4 2 Graphs Of Quadratics In Vertex And Intercept Forms Youtube

4 2 Graphs Of Quadratics In Vertex And Intercept Forms Youtube Ms. & mrs. roshan's algebra 2 class videos based on mcdougal littell's algebra 2. Learn how to graph quadratic functions in the standard form, vertex form, and intercept form in this video math tutorial by mario's math tutoring. we go thr.
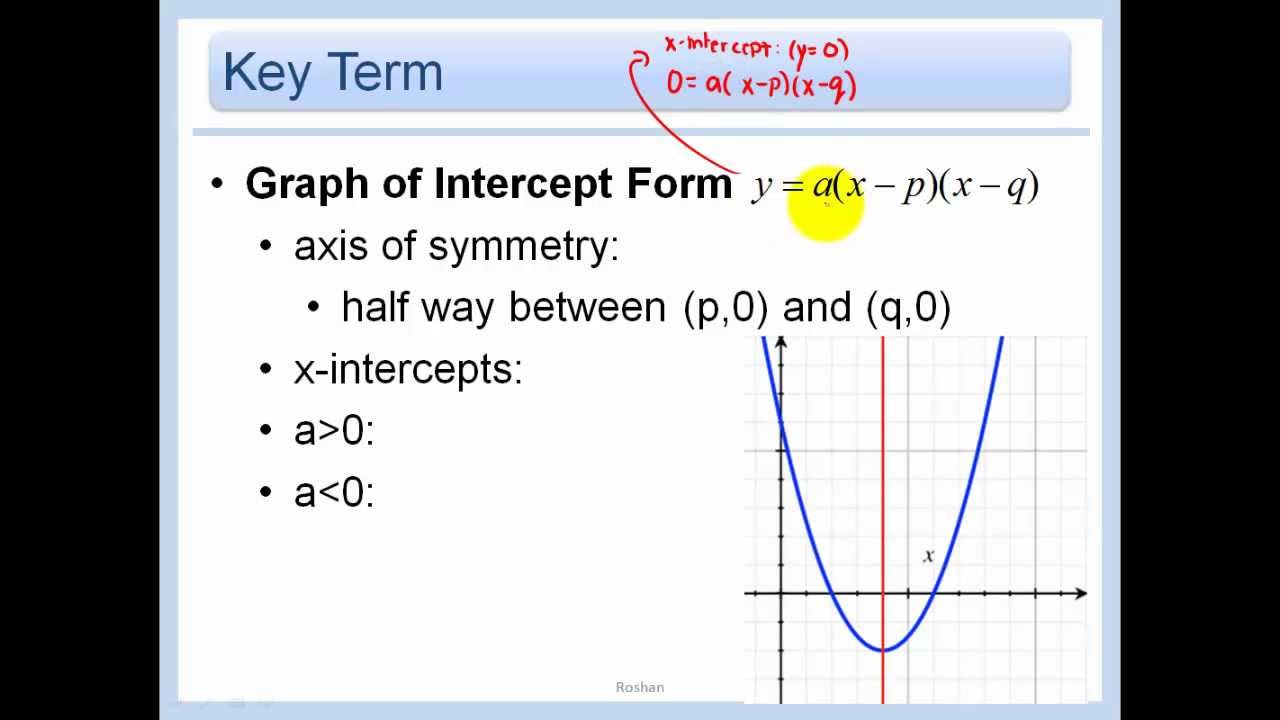
4 2 Graph Quadratic Functions In Vertex Or Intercept Form Youtube In this video, we delve into the fascinating world of quadratic equations by exploring the transformation from intercept form to vertex form and standard for. The quadratic function of the graph below written in vertex form is y= −3(x 2)2 4 y = − 3 (x 2) 2 4. in this form, a =−3, h= −2 a = − 3, h = − 2, and k= 4 k = 4. since a <0 a <0, the parabola opens downward. the vertex is at (−2, 4) (− 2, 4). figure 9 −3(x 2)2 4 − 3 (x 2) 2 4. A general note: forms of quadratic functions. a quadratic function is a function of degree two. the graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. the general form of a quadratic function is f\left (x\right)=a {x}^ {2} bx c f (x) = ax2 bx c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a\ne 0 a = 0. In this section we will be graphing quadratic functions that are written in intercept form. when quadratic functions are written in this form, it is easy to identify the [latex] x [ latex] intercepts. in order to graph the parabola, we will also need to determine the vertex, [latex] y [ latex] intercept, and the axis of symmetry.

Algebra 2 Lesson 4 2 Graph Quadratic Functions In Vertex And Intercept A general note: forms of quadratic functions. a quadratic function is a function of degree two. the graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. the general form of a quadratic function is f\left (x\right)=a {x}^ {2} bx c f (x) = ax2 bx c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a\ne 0 a = 0. In this section we will be graphing quadratic functions that are written in intercept form. when quadratic functions are written in this form, it is easy to identify the [latex] x [ latex] intercepts. in order to graph the parabola, we will also need to determine the vertex, [latex] y [ latex] intercept, and the axis of symmetry. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. the general form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax2 bx c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. the vertex (h, k) of the parabola is located at h = − b 2a, k = f(− b 2a). we learned in section 3.3, the vertex form of a quadratic function is f(x) = a(x − h)2 k. A) y = x2 − 8x 15. y = x2 − 8x 15. write the quadratic function in intercept form by factoring the right hand side of the equation. remember, to factor we need two numbers whose product is 15 and whose sum is –8. these numbers are –5 and –3. the function in intercept form is y = (x − 5)(x − 3).

Algebra Ii 4 2 Graph Quadratic Functions In Vertex Or Intercept Form The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. the general form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax2 bx c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. the vertex (h, k) of the parabola is located at h = − b 2a, k = f(− b 2a). we learned in section 3.3, the vertex form of a quadratic function is f(x) = a(x − h)2 k. A) y = x2 − 8x 15. y = x2 − 8x 15. write the quadratic function in intercept form by factoring the right hand side of the equation. remember, to factor we need two numbers whose product is 15 and whose sum is –8. these numbers are –5 and –3. the function in intercept form is y = (x − 5)(x − 3).

Comments are closed.