3 Operators In Java Arithmetic Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Modules

3 Operators In Java Arithmetic Addition Subtraction Let’s look at the various operators that java has to provide under the arithmetic operators. now let’s look at each one of the arithmetic operators in java: 1. addition ( ): this operator is a binary operator and is used to add two operands. syntax: num1 num2. example: num1 = 10, num2 = 20. sum = num1 num2 = 30. This java program asks the user to provide integer inputs to perform mathematical operations. scanner class and its functions are used to obtain inputs, and println() function is used to print on the screen. scanner class is a part of java.util package, so we required to import this package in our java program.
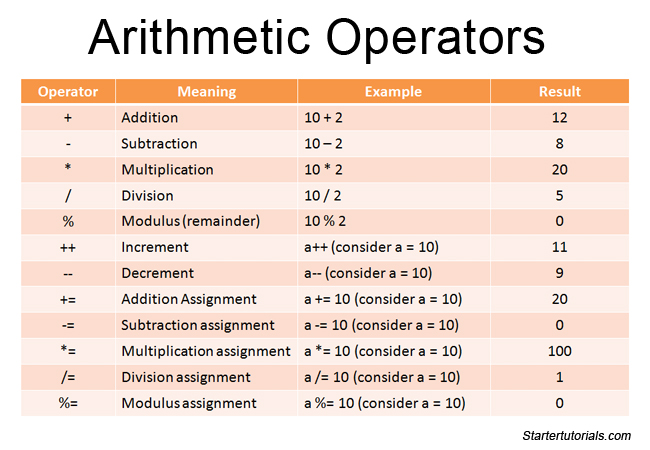
Java Operators With Examples Java Tutorial Arithmetic operators are fundamental building blocks in java programming, allowing you to perform basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. these operators are invaluable for any kind of numerical computation, data manipulation, and logic building in java applications. Operators in java can be classified into 5 types: 1. java arithmetic operators. arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on variables and data. for example, here, the operator is used to add two variables a and b. similarly, there are various other arithmetic operators in java. Java comparison operators. comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). this is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions. the return value of a comparison is either true or false. these values are known as boolean values, and you will learn more about them in the booleans and if. Arithmetic operators allow you to perform mathematical operations on numeric values. java provides all basic arithmetic operators that perform addition ( ), subtraction ( ), multiplication ( ), and division ( ). also, it offers a remainder operator (%) that returns the remainder of a division. the following table illustrates the arithmetic.

Module 3 Java Operators Object Oriented Programmingjava Java Java comparison operators. comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). this is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions. the return value of a comparison is either true or false. these values are known as boolean values, and you will learn more about them in the booleans and if. Arithmetic operators allow you to perform mathematical operations on numeric values. java provides all basic arithmetic operators that perform addition ( ), subtraction ( ), multiplication ( ), and division ( ). also, it offers a remainder operator (%) that returns the remainder of a division. the following table illustrates the arithmetic. The java arithmetic operators include addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus. all these java arithmetic operators are binary, which means they operate on two operands. the table below shows all the arithmetic operators in the java programming language with examples. operators. operation. Arithmetic operators are symbols or characters that perform mathematical operations on numeric operands. the primary arithmetic operators in java include addition ( ), subtraction ( ), multiplication (*), division ( ), and modulus (%). syntax: the syntax for using arithmetic operators in java is straightforward:.

Comments are closed.