3 26 Life Cycle Of Plants
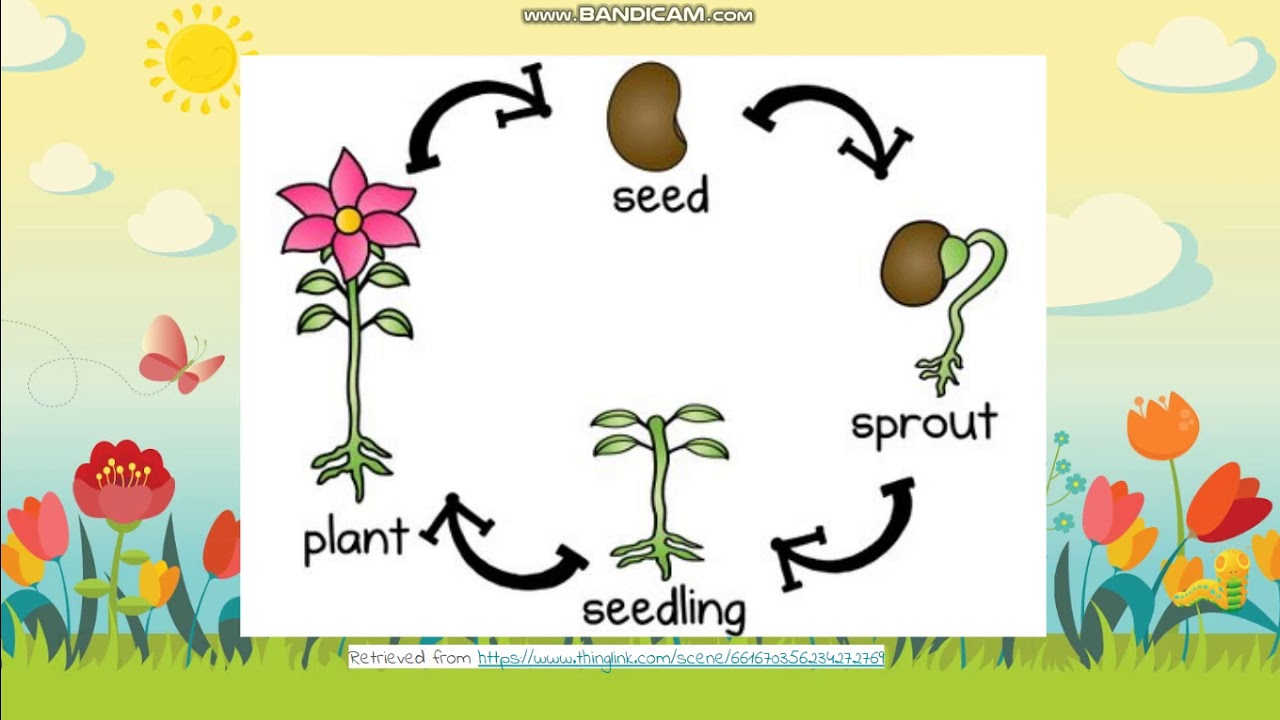
3 26 Life Cycle Of Plants Youtube A basic plant life cycle goes through five stages: 1) seed, 2) seed germination, 3) seedling, 4) adult plant, and 5) pollination and fertilization. they are discussed below in detail. 1) seed. the life cycle of a flowering plant begins with a seed. it has a protective outer covering called the shell. Instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. throughout the plant life cycle, all plants undergo the alternation of generations. this cycle of generations include both diploid (2n) phase, the sporophyte, and the haploid (n) phase gametophyte. in this page, explore at how these generations differ with each.
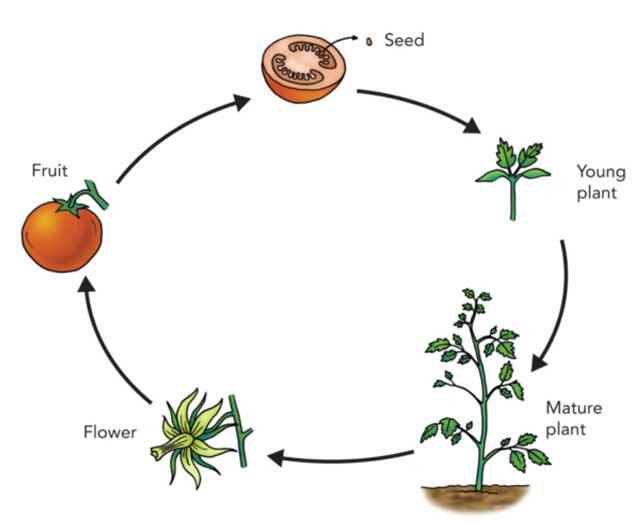
Life Cycle Of Plants 5 Stages Types Facts The life cycle of plants can be broken down into 3, 4, and 5 stages. but the most widely accepted model has 5 stages. seed. germination and seedling. growing to maturity. reproductive stage. seed dispersion. Seed dispersal. 1. seed –. the plant life cycle starts with a seed. from the outside, seeds are protected by a tough layer, called outer coat. but inside every seed, there is a tiny baby plant, known as an embryo. the embryo has a root, shoot as well as the first true leaves. seeds wait to germinate until three needs are met: water, correct. Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the gametophyte stage and the sporophyte stage. the haploid gametophyte produces the male and female gametes by mitosis in distinct multicellular structures. fusion of the male and females gametes forms the. The spores disperse and germinate into new gametophytes, repeating the process (see figure 1.1.4.1 1.1.4. 1). figure 1.1.4.1 1.1.4. 1: the p lant life cycle is haplodiplontic (alternations of generations). fern is shown as an example. the haploid (n) multicellular life stage is called the gametophyte as it produces gametes (egg and sperm cells.

