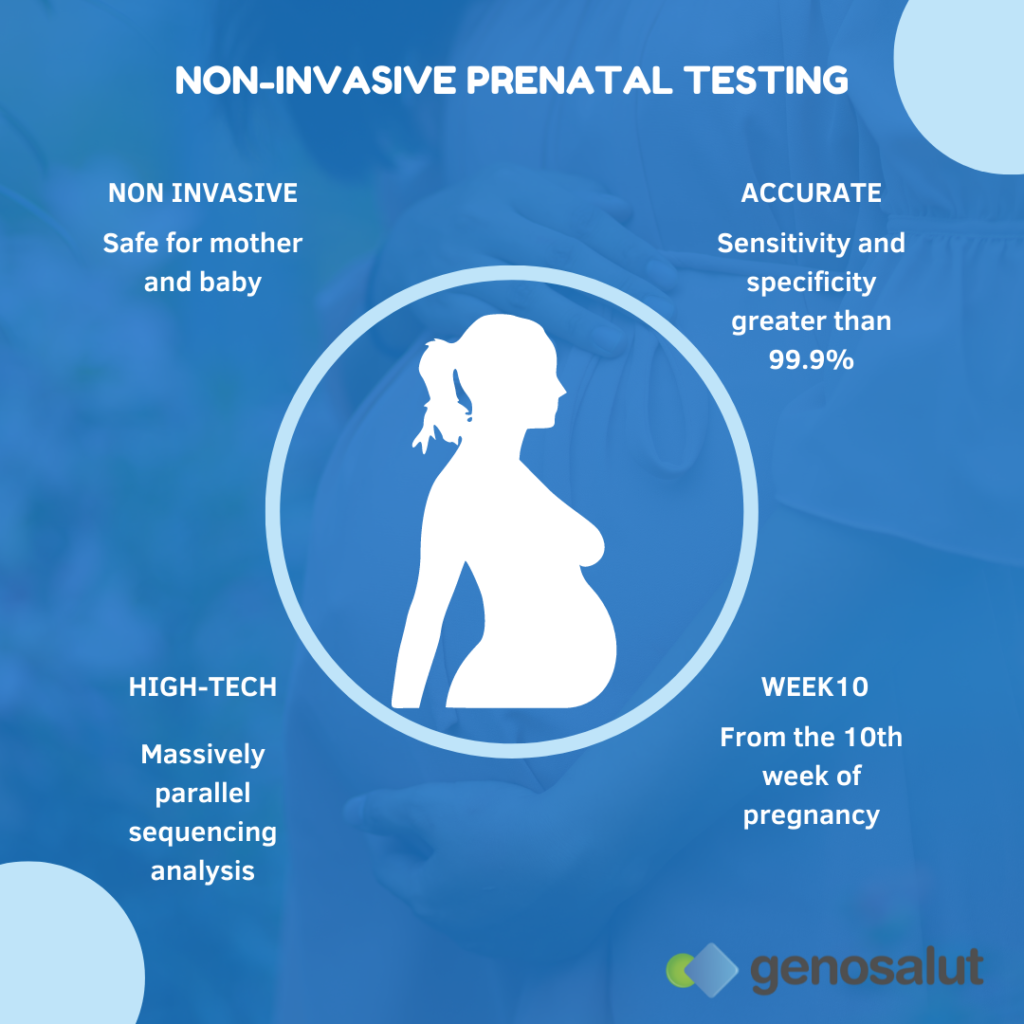
Non Invasive Prenatal Testing In Mallorca Genosalut Confined placental mosaicism occurred in 23.4% of cases without ultrasound anomalies giving a positive predictive value (ppv) of 53% in these cases. ppv was 98.9% in cases with ultrasound anomalies. whenever there is a positive nipt for scas without ultrasound features, testing through amniocentesis is recommended and this should be bear in. Amniotic fluid tests and chorionic villus sampling have a miscarriage rate of approximately 0.1–0.3% and 0.5%, respectively. noninvasive methods, such as ultrasonography and maternal serum marker screening, can also predict chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, but invasive tests are required for definitive diagnoses. Since its introduction in 2011, noninvasive prenatal testing (nipt) has spread rapidly around the world. it carries numerous benefits but also raises challenges, often related to sociocultural, legal, and economic contexts. this article describes the implementation of nipt in nine countries, each with its own unique characteristics: australia, canada, china and hong kong, india, israel. Abstract. non invasive prenatal testing was first discovered in 1988; it was primarily thought to be able to detect common aneuploidies, such as patau syndrome (t13), edward syndrome (t18), and down syndrome (t21). it comprises a simple technique involving the analysis of cell free foetal dna (cffdna) obtained through maternal serum, using.

