6 1 Plant Cells And Tissues The Science Of Plants
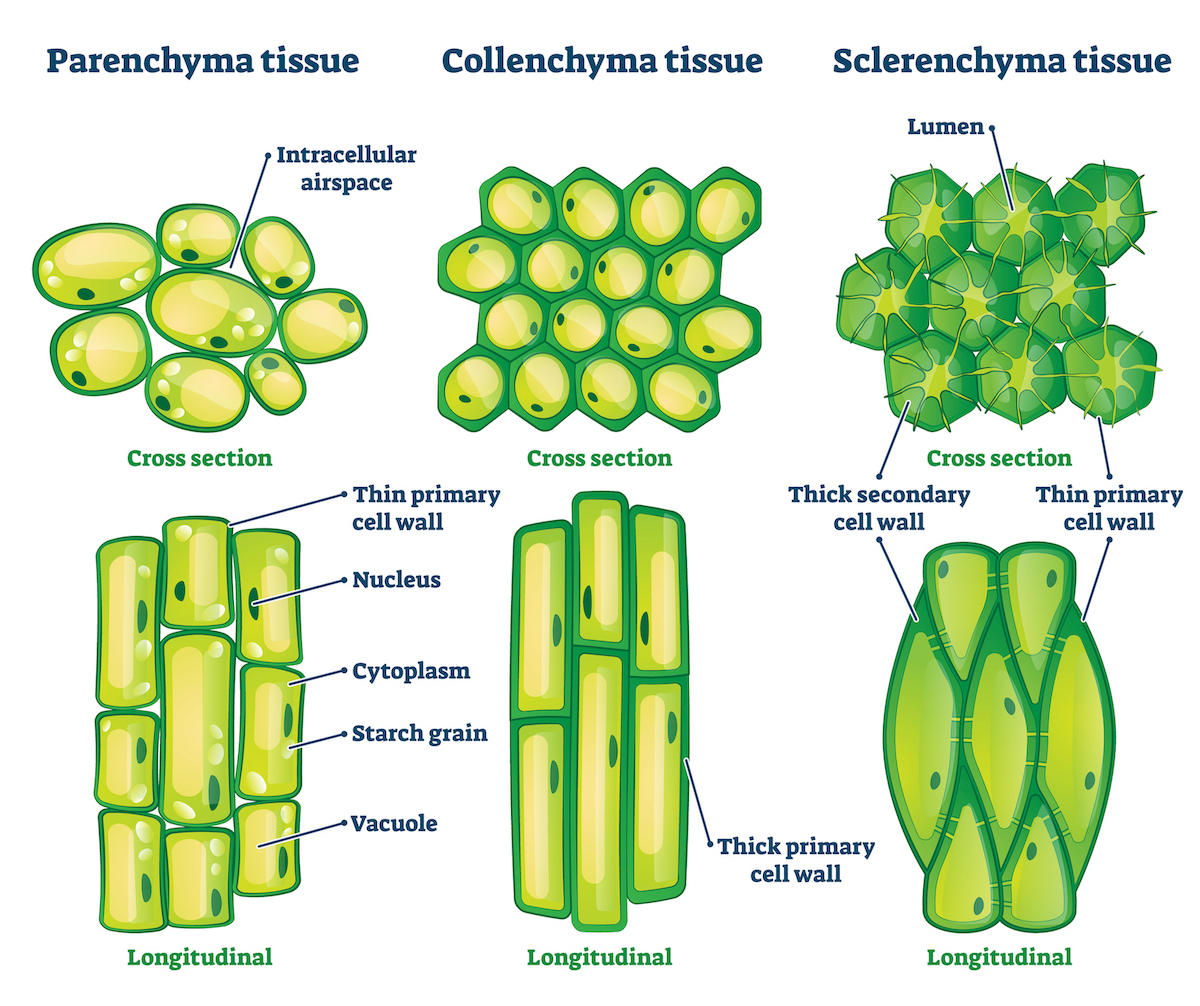
6 1 Plant Cells And Tissues The Science Of Plants 6.1 plant cells and tissues. learning objectives. by the end of this lesson you will be able to: label the parts of a plant cell. list the types of tissues in a plant and describe where they are located and the specialized cells that make up each of these tissues. summarize the key functions of those tissues. Vascular tissues form the plumbing system in the plant through which water, nutrients, sugars, and other compounds flow. these plumbing pipes and associated cells are bundled together in the plant in a structure called the vascular bundle. there are three main types of vascular tissue: xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium.