Life Cycle Of Plant With Seeds Growth In Biological Labeled Outline Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the gametophyte stage and the sporophyte stage. the haploid gametophyte produces the male and female gametes by mitosis in distinct multicellular structures. fusion of the male and females gametes forms the. The spores disperse and germinate into new gametophytes, repeating the process (see figure 1.1.4.1 1.1.4. 1). figure 1.1.4.1 1.1.4. 1: the p lant life cycle is haplodiplontic (alternations of generations). fern is shown as an example. the haploid (n) multicellular life stage is called the gametophyte as it produces gametes (egg and sperm cells. L ife cycle of plants. th is diagram shows the general life cycle of a plant. early plants reproduced mainly with spores and spent most of their life cycle as haploid gametophytes. spores require little energy and matter to produce, and they grow into new individuals without the need for fertilization. in contrast, most modern plants reproduce. Flowers come from seeds, and they create seeds too. all flowering plants go through the following life cycle. germination is the process by which a plant begins to grow from a seed. roots form.
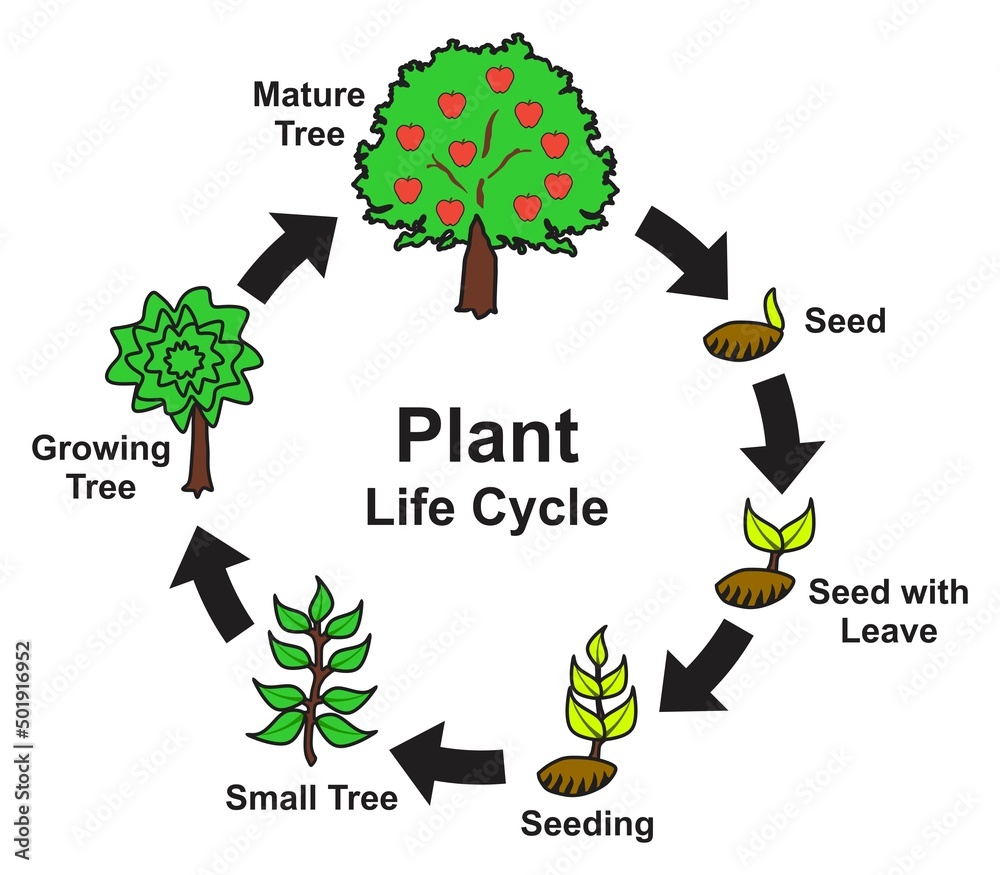
Life Cycle Of A Plant Diagram L ife cycle of plants. th is diagram shows the general life cycle of a plant. early plants reproduced mainly with spores and spent most of their life cycle as haploid gametophytes. spores require little energy and matter to produce, and they grow into new individuals without the need for fertilization. in contrast, most modern plants reproduce. Flowers come from seeds, and they create seeds too. all flowering plants go through the following life cycle. germination is the process by which a plant begins to grow from a seed. roots form.