A Brief About Non Invasive Prenatal Testing Since its introduction in 2011, noninvasive prenatal testing (nipt) has spread rapidly around the world. it carries numerous benefits but also raises challenges, often related to sociocultural, legal, and economic contexts. this article describes the implementation of nipt in nine countries, each with its own unique characteristics: australia, canada, china and hong kong, india, israel. Abstract. non invasive prenatal testing was first discovered in 1988; it was primarily thought to be able to detect common aneuploidies, such as patau syndrome (t13), edward syndrome (t18), and down syndrome (t21). it comprises a simple technique involving the analysis of cell free foetal dna (cffdna) obtained through maternal serum, using. Non invasive prenatal testing (nipt), also known as cell free dna testing, is a blood test done during pregnancy that screens for genetic abnormalities in the fetus. nipt aims to screen and diagnose any chromosomal disorders before the baby is born in order to give the parents a better idea of what their pregnancy will look like. Nipt, also known as cell free fetal dna (cffdna) testing or non invasive prenatal screening (nips), was introduced to the market in 2011. it is performed using a blood test from the expectant mother with a subsequent analysis of fetal dna fragments, which are placental in origin, found in the maternal bloodstream.
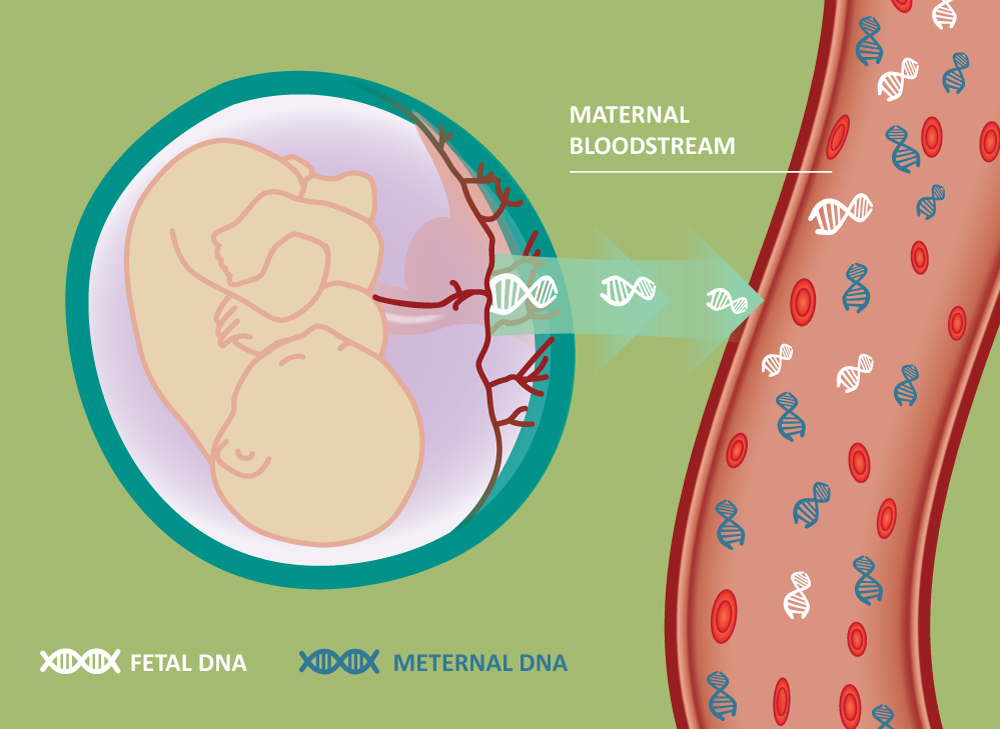
Harmony Non Invasive Prenatal Test Clinical Labs Non invasive prenatal testing (nipt), also known as cell free dna testing, is a blood test done during pregnancy that screens for genetic abnormalities in the fetus. nipt aims to screen and diagnose any chromosomal disorders before the baby is born in order to give the parents a better idea of what their pregnancy will look like. Nipt, also known as cell free fetal dna (cffdna) testing or non invasive prenatal screening (nips), was introduced to the market in 2011. it is performed using a blood test from the expectant mother with a subsequent analysis of fetal dna fragments, which are placental in origin, found in the maternal bloodstream.

Comments are closed.