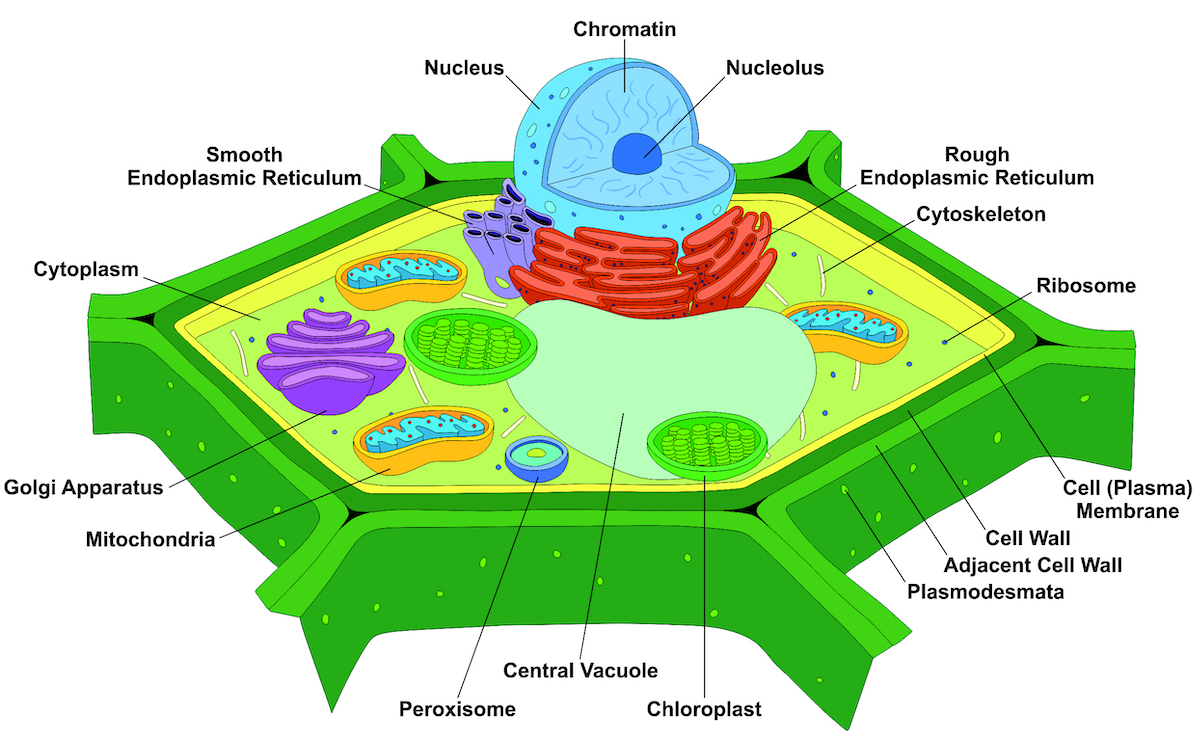
6 1 Plant Cells And Tissues The Science Of Plants Understand how cells build the plant and their origins in meristematic tissue. cells are the building blocks of the plant. even the mightiest oak begins as a single, microscopic cell produced by fertilization. that single cell replicates, differentiates, and develops into the complex tissues, organs, and systems of the plant. Distinguishing characteristics of a plant cell are its cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuole. a plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. however, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from. The root system, which supports the plants and absorbs water and minerals, is usually underground. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1 shows the organ systems of a typical plant. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1: the shoot system of a plant consists of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. the root system anchors the plant while absorbing water and minerals from the soil. Chapter 6: cells, tissues, and woody growth. cells are the building blocks of the plant. even the mightiest oak begins as a single, microscopic cell produced by fertilization. that single cell replicates, differentiates, and develops into the complex tissues, organs, and systems of the plant. in this chapter we’ll will learn about the.

Typical Plant Cell Structure The root system, which supports the plants and absorbs water and minerals, is usually underground. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1 shows the organ systems of a typical plant. figure 30.1.1 30.1. 1: the shoot system of a plant consists of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. the root system anchors the plant while absorbing water and minerals from the soil. Chapter 6: cells, tissues, and woody growth. cells are the building blocks of the plant. even the mightiest oak begins as a single, microscopic cell produced by fertilization. that single cell replicates, differentiates, and develops into the complex tissues, organs, and systems of the plant. in this chapter we’ll will learn about the. About the book. an approachable guide to the fundamentals of plant science. created for horticulture students, gardeners, science teachers, and anyone interested in understanding plants and how they grow. this is the required text for hort 1001 6001 plant propagation at the university of minnesota department of horticultural science. Membrane. the plant cell wall stretches slightly, but it resists the entry of excess water and prevents the cell from bursting. when a cell wall is slightly stretched it cell is firm or turgid. turgid cells give tissues strength. if a plant loses water the cells lose their turgidity and the plant wilts. organelles.

6 1 Plant Cells And Tissues The Science Of Plants About the book. an approachable guide to the fundamentals of plant science. created for horticulture students, gardeners, science teachers, and anyone interested in understanding plants and how they grow. this is the required text for hort 1001 6001 plant propagation at the university of minnesota department of horticultural science. Membrane. the plant cell wall stretches slightly, but it resists the entry of excess water and prevents the cell from bursting. when a cell wall is slightly stretched it cell is firm or turgid. turgid cells give tissues strength. if a plant loses water the cells lose their turgidity and the plant wilts. organelles.
