9s06 Tissues Plant Animal Tissues Types Introduction

9s06 Tissues Plant Animal Tissues Types Introduction Download the avanti gurukul app from the google store now and get all the videos by india's top teachers on your phone. click here to download: play . So, in simple terms, tissues can be defined as a group of cells performing similar functions. tissues represent a level of organization in living organisms. both plants and animals have tissues. but the kinds of tissues that are present in both the living organisms are different. if you see in animals, groups of muscle cells together form the.

Introduction To Tissues Animal Tissue Plant Tissue Videos And Examples Plant tissue definition. plant tissue is a collection of similar cells performing an organized function for the plant. each plant tissue is specialized for a unique purpose, and can be combined with other tissues to create organs such as leaves, flowers, stems and roots. the following is a brief outline of plant tissues, and their functions. This document discusses plant and animal tissues. it defines what a tissue is and explains that tissues are made of groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function. the document outlines the main types of tissues in plants and animals. in plants, the main tissues are meristematic tissue, permanent tissue and vascular tissue. Plant and animal tissue ppt. this document summarizes the four main types of tissues in the body: epithelial, muscular, nervous, and connective tissue. it describes the characteristics and functions of each tissue type. epithelial tissue forms the outer layers of the body and its subtypes include squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and stratified. Plants have simple and complex tissues. the simple tissues (tissues with uniform cells) are composed of the same type of cells; complex tissues (tissues with more than one type of cells) are composed of more than one type of cell, these are unique to plants. figure 7.14. parenchyma (figure 5.1.4 5.1.

Tissues In Plants And Animals Plant and animal tissue ppt. this document summarizes the four main types of tissues in the body: epithelial, muscular, nervous, and connective tissue. it describes the characteristics and functions of each tissue type. epithelial tissue forms the outer layers of the body and its subtypes include squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and stratified. Plants have simple and complex tissues. the simple tissues (tissues with uniform cells) are composed of the same type of cells; complex tissues (tissues with more than one type of cells) are composed of more than one type of cell, these are unique to plants. figure 7.14. parenchyma (figure 5.1.4 5.1. Plant tissue is different from those of animals. plant tissues are basically divided into two: meristematic tissue and permanent tissue. meristematic tissue. these tissues contain cells which have the dividing capacity. they are immature and help plants to divide continuously throughout life. The animal cells are grouped together to form animal tissues. these tissues vary in their structure, function, and origin. the animal tissues are divided into epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissues. let us have a glimpse of each type of animal tissue in detail. table of contents. epithelial tissue. connective tissue. muscle tissue.
Tissues And Types Of Plant Tissues Plant tissue is different from those of animals. plant tissues are basically divided into two: meristematic tissue and permanent tissue. meristematic tissue. these tissues contain cells which have the dividing capacity. they are immature and help plants to divide continuously throughout life. The animal cells are grouped together to form animal tissues. these tissues vary in their structure, function, and origin. the animal tissues are divided into epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissues. let us have a glimpse of each type of animal tissue in detail. table of contents. epithelial tissue. connective tissue. muscle tissue.

Plant And Animal Tissues Plant Tissues Animal Tissues Edu Resource
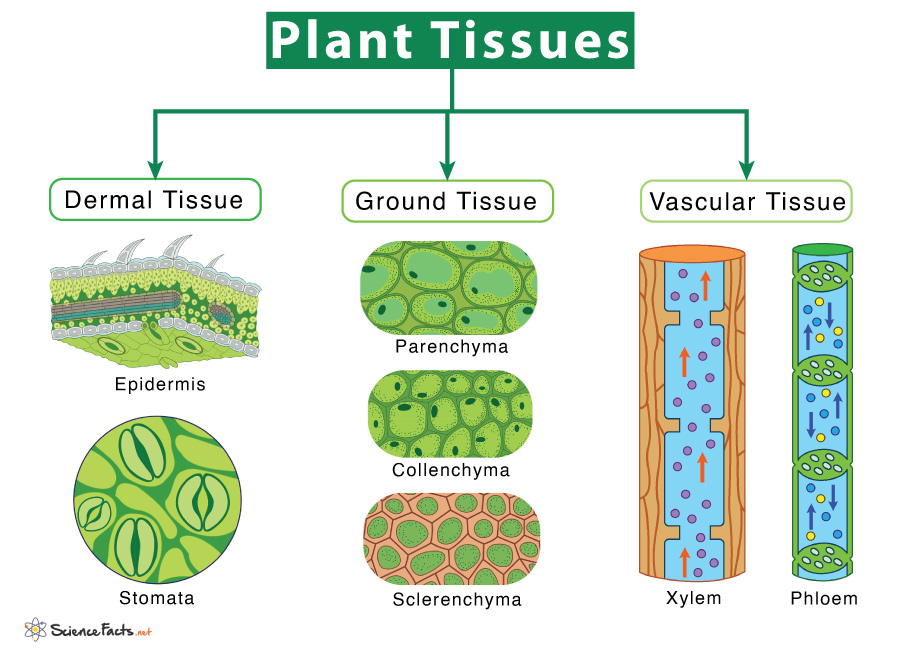
Plant Tissues Types Functions

Comments are closed.