6 Du Sol Sem 3 How A Monopoly Firm Earn Supernormal In Long Run

6 Du Sol Sem 3 How A Monopoly Firm Earn Supernormal In Long Run #6 du sol,sem 3, how a monopoly firm earn supernormal in long run | principle of microeconomics ii |. #3 how a monopoly firm earn abnormal or supernormal profit | principle of microeconomics ii | du sol.
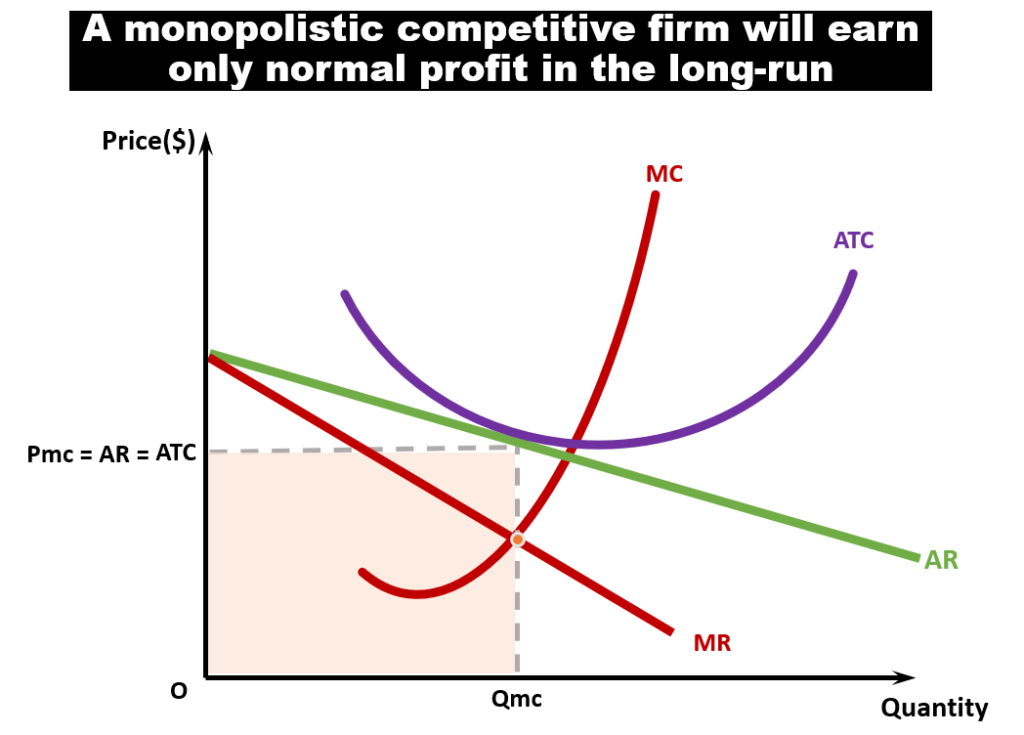
Monopolistic Competition Economics Tuition Sg Other firms will be aware of this fact. because there are no barriers to entry, firms will be encouraged to enter the market until price falls back down to p1 and normal profits are made. perfect competition in the long run. this is why only normal profits will be made in the long run. at q1 – ar=atc. supernormal profit in monopoly. Long run average costs in monopoly. it is assumed monopolies have a degree of economies of scale, which enables them to benefit from lower long run average costs. in a competitive market, firms may produce quantity q2 and have average costs of ac2. a monopoly can produce more and have lower average costs. this enables efficiency of scale. Demand curve d 3. if the demand curve lies further to the right of d 2 (like d 3), the monopolist can earn super normal profits. the equilibrium position is the point of intersection between the mc curve and the mr 3 curve at point a 3. therefore, the monopolist produces a quantity om 3 and sells it at a price e 3 m 3. a firm’s long run. D) firms earn normal profits, and demand is tangent to average total cost. answer: d) firms earn normal profits, and demand is tangent to average total cost. explanation: option a: in the long run, supernormal profits in monopolistic competition attract new firms, increasing competition until profits are eliminated. thus, firms do not earn.

With The Help Of A Diagram Explain How A Firm With Monopoly Power Can Demand curve d 3. if the demand curve lies further to the right of d 2 (like d 3), the monopolist can earn super normal profits. the equilibrium position is the point of intersection between the mc curve and the mr 3 curve at point a 3. therefore, the monopolist produces a quantity om 3 and sells it at a price e 3 m 3. a firm’s long run. D) firms earn normal profits, and demand is tangent to average total cost. answer: d) firms earn normal profits, and demand is tangent to average total cost. explanation: option a: in the long run, supernormal profits in monopolistic competition attract new firms, increasing competition until profits are eliminated. thus, firms do not earn. A diagram illustrating a monopoly making supernormal profit in the short run & long run as the ar > ac at the profit maximisation level of output (q 1) diagram analysis. the firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output where mc = mr (q 1) at this level the ar (p 1) > ac (c 1) the firm is making abnormal profit. A monopoly can increase output to q1 and benefit from lower long run average costs (ac1). in industries with high fixed costs, it can be more efficient to have a monopoly than several small firms. 2. research and development. the supernormal profit can enable more investment in research and development, leading to better products. 3. good.

Comments are closed.