1 Kinematic And Static Indeterminacy Email Info Engineersacademy

1 Kinematic And Static Indeterminacy Email Info Engineersacademy Email : info @ engineersacademy website : engineersacademy. 100 102, ram nagar, bambala puliya pratap nagar, tonk road, jaipur theory of structures determinacy indeterminacy | 1. the static indeterminacy of the structure shown below; a b c (a) 3 (b) 6 (c) 9 (d) 12. determine the degree of freedom of the following frame; a (a) 13 (b) 24 (c) 27. After that, the value of external static indeterminacy has calculated (dse). now to calculate the total degree of static indeterminacy internal and external static indeterminacy has added. at last value of kinematic indeterminacy has calculated. one support is hinge has one, and there is one hinge which has three kinematic indeterminacy.

1 1 Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Ppt 1.13 determine the static and kinematic indeterminacy for the following structures: ИИ (6) bar (a) truss o (c) beam (d) frame ref. sennet, chapter 1. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. For beams and framed structures, the formula below can be used to check the degree of static indeterminacy of the structure. d = s i 3m – 3p. where; d = degree of static indeterminacy. s = number of support reactions. i = number of internal forces in hinges (usually 2 per internal hinge) m = number of closed loops without hinges. The number of independent deflections is called the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy or the number of active degrees of freedom. it encompasses all displacements and rotations of movable joints. the determination of the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy is briefly established in the following examples. q(x) a b c ωb ωc. The degree of static indeterminacy is equal to the number of redundant equations of equilibrium and depends on the number of members (m), joints (j), and external reaction components (r). examples are given to demonstrate calculating the degree of redundancy for different plane frame and grid structures. 1.1 static and kinematic indeterminacy.

Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy For Beam Problem 3 And Problem 4 The number of independent deflections is called the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy or the number of active degrees of freedom. it encompasses all displacements and rotations of movable joints. the determination of the degree of kinematic static indeterminacy is briefly established in the following examples. q(x) a b c ωb ωc. The degree of static indeterminacy is equal to the number of redundant equations of equilibrium and depends on the number of members (m), joints (j), and external reaction components (r). examples are given to demonstrate calculating the degree of redundancy for different plane frame and grid structures. 1.1 static and kinematic indeterminacy. This document discusses indeterminacy in structures. it defines determinate, indeterminate, and unstable structures based on the number of unknowns and equilibrium equations. there are two methods to solve structures static and kinematic. static indeterminacy is calculated as f u r, where f is unknown reactions, u is equilibrium equations, and r is additional equations. frames and beams. Mathematically, static indeterminacy (ds) can be represented as: d s = r − e s where r is the number of unknown reactions and e s is the number of available static equilibrium equations. on the other hand, kinematic indeterminacy refers to the inability to determine the displacements and rotations in a structure using only the equations of.
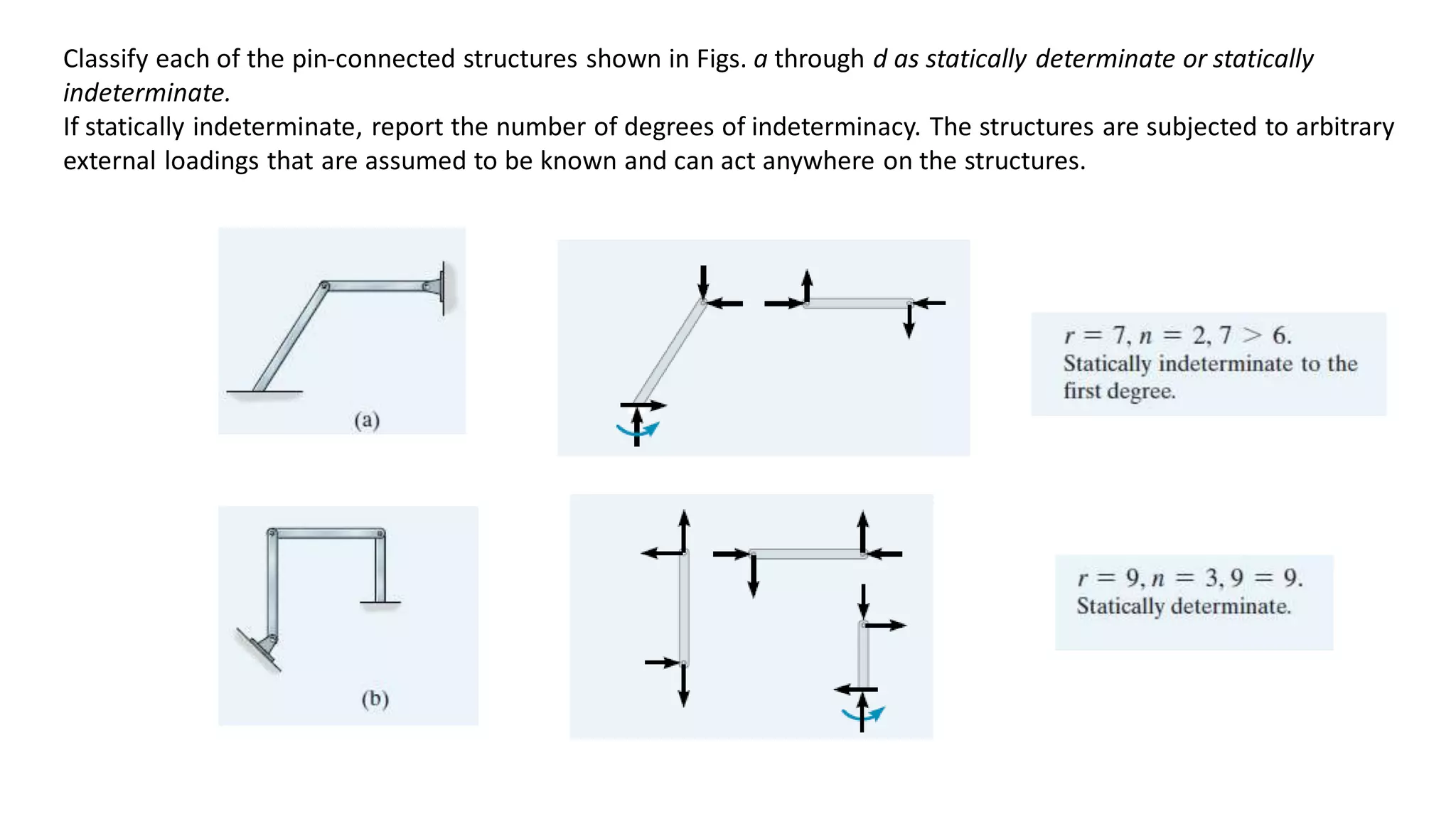
1 1 Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Ppt This document discusses indeterminacy in structures. it defines determinate, indeterminate, and unstable structures based on the number of unknowns and equilibrium equations. there are two methods to solve structures static and kinematic. static indeterminacy is calculated as f u r, where f is unknown reactions, u is equilibrium equations, and r is additional equations. frames and beams. Mathematically, static indeterminacy (ds) can be represented as: d s = r − e s where r is the number of unknown reactions and e s is the number of available static equilibrium equations. on the other hand, kinematic indeterminacy refers to the inability to determine the displacements and rotations in a structure using only the equations of.

Static And Kinematic Indeterminacy Of Structure

Comments are closed.