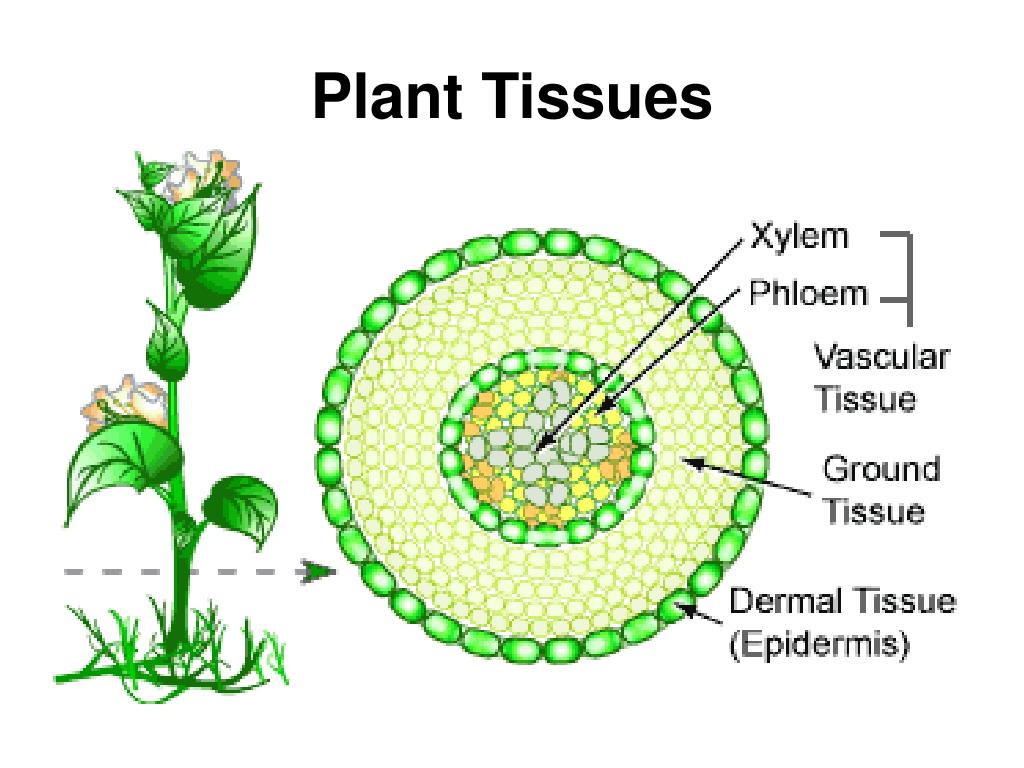
Ppt Plant Tissues Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3036671
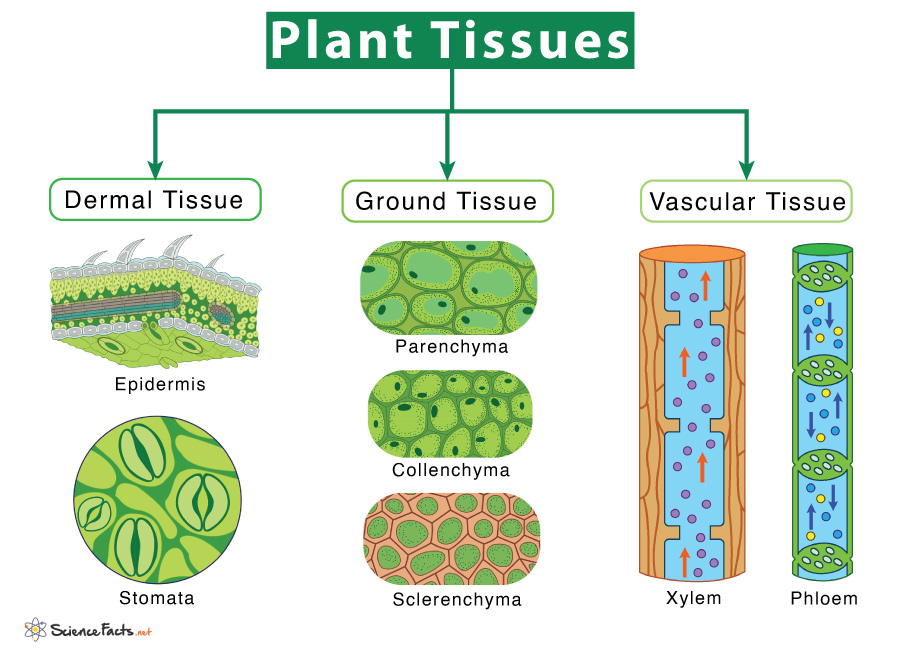
Compare The Different Types Of Plant Cells And Tissues At Jason Clark Blog

Comments are closed.