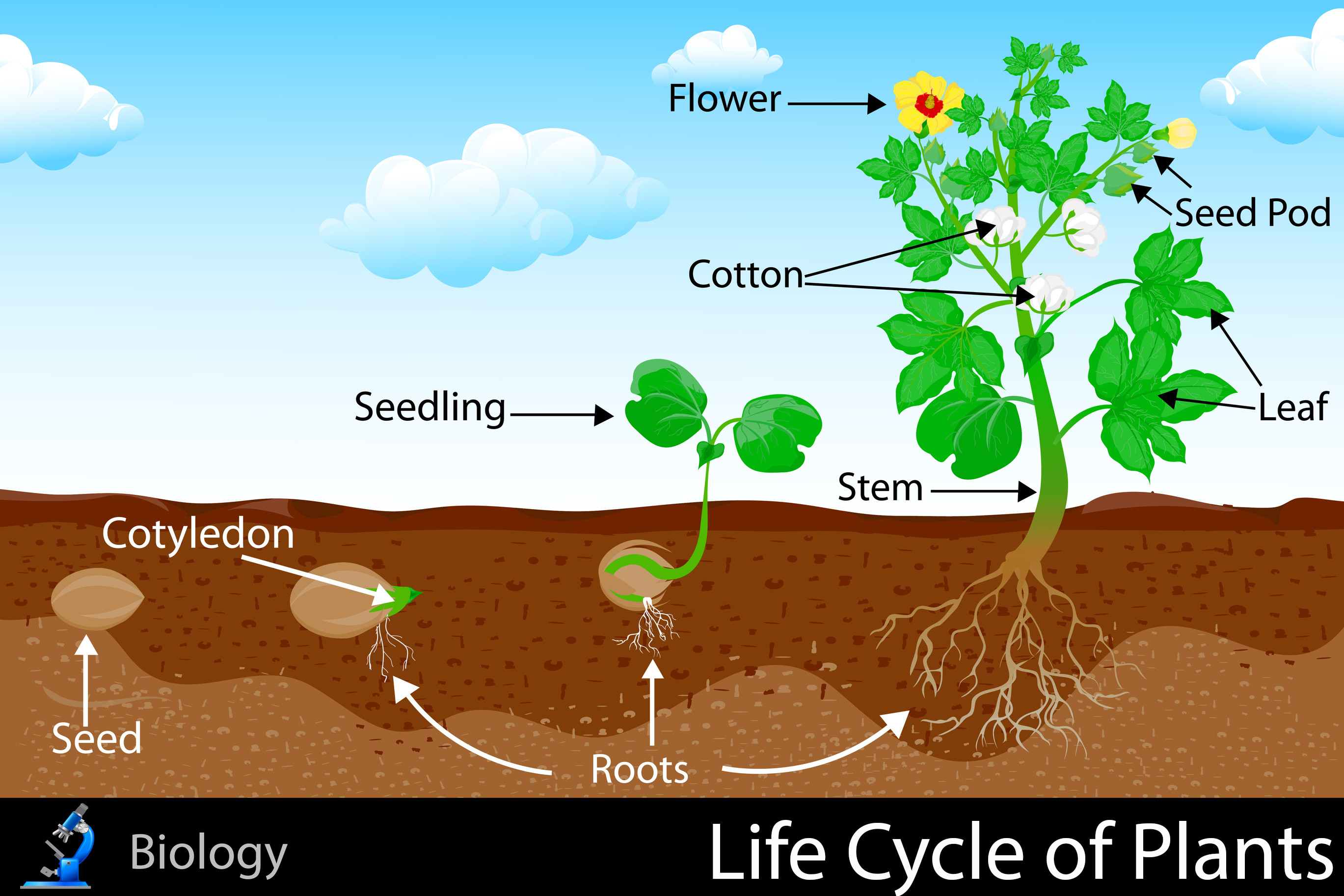
Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspressmagazine

Comments are closed.